![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
157 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are the three areas of Operation? |
• Operations during peacetime • Operations other than war • War |
|
|
Define a hazard? |
Anything that can cause harm or damage to a person |
|
|
What does CSCATTT stand for? |
• Command and control • Safety • Communication • Assessment • Triage • Treatment • Transport |
|
|
What are the 3 circles on the hazard spectrum? |
• Trauma/burns • Medical/Toxicological • Environmental |
|
|
What does METHANE stand for? |
• My call sign • Exact location • Type of incident • Hazards • Access • Number and severity of casualties • Emergency services required |
|
|
What is triage? |
The assignment of treatment and evacuation priorities to the wounded and sick at each echelon of medical care. |
|
|
What are the triage priorities and their respective colour codes/meaning |
• T1 = Red - Immediate • T2 = Yellow - Urgent • T3 = Green - Delayed • T4 = (Expectant) White • DEAD = Black |
|
|
Define mass casualty? |
Where the number of casualties is outnumbered by the amount of avaliable resources temporarily. |
|
|
What are the major incident levels of command? |
• Bronze • Silver • Gold |
|
|
What is extrication? |
Removal or withdrawal of a trapped casualty. |
|
|
What are two types of entrapment? |
• Actual • Relative |
|
|
What are 3 levels of extrication? |
• Routine • Urgent • Emergency |
|
|
What are the 8 technical rescue skills? |
• Rope • Water • Search and rescue • Confined space • Fire fighting • Heavy • Collapsed structure • Tactical |
|
|
What are the 2 principles of CUF? |
• Win the fire fight • Casualty self treat and return fire |
|
|
What are the 5 limitations to CUF? |
• Hostile forces and enemy fire • Equipment limitations • Limited Visibility • Comms difficulty • Time |
|
|
What are the 3 environments of CUF and what treatment can be provided? |
• Non-permissive - CUF • Semi-permissive - TraPS • Permissive - Detailed Primary Survey |
|
|
What are the compressible and non-compressible haemorrhages controlled by? |
• Compressible - CAT, pressure points, ECB, Elevation • Non-compressible - Urgent evac, blood transfusion, surgery |
|
|
5 types of Haemorrhage Control? |
• Direct pressure • Elevation • Indirect pressure • Haemostatic agents • Splinting |
|
|
3 pressure points |
• Subclavian • Femoral • Brachial |
|
|
What is direct pressure? |
Pressure that can be applied directly onto a wound using a fist, hand or ECB |
|
|
What is Indirect pressure? |
The application of pressure to control a haemorrhage by using pressure points above the affected area. |
|
|
What are the 3 types of bleeding? |
• Arterial • Venous • Capillary |
|
|
What is a pneumothorax and what are the causes? |
• Air or gas in pleural cavity • Causes: Spontaneous, trauma, blunt, disease, penetrating |
|
|
What are the types of pneumothorax? |
• Open/sucking • Simple • Tension |
|
|
Signs and symptoms of an open pneumothorax? |
• Reduced air entry • Unequal chest movement • Emphysema • Cyanosis • Hyper resonance |
|
|
Causes of tension pneumothorax? |
• Blunt chest trauma • Penetrating trauma |
|
|
What is a haemothorax? |
Blood in the pleural cavity |
|
|
2 types of Haemothorax? |
• Massive • Simple |
|
|
How many litres of blood can each lung hold? |
2 litres |
|
|
What is a flail segment? |
A breaking of 2 or more ribs in 2 or more adjacent places |
|
|
What is the movement caused by flail chest called? |
