![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
11 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Joule's Law
|
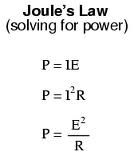
|
|
|
Total Current in Series
|
Components in a series circuit share the same current. I total = I1 = I2 = . . . In
|
|
|
Total Resistance in Series
|
Total resistance in a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual resistances, making it greater than any of the individual resistances. R total = R1 + R2 + . . . Rn
|
|
|
Total Voltage in Series
|
Total voltage in a series circuit is equal to the sum of the individual voltage drops. E total = E1 + E2 + . . . En
|
|
|
Voltage in Parallel
|
Components in a parallel circuit share the same voltage. Etotal = E1 = E2 = . . . En
|
|
|
Total resistance in parallel
|
Total resistance in a parallel circuit is less than any of the individual resistances. Rtotal = 1 / (1/R1 + 1/R2 + . . . 1/Rn)
|
|
|
Total current in parallel
|
Total current in a parallel circuit is equal to the sum of the individual branch currents. Itotal = I1 + I2 + . . . In
|
|
|
Series and Parallel resistances
|
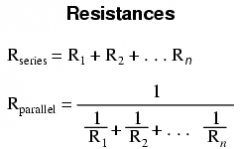
|
|
|
Series and Parallel Capacitances
|
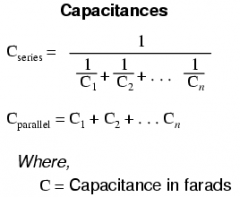
|
|
|
Ohm's Law for AC
|
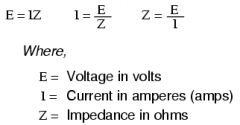
|
|
|
Series and Parallel Impedances
|
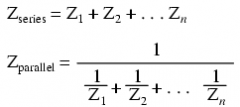
|

