![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Angio- |
vessel |
|
|
Arterio- |
artery |
|
|
Arteriolo- |
arteriole-small |
|
|
A/telo- |
incomplete or without/end |
|
|
Atrio- |
atrium/upper heart chamber |
|
|
Auriculo- |
ear-shaped-heart part |
|
|
Cardio-, Car- |
heart |
|
|
Conio- |
dust |
|
|
-ectesis |
dilation |
|
|
Lympho- |
watery |
|
|
Phlebo- |
vein |
|
|
Plasmo- |
blood fluid, cells float |
|
|
Sanguino- |
blood |
|
|
Sero- |
blood serum |
|
|
Veso- |
vessel |
|
|
Veno- |
vein |
|
|
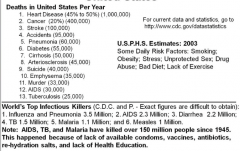
13 Leading Premature Killers in the US |
|
|
|
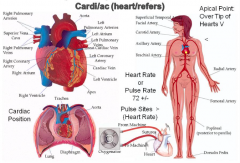
Car-, Card-, Cardi-, Cardio- |
|
|
|
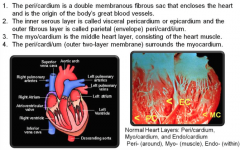
Cardi/um-, Cardi/o-, Cardi-, Card-, Car- (kardia means heart Gk., -ium means refers to Lt.) |
|
|
|
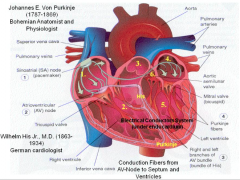
Heart |
|
|
|
Heart Anatomy Heart Rate (HR) and Pulse Rate (PR) |
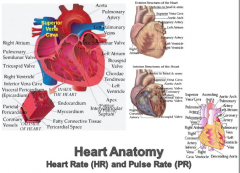
|
|
|
Cardiac Sy/stole (Systole means Contraction in Greek) |
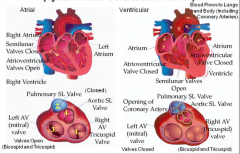
|
|
|
Adipose Peri/cardium and Myo/cardial Infiltration |
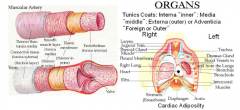
Heart's right side is for pulmonary (lung) circulation and left side is for systemic (body) circulation. |
|
|
Blood |
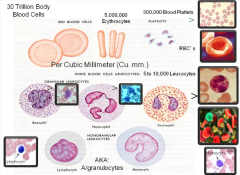
|
|
|
Stem Cell |
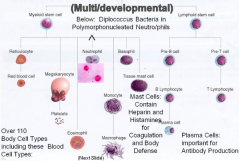
|
|
|
Anti/hypertensive Drugs |
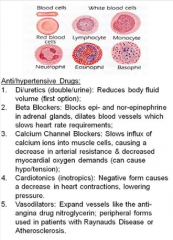
|
|
|
Pulse (sphygmo-) |
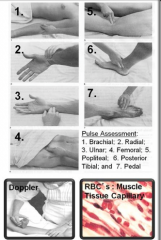
|
|
|
An/emia (without blood) |
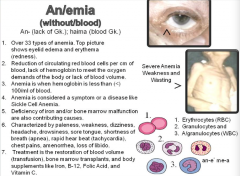
|
|
|
Sickle Cell An/emia (sickle-shaped RBC's: lack/of blood) |
Hereditary, chronic, hemo/lytic an/emia. Large numbers of sickle-shaped or crescent red bloom cells (trait exists without disease). Most often seen in black population (1/500) but also seen in Hispanic (1/1500) Sickle cells cause clots and clumping which are part of a true sickle cell crisis. |
|
|
A/plastic An/emia (without/formation: lack of/blood) |
Caused by lack of development of bone marrow or its destruction by chemicals, such as arsenic of physical factors, such as x-rays. It occasionally develops with unknown causes (idio/pathic). |
|
|
Coronary (crown or circle) |
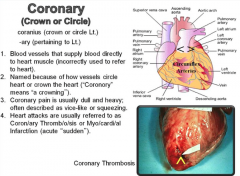
|
|
|
Vascular Occlusion (vessel: closure) |
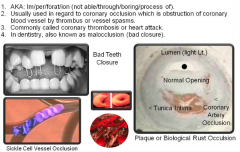
|
|
|
Infarct/ion (stuffed/process) |
Tissue undergoes necr/o/sis when blood flow stops. Infarcts may result from flow occlusion or stenosis (narrowing). Usually occur in arteries. There are 11 major types, including uric acid crystals from the kidney and clots or plaques. |
|
|
Infarct/ion |
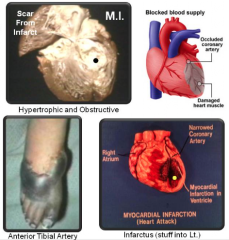
|
|
|
Isch/emia (to hold back/blood) |
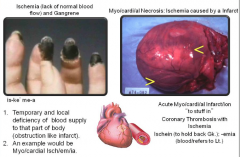
|
|
|
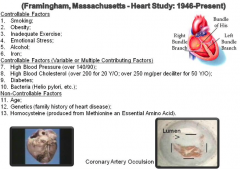
Heart Attack Risk Factors |
|
|
|
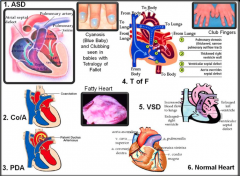
Heart |
|
|
|
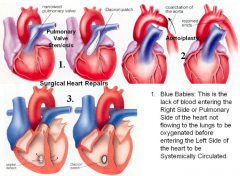
Surgical Heart Repairs |
|
|
|
Heart Defect of Murmur |