Paradoxical movement |
|
|
What is in the upper airway? |
• Pharynx (Nasopharynx, Oropharymx, Laryngopharynx) • Larynx (Vocal cords) • Trachea |
|
|
What are the rings of cartilage in the trachea and how long and wide are they? |
C shaped rings, approx 12cm long and 1-2 cm wide |
|
|
What does the lower airway consist of? |
• Lungs • Bronchi • Bronchus • Bronchioles • Pleura • Thoracic diaphragm |
|
|
How many lobes does the left and right lung have? |
• Left - 2 • Right - 3 |
|
|
What is respiratory arrest and what are the causes? |
• Cessation of breathing • Causes: Airway obstruction, damaged respiratory centre, trauma, drugs |
|
|
What are the ideal resp rates for adults, children and infants? |
• Adult - 10-20 rpm • Children - approx. 24 rpm • Infants - 40-60 rpm |
|
|
5 types of drowning |
• Near • Dry • Salt water • Fresh water • Secondary |
|
|
Complications associated with drowning? |
• Hypothermia • Prolonged Immersion |
|
|
How long can secondary drowning occur? |
Up to 72 hours after |
|
|
7 ways to manage drowning? |
• Do not apply direct heat • Remove wet clothing and place in dry blanket • If in shallow water consider Spinal/Head Injury • Establish airway/aspirate • CPR if required • 100% Oxygen • Check pulse at 2 sites |
|
|
Define anaphylaxis |
An acute allergic reaction that can effect the whole body and can be fatal. |
|
|
What is the management of anaphylaxis? |
• Lay casualty down legs elevated • Epinephrine/adrenaline 1:1000 IM • Salbutamol |
|
|
Define Asthma |
Recurring sudden attacks of difficult breathing characterised by wheezing and difficulty in expiration. |
|
|
Management of Asthma? |
• 0² • Salbutamol with 0² Nebuliser • Salbutamol with 1-2 puffs with inhaler |
|
|
What are the 3 categories of Asthma? |
• Mild • Severe • Life threatening |
|
|
3 Signs of mild asthma |
• Wheezing • PEFR of 50% predicted • RR high <25 |
|
|
3 signs of severe asthma |
• Increasing wheeze • Can't complete sentences • Reduced PEFR <50% of expected |
|
|
3 signs of life threatening asthma |
• Silent chest • Cyanosis • PEFR of <33% |
|
|
Define acute poisoning |
Any substance which if taken into the body in sufficient amounts may cause harm or even death. |
|
|
3 types of poisoning |
• Toxins • Carbon monoxide • Opiates |
|
|
4 ways to recognise poisoning |
• Nasal bleeding • Drowsiness • Puncture marks • Excessive sweating |
|
|
Poison management? |
• Initial assessment and Primary Survey • Give Antidote if available • Evacuate and take evidence of poison with you |
|
|
3 do's and don'ts of snake bites/scorpion stings? |
Do - • Gain IV access • Pressure Immobilisation • Arrange transfer Don't • Feed patient • Elevate limb • Wash limb |
|
|
What is hypoglycaemia |
Low levels of blood sugar <4mmols |
|
|
4 signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia? |
• Sweating • Tachycardia • Irritable/aggressive • History of diabetes |
|
|
Management of hypoglycaemia? |
• Ensure ABC stable • Ascertain BM levels • Recovery position • Evacuate |
|
|
Define diabetic Coma? |
Collapse or acute illness caused by hypo/hyperglycaemia |
|
|
What is an open wound? |
Where there is a disruption in the continuity of the skin |
|
|
What is a closed wound? |
It is where trauma has caused damage to the underlying tissue and has not broken the skin. |
|
|
4 types of open wounds? |
• Laceration • Burns • Fragmentation • Impalement |
|
|
2 Types of closed wounds? |
• Internal Haemorrhage • Fracture |
|
|
What is a Fracture? |
