![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
215 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
what is the main objective of devoting energy to finding food
|
growth
reproduction |
|
|
types of eating preferences in fish
|
omnivores
carnivores piscivores herbivores detritavores |
|
|
optimal foraging theory
|
the idea that fish will adapt their eating preferences to what is most abundant to eat
|
|
|
types of feeding behaviors
|
specialists--specific things they eat
generalists--eat a variety of things opportunists--eat food not normally on their menus |
|
|
home range
|
the entire area that an organism will live in, not just defend
|
|
|
territory of fish relates to
|
size of fish
competition for resources |
|
|
quiet period
|
period of about 20 minutes where fish will go to sleep and the nocturnal fish will come out
|
|
|
shadow feeding
|
when fish will follow behind other fish that are feeding to catch food that they stirr up
|
|
|
roving predators
|
will stalk or chase prey
|
|
|
lie and wait predators
|
will sit stationary until prey approaches area
|
|
|
Types of group spawning
|
resident
transient (travel to) |
|
|
Benefits of monogamy
|
do not have to find a mate
guarding limited resources biparental care |
|
|
Aspects of polygamy
|
herems and dichromatic
|
|
|
dichromatic
|
male and females are of different colors
|
|
|
pair spawning and benefits
|
always have a mate nearby
increases parental care and reproductive success |
|
|
benefits of spawning in groups
|
genetic varience
increased chance of finding a mate refuge in size and numbers |
|
|
downside of spawning in groups
|
fishing and decimating populations
|
|
|
Variations in timing of spawning
|
annual
with lunar cycle daily (based on time of day) |
|
|
Ex of fish that breed daily
|
mid day-bluehead wrasse
late afternoon-parrotfish dusk-hamlets |
|
|
Examples of benthic egg laying
|
Sergent majors that lay eggs on patches and guard them
Chromis Damselfish |
|
|
Considerations of site and timing of spawning
|
Selected for maximal eggs and larvae
-dusk -downcurrent of edge of reef -prominent topographical features -tides/currents to transport eggs offshore -traditional sites |
|
|
Color changes and reproduction
|
some will undergo color changes to signal that they are reading for mating
trunkfish seargent majors honeycomb cowfish whitespotted filefish |
|
|
Examples of courtship
|
males chasing away other males
fin displays body twitches color changes position in the water column |
|
|
Factors that contribute towards reproductive success
|
how vigorous courtship display is
control of spawning location brighness of coloration |
|
|
Spawning rise
|
when two fish rise in the water column to release gametes
|
|
|
Streakers
|
initial phase males that race and release gametes during a spawn rise
|
|
|
Sneakers
|
initial phase males will secretely court females of a terminal phase males
|
|
|
Purpose of cleaning stations
|
where larger fish are cleaned by smaller fish
|
|
|
Signs of cleaning
|
clients: change of colors, turn vertical, fan fins, hovering, open mouth
cleaners: come out, coloration (yellow/white), noise/vibrations, stroke clients, flit back/forth |
|
|
Is cleaning parasitic or commensalate?
|
cleaners could be trying to obtain flesh
seen when clients chase away cleaner commensalate because both benefit, wound healing |
|
|
Shadow feeding
|
predator following a less threatening species jumps out and gets smaller fish
|
|
|
Nuclear hunting
|
eel flushes prey out and grasby and other fish benefit
|
|
|
shadow stalking
|
fish will hang out over another fish
|
|
|
Tarpons and night diversq
|
will use light to get fish who are stunned
|
|
|
Color change as a hunting strategy
|