|
|
|
Abnormal Heart Sounds |

|
|
|
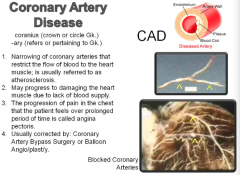
Coronary Artery Disease |
|
|
|
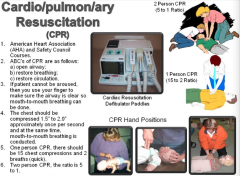
Cario/pulmon/ary Resuscitation CPR |
|
|
|
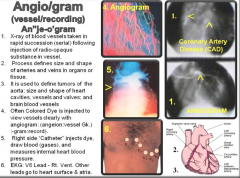
Angio/gram (vessel/recording) |
|
|
|
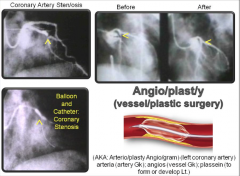
Angio/plast/y (vessel/plastic surgery) |
|
|
|
Smokers Gangrene (necrotic tissue) |

The etiology or the cause is vasoconstriction of arteries, arterioles, and capillaries with extremity hypo/thermia. |
|
|
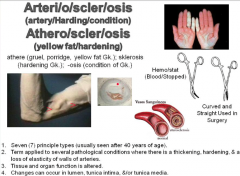
Arteri/o/scler/osis (artery/hardining/condition) Athero/scler/osis (yellow fat/hardening) |
|
|
|
Arteri/o/scler/osis and Athero/scler/osis |
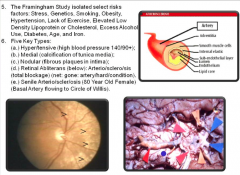
|
|
|
Cardio/myo/path/y (heart/muscle/disease/process of) |
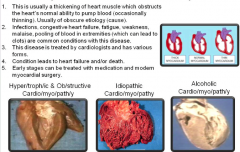
|
|
|
Hypertrophic and Obstructive |
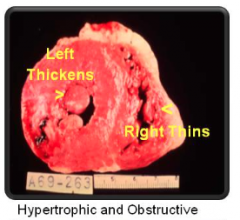
|
|
|
Thinning Type (cardio/myo/pathy) |
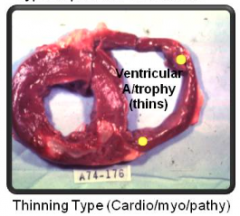
|
|
|
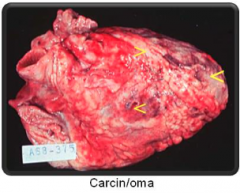
Carcin/oma |
|
|
|
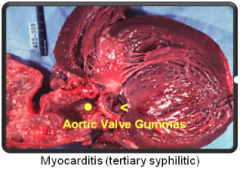
Myocarditis (tertiary syphilitic) |
|
|
|
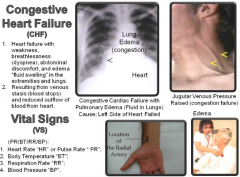
Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) |
|
|
|
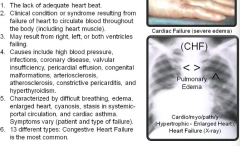
Heart Failure Edema (fluid swelling) |
|
|
|
Edema (swelling) |