A chip, crack or break in the continuity of the bone |
|
|
4 types of Fracture? |
• Closed • Open • Complicated • Comminuted |
|
|
Why might you not give oral fluids? |
• Those who require surgery • Major abdominal trauma • Risk of vomiting |
|
|
5 burn categories |
• Thermal • Electrical • Chemicals • Radiation • Friction |
|
|
3 burn depths |
• Superficial • Partial thickness • Full thickness |
|
|
Wallace rule of 9's for body burns. What are the percentages? |
• Head and neck 9% • Chest and abdomen 18% • Back 18% • Arm and hand 9% • Leg and foot 9% • Genitals 1% 🥲 |
|
|
Management for burns Name 5 things |
• Apply clingfilm in strips • Rinse with cold water for 10-20 minutes • Treat for shock • Oxygen • Place extremities in burn bags |
|
|
4 signs of smoke inhalation? |
• Hoarse voice 🐴 • Casualty has been in a Confined area • Soot around nose or mouth • Stained sputum • Singed nasal and facial hair |
|
|
Treatment for smoke inhalation |
• Maintain airway and humidified O² • Nebulised salbutamol • Urgent Evacuation |
|
|
3 types of pain relief? |
• Physical - Splintage/cooling • Pharmacological - drugs • Psychological - reassurance |
|
|
2 splinting methods? |
• Purpose made • Improvised |
|
|
What percentage of fentanyl is absorbed through the mucosa membrane? |
25% |
|
|
3 contra-indications for fentanyl |
• P or U on AVPU • Respiratory rate below 10/min • A head injury |
|
|
What drug is used to reverse opiate overdoses? |
Naloxone hydrochloride |
|
|
Contra Indications for Naloxone? |
• Known hypersensitivity |
|
|
When would eyes be bilaterally fixed? |
• Dead • Hypoxia • Hypovalemic • Atropine/ecstasy OD |
|
|
When would eyes be unilaterally fixed? |
• Brain Injury • Stroke |
|
|
3 types of brain Injury? |
• subdural haematoma • extradural haematoma • subarachnoid haemorrhage |
|
|
Three classifications of head injury? |
• Scalp wound • Skull Fracture • Brain injury |
|
|
5 symptoms of a head injury? |
• Memory loss • Aggression • Headache • Nausea/vomiting • Dizziness |
|
|
4 signs and symptoms of basal skull fracture? |
• Raccoon eyes • Bleeding from the ear • Rhinorhea/otthorhea • Battle signs |
|
|
4 signs and symptoms of raised ICP? |
• hypertension and bradycardia • reduction in consciousness • abnormal posturing • abnormal respiration patterns |
|
|
Management of ICP 4 things |
• Primary Survey • Monitor regularly • Evacuate ASAP • Give oxygen |
|
|
What are 2 types of posturing during ICP? |
• Decortiate • Decerebrate |
|
|
2 types of seizures |
• Generalised • Partial |
|
|
4 causes of seizures? |
• Mental illness • Battle shock • Drugs/intoxication • Hyperventilation • Hypoglycaemia • Hypothermia • Grand Mel epilepsy |
|
|
Management of a fit? 4 things |
• Get a History • protect the patient from harm • Primary Survey • Oxygenation • Ensure seen by MO if first episode • Packaging/evacuate |
|
|
The 4 steps for continuous care? |
• Monitoring • Re-assess • Documenting • Caring |
|
|
How often should you take obvs in Prolonged Field Care? |
• On own - every 15 mins for first 2 hours • If stable- decrease to every 30 minutes for next 4 hours |
|
|
5 of the 10 principles of continuous care? |
• Personal hygiene • Safety • Controlling body temperature • Maintain dignity • Pressure areas • Dying • Communication • Food and drink • Toileting • Dressings |
|
|
HITMAN means what? |
• Head to toe examination • Infection • Tubes • Medication • Analgesia • Nutrition |
|
|
3 indications for advanced airway? |