used to hide from prey
|
|
|
Predator/prey avoidance strategies
|
hiding in holes
diving in sand schooling staying shallow moving faster camoflague |
|
|
Unique conditions for mangroves
|
high salt
low oxygen high light frequent tidal inundation |
|
|
How do mangrove seeds spread
|
water borne
propagule falls in water and is despersed |
|
|
How do mangroves cope with high salinity
|
stomata that open and close to bring in co2 and let out h2o; close in drought
thick cuticle Mg-Na pump (red mangroves) Vaculoles that encapsulate salt Glands that secrete salt |
|
|
How do mangroves deal with tidal flux
|
pheumatophores to take in oxygen during low tides
anaerobic respiration (short term) prop and ariel roots for gas exchange lenitcels for co2 and gas exchange |
|
|
What type of mangrove has pnuematophores
|
black mangrove
|
|
|
Unique conditions for mangroves
|
high salt
low oxygen high light frequent tidal inundation |
|
|
How do mangrove seeds spread
|
water borne
propagule falls in water and is despersed |
|
|
How do mangroves cope with high salinity
|
stomata that open and close to bring in co2 and let out h2o; close in drought
thick cuticle Mg-Na pump (red mangroves) Vaculoles that encapsulate salt Glands that secrete salt |
|
|
How do mangroves deal with tidal flux
|
pheumatophores to take in oxygen during low tides
anaerobic respiration (short term) prop and ariel roots for gas exchange lenitcels for co2 and gas exchange |
|
|
What type of mangrove has pnuematophores
|
black mangrove
|
|
|
heliotrophism
|
reorienting leaves to point straight at the sun so that mangroves don't get as much light
|
|
|
tannins
|
UV absorbing compounds in mangroves
|
|
|
Rizophora mangle
|
red mangrove
|
|
|
Characteristics of red mangroves
|
grow on the fringe of bays
prop roots for gas exchange banana shaped seedling thick cuticle |
|
|
Avicennia germinans
|
black mangrove
|
|
|
Characteristics of black mangroves
|
pneumatophores
skinnier/pointy leaves teardrop shaped seeds |
|
|
Laguncularia racemosa
|
whie mangrove
|
|
|
characteristics of the white mangrove
|
oval leaves
nectaries at base of leaves eaten a lot on bonaire salt excreting pores on leaves |
|
|
Salt tolerant succession of mangroves
|
red --> black --> white
|
|
|
Spartina salt marsh
|
foundin temperate regions
more tolerant to freezing conditions filled with grass |
|
|
limit in spartina salt marshes
|
light @ high latitudes
|
|
|
limit for mangroves
|
nutrients @ low latitudes
|
|
|
Sedimentation and mangroves
|
slow down, bind, and settle sediment.
use nutrients |
|
|
How much of mangrove PP is directly consumed
|
less than 5%
|
|
|
how is most of mangrove productivity consumed
|
as detritus by the microbial loop
|
|
|
Characteristics of sea grass
|
flowering plants
need photic zone shelter coastal zone anchored in sand/mud 60 spps entire life cycle underwater |
|
|
Productivity of seagrass
|
800 g
|
|
|
Importance of seagrass
|
-epibionts
-refuge nutrient export herbivores food source |
|
|
how is seagrass many consumed
|
as detritus
|
|
|
Halodule wrightii
|
shoal grass
|
|
|
Syrigodium filiforme
|
manatee grass
|
|
|
Do an exercise of the connectivity of coral reefs, mangroves, land, sea grass, and the open ocean
|
done
|
|
|
Shared importances of mangroves, sea grass, and coral reefs
|
high biodiversity
size of landmass and terrestrial runoff influence same physical and ecological roles despite different spp |
|
|
Interactions between mangr, sg, and cr
|
flow of nutrients
exchange of juveniles buffering pollutants and nutrients, and waves |
|
|
Ways mangrove importance has been tested for
|
looking at otiliths of fish to see chemical composition during life phase
increased biomass with size of mangroves |
|

