![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
70 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Standards |
|
|
|
Protocol |
A set of rules governing the communications between Network Devices and computers |
|
|
Physical Layer of the OSI |
|
|
|
Data Link Layer of the OSI |
|
|
|
Network Layer of the OSI |
|
|
|
Transport Layer of the OSI |
|
|
|
Session Layer of the OSI |
|
|
|
Presentation Layer of the OSI |
|
|
|
Application Layer of the OSI |
|
|
|
Why do we use the OSI Model? |
|
|
|
What are the layer of the TCP/IP |
|
|
|
Name some protocols for Data Link |
|
|
|
Name some protocols of Network |
|
|
|
Name some protocols of the transport layer |
IP Service Protocols
|
|
|
Name some protocols of the Application Layer |
|
|
|
PDUs of the physical layer |
Bits
|
|
|
PDUs of the Data Link Layer |
Frames
Device Switch PDE:Frame MAC Address |
|
|
PDUs of the Network Layer |
Packets
|
|
|
PDUs of the Transport Layer |
Segments
|
|
|
Encapsulation |
As data moves down the stack, each layer adds its header and footer (if applicable), and removes them as the data moves back up |
|
|
Deencapsulation
|
Parameters set within a layer at the source device are used by the corresponding layer at the destination device
|
|
|
Bit |
A bit is the basic unit of information in Computing and digital communications |
|
|
Byte |
8 bits |
|
|
How are data rates measured |
bit/sec |
|
|
IDF is often called ? |
Wiring Closed
|
|
|
IDF |
Intermediate Distribution Frame
|
|
|
MDF |
Main Distribution frame
|
|
|
How are buildings connected on a campus LAN |
A Campus LAN is connected together using Fiber Optic Cables to connect the MDFs of each building |
|
|
10BASE5 |
|
|
|
10BASE2 |
|
|
|
10 BaseT |
|
|
|
What is the speed of Ethernet? |
10 Mbps |
|
|
What is the speed of Fast Ethernet? |
100 Mbps |
|
|
What is the speed of Gigabit Ethernet? |
|
|
|
What is the speed of 10 Gigabit? |
|
|
|
What is the speed of 40 Gigabit |
40 G |
|
|
What is the speed of 100 Gigabit |
100 G |
|
|
MAC Address |

|
|
|
What are basic Ethernet operations of using a Hub? |
|
|
|
What are basic Ethernet operations using a switch? |
|
|
|
What is the Basic LAN Design |
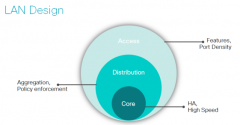
|
|
|
Why are WANs a persistent OPEX expense to the business? |
|
|
|
What are WAN topologies? |
|
|
|
Full Mesh |
Fail Save Everything is connected |
|
|
Partial Mesh |
|
|
|
Hub and Spoke |
|
|
|
DS-0 |
# of DSO: 1
Bandwidth (Mbps): 0.064
Smallest piece of bandwidth
|
|
|
DS-1 |
T1 Line
# of DSO: 24
Bandwidth (Mbps): 1.544 |
|
|
E1 |
Europe's equivalent to T1
# of DSO: 30
Bandwidth (Mbps): 2.048 |
|
|
DS-3 |
T3
# of DSO: 672
Bandwidth (Mbps): 44.736 |
|
|
OC-1 |
# of DSO: 54.84
Bandwidth (Mbps): 1 |
|
|
OC-3 |
STM-1
# of DSO:
Bandwidth (Mbps): |
|
|
DSO |
Channel |
|
|
Characteristics of a leased line |
|
|
|
Characteristics of frame relay |
|
|
|
Packet Switched |
Each individual packet (data) can take any available path during transmission |
|
|
How are virtual circuits usually used? |
1 VC per branch Office using a Hub-and Spoke WAN topology (like an airport, you leave out one terminal and arrive on another) |
|
|
ATM |
Asynchronous Transfer Mode
is a dedicated-connection switching technology that organizes digital data into 53-byte cell units and transmits them over a physical medium using digital signal technology |
|
|
Why is MPLS the current choice for many business? |
Best of both worlds (frame relay, ATM)
|
|
|
In MPLS how is packet forwarding done? |
Based on labels (tag) |
|
|
In MPLS when are labels assigned? |
When they enter the network |
|
|
Where are MPLS labels inserted? |
Between layer 2 and 3 headers |
|
|
The difference between routing and forwarding? |
Routing uses IP Address
Forwarding Uses Labels |
|
|
Can labels be stacked in MPLS? |
Yes |
|
|
Characteristics of xDSL |
|
|
|
What kind of Services to x DSL users buy? |
|
|
|
Variations of DSL |
NOTE: Speed Decreases with DIstance |
|
|
What is the Max Download speed for ADSL (consumer technology) |
24 Mbps |
|
|
What can be a problem since cable is a shared service? |
Contention
Definition: In contention, any computer in the network can transmit data at any time (first come-first served). |
|
|
Facts about cable |
|