• Protect airway from obstruction • Control Oxygenation and ventilation • Inability to clear/maintain airways using simple techniques |
|
|
Define ET intubation? |
Passing of a cuffed endotracheal tube through the vocal cords into the trachea. |
|
|
4 Indications for ET tube? |
• Deeply unconscious Patient • management of cardiac arrest • Potential airway obstruction • management if chest/Head Injuries |
|
|
Contraindications of an ET tube? |
• Trismus • Concious casualty |
|
|
4 Difficulties for ET intubation? |
• shape of trachea • Trauma • entering the right bronchus • pre-existing disease |
|
|
4 Complications of ET tubing? |
• Hypoxia • Damage to teeth • Spinal cord injury • Intubation of right bronchus? • Failed intubation |
|
|
Define surgical cricothyroidotomy? |
An insertion of a tube through the cricothyroid membrane into the trachea via an incision. |
|
|
3 Indications for a surgical crike? |
• Severe facial trauma • Foreign body in upper airway • Clenched teeth (trismus) • Upper airway burns |
|
|
4 Potential complications of a surgical crike? |
• Asphyxia • Aspiration of blood • Bleeding • Laceration of trachea |
|
|
4 indications for IV access? |
• To administer drugs • Fluid resuscitation • prior to chest drain • Prolonged entrapment • Major burns • Profound shock |
|
|
With what injuries should care be taken when giving iv fluids (give 4) |
• Head injury • Renal trauma • Cardiac arrest • Cerebro vascular accident |
|
|
How many attempts with IV before you consider IO? |
2 attempts |
|
|
3 EZ IO sizes? |
• Pink - 15mm • Blue - 25mm • Yellow - 45mm |
|
|
4 Indications for IO access? |
• Emergency Vascular access • Major burns • Profound shock • Overwhelming Sepsis • Other methods have failed |
|
|
3 Contraindications to IO access |
• Fractures • Infections • Osteoporosis |
|
|
What is Hypovalemic shock? |
It is a result from whole blood and plasma loss, fluid and electrolyte loss |
|
|
4 Specific symptoms of Hypovalemic shock |
• peripheral vasoconstriction • Hyperventilation • Reduced pulse pressure • Sweating |
|
|
Treatment of Hypovalemic shock? |
• Control any bleeding • Fluid resuscitation • Boluses of 250ml crystalloid fluid until radial pulse is detected |
|
|
Who is authorised to give a third fentanyl lozenge? |
The MO |
|
|
What are the three headings in the hazard spectrum? |
• Trauma/burns • Medical/Toxicological • Environmental |
|
|
What are the two types of MOD reports that are used? |
9 Liner METHANE report |
|
|
List 3 principles of extrication |
Teamwork Preparation Training Correct equipment |
|
|
Give 4 signs and symptoms of mild Hypothermia |
• Sweating • Thirst • Dizzyness • Nausea |
|
|
List three types of ICP? |
Subdural haematoma Extradural haematoma Subarachnoid haemorrhage |
|
|
Hypovolemic is one type of shock, list 4 others. |
Anaphylactic Neurogenic Cardiogenic Septic |
|
|
Two contra indications of fentanyl? |
Hypersensitivity Severe respiratory depression |
|
|
What are the 3 layers of the brain, inside to out? |
Pia mater Arachnoid mater Dura mater |
|
|
Define hypoglycaemia and what reading this would indicate? |
Abnormally low blood sugar of <4mmols |
|
|
Give 3 signs and symptoms of a basal skull fracture? |
Raccoon eyes Bleeding from ears Blood in whites of the eyes Battle signs |
|
|
What are 3 treatment aims for the mothers in emergency childbirth? |
Prevent infection Prevent trauma Pain relief |
|
|
List 3 indications for nasal gastric intubation? |
Pre/post abdominal surgery Abdominal injury Intestinal blockage |
