![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an artery? |

A blood vessel that carries blood away from the heart. |
|
|
What is the change in the diameter of the arteries following heart contractions called? |

Pulse |
|
|
What is the autonomic nervous system? |
The part of the nervous system that controls the motor nerves that regulate equilibrium, and that is not under conscious control. |
|
|
What are the two branches of the autonomic nervous system? |
Sympathetic and Parasympathetic |
|
|
What does the sympathetic nervous system do? |
Prepares your body for stress. |
|
|
What does the parasympathetic nervous system do? |
Returns the body to normal resting levels following adjustments to stress. |
|
|
What is the narrowing of blood vessels, allowing less blood to the tissues called? |
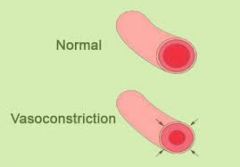
Vasoconstriction |
|
|
What is vasodilation? |

The widening of blood vessels, allowing more blood to the tissues. |
|
|
What is a degeneration of blood vessels caused by the accumulation of fat deposits in the inner wall called? |
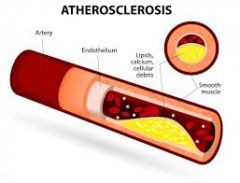
Atherosclerosis |
|
|
What is arteriosclerosis? |
A group of disorders that cause the blood vessels to thicken, harden, and lose their elasticity. |
|
|
What is a bulge in the weakened wall of a blood vessel (usually an artery) called? |
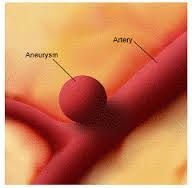
An aneurysm |
|
|
What is a vein? |
A blood vessel that carries blood toward the heart. |
|
|
What is the wall of muscle that separates the right and left sides of the heart called? |
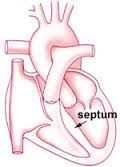
the Septum |
|
|
What is the pulmonary circulatory system? |
The system of blood vessels that carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs and oxygenated blood back to the heart. |
|
|
What is the system of blood vessels that carries oxygenated blood to the tissues of the body and deoxygenated blood back to the heart? |
The systemic circulatory system. |
|
|
What are the atria? |
The thin-walled chambers of the heart that receives blood from the veins. |
|
|
What are the muscular, thick-walled chambers of the heart that delivers blood to the arteries called? |
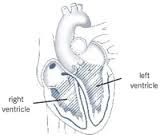
The ventricles. |
|
|
What is the atrioventricular (A.V.) valve? |
A heart valve that prevents the back flow of blood from a ventricle into an atrium. (Right one is a.k.a the tricuspid valve, and the left one is a.k.a the bicuspid valve) |
|
|
What is the valve that prevents the back flow of blood from an artery into a ventricle called? |
The semilunar valve. |
|
|
What is the aorta? |
The largest artery in the body; carries oxygenated blood to the tissues. |
|
|
What is the artery that supplies the myocardium with oxygen and nutrients called? |
The coronary artery. |
|
|
What is myogenic muscle? |
Muscle that contracts without external nerve stimulation. (ie. heart muscle) |
|
|
What is the small mass of tissue in the right atrium that originates the impulses stimulating the heartbeat called? |
The sinoatrial (S.A.) node. |
|
|
What is the artioventricular (A.V.) node? |
A small mass of tissue in the right atrioventricular region through which impulses from the sinoatrial node are passed to the ventricles via Purkinje fibers. |
|
|
What are the nerve fibers that branch out and carry electrical signals throughout the ventricles called? |
Purkinje fibers. |
|
|
What is diastole? |
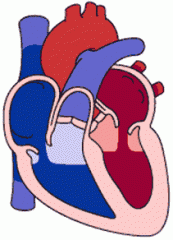
The relaxation (dilation) of the heart, during which the ventricles fill with blood. |
|
|
What is the contraction of the heart, during which blood is pushed out of the heart called? |
Systole |
|
|
What is cardiac output? |
The amount of blood pumped from the heart each minute. |
|
|
What is the quantity of blood pumped with each beat of the heart called? |
Stroke volume. |
|

