![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
function of circulatory system
|
distribution of materials throughout body
|
|
|
phyla with NO circulatory system
|
porifera
cnideria platyhelminthes nematoda |
|
|
open circulatory system
Pros? |
circulatory fluid spends time outside of system
+less energy required +less pressure required |
|
|
Phyla with open circulatory system
|
Mollusca (except squid)
arthropoda echinodermata (BUT also use Water vascular system) Annelida (numerous hearts) |
|
|
closed circulatory system
|
blood remains inside system at all times
|
|
|
phyla with closed circulatory system
|
Chordata
Mollusca- Squids and octopi |
|
|
Which type of chordata has only one circuit?
|
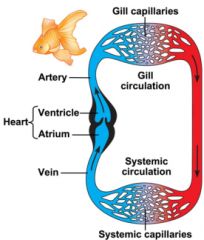
Fish
2 chambers 1 circuit |
|
|
Which type of chordata has a system in which blood mixes?
|
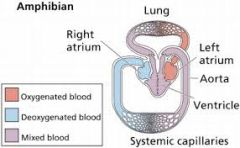
Amphibian
3 chambers (2 atria, 1 ventricle) 2 circuits mixing of blood - less efficient |
|
|
Which type of Chordata has 3 and a half circuits?
|
Reptiles
3.5 chambers (2 atria, 2 connected ventricles) 2 circuits |
|
|
pulmocutaneous circuit
|
heart to lung capilliaries to heart
|
|
|
heart to body capilliaries to heart
|
systemic circuit
|
|
|
How do reptiles survive for extended periods without breathing?
|
because of their 3.5 chambers, blood can bipass the lungs via the RIGHT SYSTEMIC AORTA and use ALL oxygen within blood cells
|
|
|
Human heart
|
4 chambres
|
|
|
arteries
|
carry blood AWAY from heart
|
|
|
carry blood towards heart
|
veins
|
|
|
capilliaries
|
exchange with other tissues
|
|
|
Which vessel has the highest surface area?
|
capilliaries - to allow for gas exchange
|
|
|
which vessel has the highest velocity of blood?
|
Aorta and arteries
|
|
|
what is beneficial to capiliaries' low velocity of blood?
|
allows for slow and efficient diffusion
|
|
|
which vessel has the highest pressure?
|
aorta, arteries
|
|
|
blood pressure is measured as
|
max pressure over min pressure
|
|
|
max pressure is
|
systolic pressure (audible) the sound of your VENTRICLES contracting
|
|
|
min pressure is
|
diastolic pressure (inaudible) your ventricles relax
|
|
|
normal blood pressure is
|
120/80
|
|
|
What are the tissue layers in arteries?
1. 2. 3. |
Outer to Inner
1. surrounded by loose connective tissue -contains elastin fibres to allow artery to stretch 2. smooth muscle -contract and dialate to control blood flow 3. single endothelium layer of epithelial cells to allow gas exchange |
|
|
What are the tissue layers in capilliaries?
|
single layer of endothelium, epithelial cells to allow diffusion of gas between tissue and surrounding cells
|
|
|
What are the tissue layers in veins?
1. 2. 3. 4* |
Outer to inner
1. loose connective tissue - thinner than arteries 2. smooth muscle - thinner than arteries 3. single endothelium layer of epithelial cells 4* contain ONE WAY VALVES to stop backflow in extreme low pressure and from gravity |
|
|
What percentage of blood is plasma?
|
55%
|
|
|
what percentage of blood are cellular elements?
|
45%
|
|
|
matrix of connective tissue, composed of mostly water
|
plasma
|
|
|
What is the purpose of H2O in plasma?
|
it acts as a solvent for carrying substances
|
|
|
What is the purpose of ions in plasma?
|
water concentration balance, adjust acidity (buffer)
|
|
|
What other elements are in plasma?
|
proteins, nutrients, waste, gases, hormones
|
|
|
Cellular components of plasma
|
erythrocytes (RBC)
leukocytes (WBC) thrombocytes (platelets) |
|
|
what iron-containing-protein allow O2 to be carried by erythrocytes?
|
hemoglobin
|
|
|
Where are blood cells made?
|
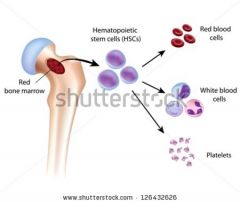
stem cells of bone marrow of the skeletal system
|
|
|
where is hemoglobin produced?
|
liver
|

