![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
28 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Enterprise
|
Corporation, business, or other entity that uses computers in a networked environment. An enterprise usually refers to large companies or organizations with complex networks.
|
|
|
Intranet
|
Networks accessible to internal users of an organization. An intranet is used to share internal information and computing resources.
|
|
|
Extranet
|
Network that provides access to information or operations of an organization to suppliers, vendors, partners, customers, or other businesses. Extranet is a private network using Internet protocols and the public telecommunication system to share internal resources. It may be considered an extension of an intranet.
|
|
|
Telecommuter
|
One who works from a location other than the centralized office.
|
|
|
VPN
|
"virtual private network"
Network through which data is sent through a public telecommunication infrastructure while maintaining the privacy of the data by creating a tunnel through the public telecommunication infrastructure. |
|
|
Enterprise Network
|
Network that integrates all systems within a company or organization.
*Support for critical applications *Support for converged network traffic *Need for centralized control *Support for diverse business requirements |
|
|
Converged Network
|
A network capable of carrying voice, video and digital data.
|
|
|
Mission-critical
|
Type of network or computing process that is vital to an organization. Mission critical applications that are halted often or for too long may have negative consequences.
|
|
|
Failover
|
Occurrence of a redundant network device performing the load or function of another device automatically if the initial device fails. The failover scheme creates a backup system for mission-critical hardware and software. The objective is to reduce the impact of system failure to a minimum by actively monitoring and identifying system failure.
|
|
|
Hierarchical Design Model
|
Representation of a network featuring an access layer, a distribution layer, and a core layer.
|
|

Hierarchical Design Model [graphic]
|
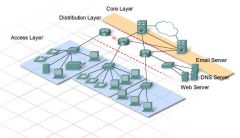
Access Layer, Distribution Layer, and Core Layer.
|
|
|
QoS
|
"quality of service"
Standard for monitoring and maintaining a level of transmission performance and service, such as available data transmission bandwidth and error rate. |
|
|
Enterprise Campus
|
Consists of the campus infrastructure with server farms and network management
|
|
|
Enterprise Edge
|
Consists of the Internet, VPN, and WAN modules connecting the enterprise with the service provider's network
|
|
|
Service Provider Edge:
|
Provides Internet, Public Switched Telephone Network (PSTN), and WAN services
|
|
|
ECNM
|
"Enterprise Composite Network Model"
Cisco network design that divides the network into functional components while still maintaining the concept of Core, Distribution and Access layers. The functional components are the Enterprise Campus, Enterprise Edge, and Service Provider Edge. |
|
|
failure domain
|
Is the area of a network impacted when a key device or service experiences problems.
|
|
|
back end
|
Application that performs final or hidden functions in a process.
|
|
|
LAN
|
*Organization responsible for managing infrastructure
*Ethernet *Access & Distribution layers *Local applications & server farms *Devices are in same building or campus |
|
|
WAN
|
*Sites are geographically dispersed
*Connections through CSU/DSU *ISP services like T1/T3, E1/E3, DSL, Cable, Frame Relay, ATM *ISP responsible for maintenance *Edge devices modify encapsulation from Ethernet to Serial |
|
|
CSU/DSU
|
"channel service unit/data service unit"
Network devices that connect an organization to a digital circuit. |
|
|
HDLC
|
"High-Level Data Link Control"
Bit-oriented synchronous Data Link layer protocol developed by ISO. HDLC specifies a data encapsulation method on synchronous serial links using frame characters and checksums. |
|
|
PPP
|
"Point-to-Point Protocol"
Standard that provides router-to-router and host-to-network connections over synchronous and asynchronous circuits. |
|
|
Frame Relay
|
Industry-standard, switched, WAN standard that operates at the Physical Layer and Data Link Layer of the OSI Reference Model. Frame Relay handles multiple virtual circuits using HDLC encapsulation between connected devices. It is more efficient than the X.25 protocol that it replaced.
|
|
|
ATM
|
"asynchronous transfer mode"
International standard for the cell relay of service types, such as voice, video, or data. In ATM, the services are conveyed in fixed-length, 53-byte cells. Fixed-length cells reduce transit delays because cell processing occurs in the hardware. ATM is designed for high-speed transmission media such as E3, SONET, and T3. |
|
|
UDP
|
"User Datagram Protocol"
Standard for connectionless transmission of voice and video traffic. Transmissions using UDP are not affected by the delays caused from acknowledgments and retransmitting lost packets. |
|
|
Jitter
|
Caused by network congestion, is the variation in time of the packets arriving at their destination.
|
|
|
IPSec
|
*Data encryption
*Integrity validation *Peer authentication *Key management |