What is a sphygmomanometer? |
A device used to measure blood pressure. |
|
|
What is the maintenance of body temperature within a range that enables cells to function efficiently called? |
Thermoregulation |
|
|
What is the hypothalamus? |
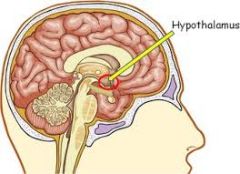
The region of a vertebrate's brain responsible for coordinating many nerve and hormone functions. |
|
|
What is the fluid that occupies the spaces between cells and tissues (including plasma and interstitial fluid) called? |
Extracellular Fluid (ECF) |
|
|
What is filtration? |
The selective movement of materials through capillary walls by a pressure gradient. |
|
|
What is the fluid found in lymph vessels (similar to blood plasma) that contains some proteins that have leaked through capillary walls called? |
Lymph. |
|
|
What is a lymph node? |
A mass of tissue that stores lymphocytes and removes bacteria and foreign particles from the lymph. |
|
|
What is a white blood cell that produces antibodies called? |
A lymphocyte. |
|
|
What is the spleen? |
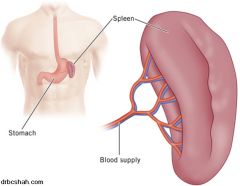
A lymphoid organ that acts as a reservoir for blood and a filtering site for lymph. |
|
|
What is the lymphoid organ in which T lymphocytes mature called? |
The thymus gland. |
|
What is the Circulatory system's function? |
To carry blood to all the cells in an organism. It also transports hormones, distributes heat, maintains body fluid levels, and provides transport for cells providing defense against disease. |
|
|
What does blood carry, and what does it pick up? |
Necessary materials such as oxygen and nutrients, and picks up carbon dioxide as a waste material. |
|
|
What is the Circulatory system composed of? |
The heart, arteries, arterioles, capillaries, venules, and veins.
|
|
|
Why do arteries have thicker walls than veins? |
Because of their middle layer of muscle which allows them to handle the extra blood pressure found in these vessels. |
|
|
What are capillaries and what is their function? |
They are tiny vessels that connect arteries and veins, and their function is to be the site of fluid and gas exchange. |
|
|
What do veins have that arteries don't? |
One-way valves. (Which along with muscle contractions help move blood against gravity back to the heart) |
|
|
What is an arteriole? |
A small artery |
|
|
What is the fluid filled sac that the heart sits in and what is it's function? |
The pericardium, and the heart bathes in this fluid preventing friction. |
|
|
What is an electrocardiogram? |
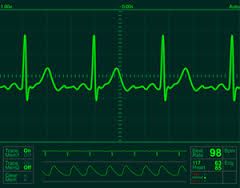
A record or display of a person's heartbeat produced by electrocardiography. |
|
|
What is it called when the heart rate exceeds 100 BPMs due to our sympathetic nervous system? |
Tachycardia |
|
|
What is bradycardia? |
When the heart rate is slower than normal due to the parasympathetic nervous system. |
|
|
What is a heart murmur? |
The gurgling sound produced by a leak in a heart valve. |
|
|
What is a baroreceptor? |
A receptor that senses blood pressure and sends this information to the brain so that proper pressure can be maintained. |
|
|
What is osmotic pressure? |
The movement of fluid into the capillaries (assisted by fluid pressure). |
|
|
What is a condition identified by an excess of watery fluid collecting in the cavities and tissues of the body called? |
Edema. |
|
|
What five factors affect blood pressure? |
-Amount of blood (greater volume means greater pressure) -Elasticity of arteries (greater elasticity means less pressure) -Heart rate (greater rate means more pressure) -Size of artery (vasodilation means less pressure) -Viscosity of blood (greater viscosity means greater pressure) |