|
|
|
Angina Pectoris (vessel/chest) |
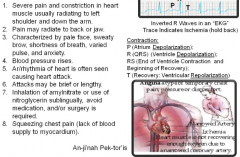
|
|
|
Carot/id Sten/o/sis (deep/sleep: narrowing/condition) |
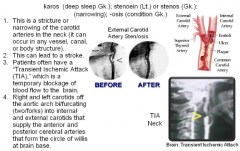
|
|
|
Mitr/al Sten/osis (headband or Turban) |

8. Reduced blood pumping causes weakness, difficulty breathing, and cyanosis of skin. 9. Surgery may be performed to remove adhesions or the valve may be replaced. 10. Malar or reddening of cheeks is sign of MVS |
|
|
Matrial Valve In/competence |
Malfunctioning or failure to close causing leakage of valve. Cause varies from abnormal tissue formation to infections |
|
|
Rheumatic Fever (often caused by: Scarlet Fever) |
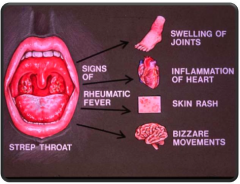
|
|
|
Rheumatic Fever (heart valve) |

|
|
|
Septic/emia (poisoned/blood) |
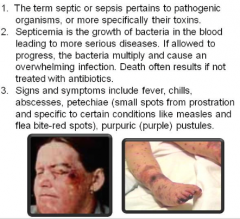
|
|
|
Endo/card/itis (within/heart/inflamed) |
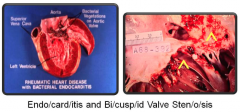
The endocardium is the serious lining membrane on the inner surface of the heart and its cavities. Continuation of tunica (coat) intima (inner) of arteries |
|
|
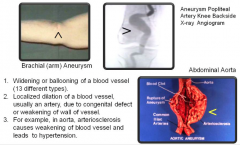
Aneurysm (ballooning; dilation; to widen) |
|
|
|
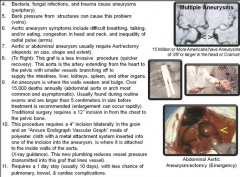
Aneurysm |
|
|
|
Ather/oma (yellowing fatty plaques/swelling) |

Treatment: improved risk factors (behavior modification, surgical procedures, drugs. |
|
|
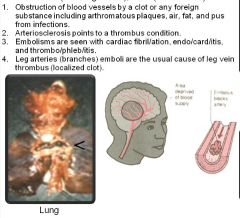
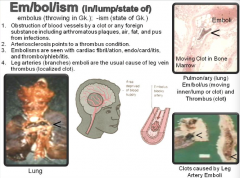
Em/bol/ism (in/lump/state of) |
|
|
|
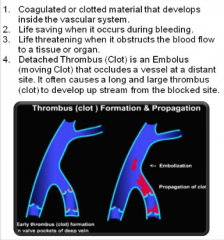
Thromb/us (thrombus means clot or clump in Gk.) |
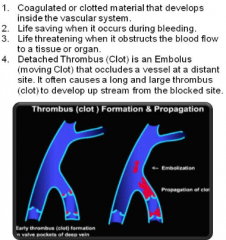
|
|
|
Rheumatic Fever (often caused by Scarlet Fever) |
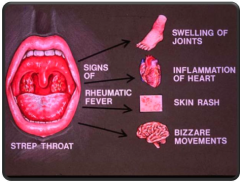
|
|
|
Rheumatic Fever (Heart Valve) |