|
|
List 5 treatments that you would carry out when dealing with burns? |
• Cool for 20 minutes • Apply clingfilm • pain relief • O² or entonox • Monitor vital signs • Replace fluids • Remove restrictions |
|
|
What are 3 tiers of command when applying MIMMS? |
Gold Silver Bronze |
|
|
One potential complication of ET tubing is Hypoxia, give 3 others. |
• Laryngospasm • Damage to teeth • Intubation of the right main bronchus • Spinal cord injury |
|
|
Name 3 potential complications of needle thoracentesis? |
• Local haematoma • Pneumothorax • local or pleural Infection |
|
|
Define the rate of Tachycardia |
A pulse of more than 100bpm |
|
|
Define the rate of bradycardia? |
A pulse of less than 60 bpm |
|
|
List 3 types of shock |
Septic Anaphylactic Neurogenic Cardiogenic Hypovalaemic |
|
|
Name the 2 sites used for easy IO? |
Tibial plateau Head of the humorous |
|
|
Side used for FAST IO? |
The sternum |
|
|
Define hyperglycaemia and what reading would indicate this? |
Abnormally high blood sugar levels of >7mmols |
|
|
Give 3 methods of managing hyperthermia |
• strip down to underwear • keep in cool shaded area • spray skin with water • fan • Give fluids • assess ABC |
|
|
Give 3 signs and symptoms of severe asthma? |
PEFR 33%-50% RR over 25 HR over 110 Spo² below 92% |
|
|
Give three reasons why you would insert an NPA? |
• cannot tolerate OPA • Trismus • Jaw injury |
|
|
How much blood will be lost for class 3 hypovalemic shock? % or ml |
1500ml - 2000ml 30%-40% |
|
|
Give 3 signs and symptoms of moderate Hypothermia |
shivering Loss of dexterity Uncontrolled shivering Loss of dexterity Change in behaviour - agitated Change in behaviour - agitated |
|
|
List 3 signs and symptoms of mild asthma |
• Increasing symptoms • no features of acute or severe asthma • PEFR 50%-70% expected |
|
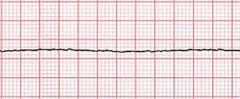
What is this called? |
Asystole |
|
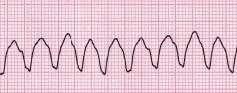
What does this mean? |
Ventricular Tachycardia |
|
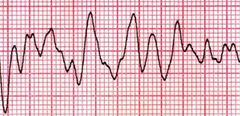
What is this called? |
Ventricular Fibrilation |
|
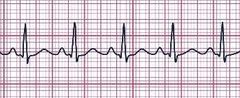
What is this called? |
Normal synus rythym |
|
|
4 signs of smoke inhalation? |
• Soot around mouth • swelling around face, lips and mouth • In a Confined space • Hoarse voice |
|
|
4 IV indications? |
• Fluid resuscitation • Administration of drugs • Prolonged entrapment • Prior to chest drain |
|
|
4 IV contra-indications |
• Raised ICP • Renal trauma / kidney failure • Cardiac failure • Cerebro vascular accident |
|
|
Sizes of IO and their meaning? |
Pink- children Yellow - Muscular or obese Blue - normal |
|
|
3 pressure points? |
• Femoral • Brachial • Subclavian |
|
|
4 Fentanyl side effects? |
• Nausea • Vomiting • Constipation • Dizziness |
|
|
Equation for burns? |
(4ml x weight x %burns) ÷2 8h 16h |
|
|
5 principles of patient care? |
• Nutrition • Hygiene • Communication • Safe environment • Dignity • Body temp • Dressing |
|
|
NPA sizes for female and male? |
F 6 M7 |
|
|
OPA sizes |
3F 4M |
|
|
3 burn depths |
Superficial Partial thickness Full thickness |
|
|
Blood in cavities |
Fractured rib - 150ml Closed Femoral Fracture- 1.5l Haemothorax - up to 2l in each side of the chest Closed tibial fracture - 500ml Fractured pelvis - 3L A fist sized blood clot - 500ml |
|
|
Fluid loss classes ml and percentage |
Class 1. <750ml/ 15% Class 2. 750ml-1500ml 15%-30% Class 3. 1500ml - 2000ml 30-40% Class 4. >2000ml >40% |