|
|
|
Septic/emia (poisoned/blood)
|

|
|
|
Endo/card/itis (within/heart/inflamed) |
The endocardium is the serious lining membrane on the inner surface of the heart and its cavities. Continuation of tunica (coat) intima (inner) of arteries. |
|
|
Aneurysm (ballooning; dilation; to widen) |
Widening or ballooning of a blood vessel (13 different types) Localized dilation of blood vessel, usually an artery, due to congenital defect or weakening of wall of vessel. For example, in aorta, arteriosclerosis causes weakening of blood vessel and leads to hypertension. |
|
|
Aneurysm |
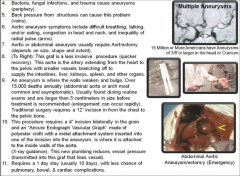
|
|
|
Ather/oma (yellowish fatty plaques/swelling) |
A mass of atheromat/ous placing material lining the lumen of an artery. Changes occur within lining cells and/or between these lining cells. Simple form of arteriosclerosis with tiny athr/oma deposits within and beneath tunica intima. Leads to heart attacks and strokes which cause 45%-50% of all deaths in the US/year. |
|
|
Atheroma |
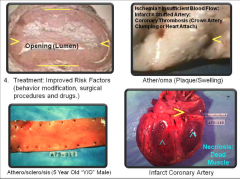
|
|
|
Em/bol/ism (in/lump/state of)
|
|
|
|
Thromb/us (thrombus means clot or clump in Gk.) |
|
|
|
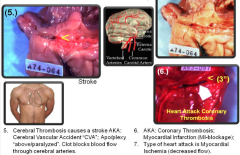
Cerebr/al Thrombo/sis (stroke, apoplexy, or CVA) (Brain: clot/condition) |
|
|
|
Pulmon/ary Artery Thromb/osis (lung/refers: arteria "windpipe like" Gk.): clot/condition) |
Clot results from congestive heart failure and pulmonary edema "lung/fluid" Pulmonary arteries go from heart to lungs and carry deoxygenated blood. Necr/ops/y (death/view/process of) |
|
|
Ec/chym/o/sis (out/juice/refers) |
Form of hemorrhages under the skin that is usually irregular and large. The color is blue-black changing to greenish-brown or yellow as area heals (usually resulting from bruise). |
|
|
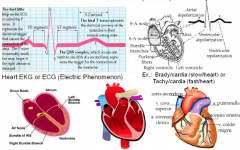
Cardiac Ar/rhythmia (heart: without/rhythm) |
|
|
|
Electro/cardio/gram (electric/heart/record) |
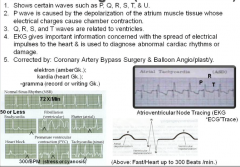
|
|
|
Electrocardiogram |
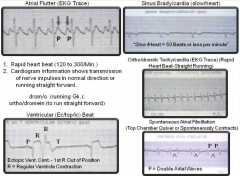
|
|
|
Hyper/tension (increased or above Gk./stretching Lt.) (AKA: High Blood Pressure "HBP') |
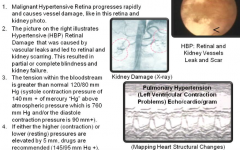
|
|
|
Hypertension |
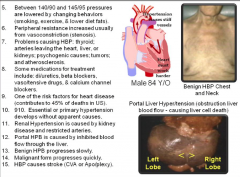
|
|
|
Hem/o/rrhage (blood/burst forth) |
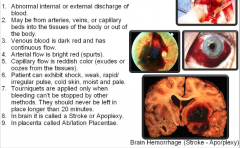
|
|
|
Hypo/tens/ion (under/contraction/process) AKA: Low Blood Pressure |

|
|
|
Ultra/sono/graph (beyond normal/sound/instrument) Ultra/sono/gram (kidney: beyond/sound/recording) |
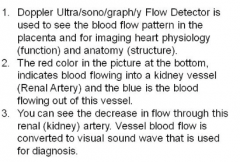
|
|
|
Lymphatic Circulatory System |
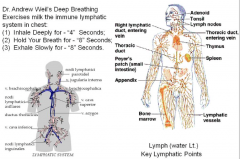
|
|
|
Lymphatic Circulatory System
|
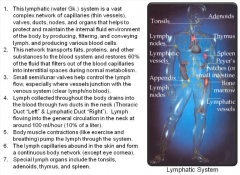
|
|
|
Mono/nucleosis (one/nut or kernel Gk.) |
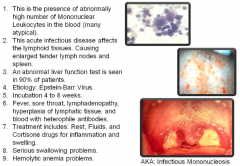
|