id
|
Caulerpa sertularioides
|
|

|
udotea fabellum
|
|

|
Syringodium filiforme
|
|

|
Caulerpa racemosa
|
|

|
Thallasia testudinum
|
|

|
Halimeda incrassata
|
|

|
Acetabularia crenalata
|
|

|
Caulerpa verticillata
|
|

|
Caulerpa cypressoides
|
|
|
apex predator
|
carinivore of larger animals
top predator large mobile and not preyed on as adults ex: orca, cros, sharks, humans |
|
|
Importance of apex predators
|
population regulation
affect evolution (prey on weak and sick) |
|
|
mega grazers
|
large bodied animals that graze
whales and manatees |
|
|
keystone species
|
have an impact on an ecosystem that is disporportionate to their abundance
|
|
|
What are indirect consequences of the presence of apex predators
|
prey will shift eating habits from the best foraging grounds in order to void predators
|
|
|
Predatory release
|
refers to when there is a decrease in predators that there is a increase in prey abundance
|
|
|
Ex of a trophic cascade
|
increase in black tip shark
decrease in cattlenose ray increase in scallops |
|
|
what is a problem with understanding top down effects
|
predators have been overfished for a long time
|
|
|
Explain yellowstone as an example of reintroducing apex predators
|
reintroducing wolves
decrease elk and change in grazing behavior increase in trees increase in predators that feed on wolf kills |
|
|
decrease in apex predators leads to
|
change in diversity (extinction, change community structure)
abundance, density, and biomass changes smaller body size with lower fecundity |
|
|
Mumby et al 2006
|
showed that apex predator presence increases the biomass of lower trophic levels, especially herbivores
|
|
|
What was the main point of Brian's talk?
|
He uses AUVs with lazers to determine the bathymetry of the sea floor
|
|
|
4Ds of AUVs
|
Dirty
Daring Dull Dangerous |
|
|
what was the status of sea turtles on Bonaire in 1991
|
They were not protected
poached and eaten (eggs too) |
|
|
3 main areas of STCB
|
research - 4 mo out of the year
conservation - enforcing laws education - schools and public |
|
|
carapis
|
shell of sea turtle that contains vertebrae fused into
|
|
|
skin of sea turtle
|
waterproof and not let in salt because it would lead to dehydration
|
|
|
what do turtles breathe
|
air
|
|
|
how many sea turtles are there
|
7 spp worldwide
|
|
|
how many sea turtles come to bonaire and which kind?
|
5
3 regular: hawksbill, loggerhead, green 2: leatherback, olive ridley |
|
|
compare green and hawksbill turtles
|
green is round head, eats seagrass, flat scales and round edge carapis
hawksbill sharp head, scrape sponges, skkoots overlap on carapis with serrated edges |
|
|
how many days does it take for an egg to hatch
|
60 days
|
|
|
what type of feeders are juv turtles
|
opportunitistic. usually eat jellies (can be confused with trash)
|
|
|
how many years until a turtle is sexually mature?
|
20 years
|
|
|
how do you track where sea turtles are?
|
satellite trasmitters on shells
|
|
|
describe turtle diving behavior
|
surface 20-60 min
night they stay down longer adults go as deep as 200 m (juv 50m) |
|
|
how do you tell male and female sea turtles apart?
|
males- long tail, and long nail that hooks onto female during sex
|
|
|
how many eggs does a turtle lay on average
|
100-150 eggs
|
|
|
how is sex determined in sea turtles
|
temperature
cool -> male warm -> female |
|
|
Porifera
|
sponges
|
|
|
unique features of sponges
|
spongin
spicules ostia/oscula chaonocytes collagen |
|
|
spongin
|
a protein that helps form the skeleton of sponges
,made of collagen for elasticity |
|
|
spicules
|
provide protection and structure to sponges
|
|
|
chaonocytes
|
aka collar cells
flagella resp for digestion whip to filter h2o |
|
|
oscula and ostia
|
oscula- opening at top where water flows out of
ostia tiny pores where water enters |
|

|
Class Demonspongiae
Genus: Aplysina Stove-Pipe sponge |
|
|
phylum cnidaria
|
jellies, fire coral, things with nematocysts, anemones and schleractinian corals
|
|
|
class anthozoa
|
true corals, anemones, and sea pens
|
|
|
class scyphozoa
|
true jellies
|
|
|
class hydrozoa
|
box jellies
hydrocorals |
|
|
class cubozoa
|
sea wasps
|
|
|
characteristics of cnidaria
|
nematocysts
radial symmetry single opening gastrocavity alternating generations |
|
|
alt gen phases of cnidaria
|
medusa-free swimming stage
polyp-sessle phase |
|
|
characteristics of scphozoa
|
large medusa
sometimes no polyp phase has oral arms that help with feeding |
|

|
Phylum Cnidaria
Class Scyphozoa Genus: Cassiopea Upsidedown jellyfish |
|
|
Class Hydrozoa
|
velum-membrane on the subumbrella surface of the jelly
polyp is asexual medusa is sexual polyps for together to have different functions that benefit each other |
|

|
Phylum Cnidaria
Class Hydrozoa Genus: Halocordyle Christmas Tree Hydroid |
|
|
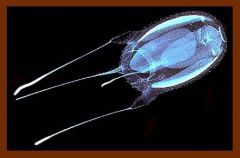
Class cubozoa
|
tentacles suspended from pedalium
developed eye cube like bell |
|
|
Phylum cnidaria
Class cubozoa Genus carydbea Sea wasp |
|
|
Class Anthozoa characteristics
|
tubular body
hollow tentacles oral disc pharhynx suppressed medusa phase solitary or colonial int or ext skeleton Only lives in salt water |
|
|
Subclass Octocorallia
|
8 tentacles
|
|
|
Subclass Hexacorallias
|
6 tentacles
|
|
|
Phylum Ctenophore characteristics
|
no stinging cells
ctenes used for locomotion bioluminesce |
|
|
Phylum Annelida characteristics
|
segmented worms
nervous, digestive, and circulatory systems leg appendages trocophore larvae |
|
|
Class Polychaeata
|
parapodia for gas exchange and movement
chitinous setae |
|

|
Phylum: Annelida
Class: Polychaeata Genus: Spirobranchus Christmas Tree Worm |
|

|
Phylum: Annelida
Class: Ploychaeta Genus: Hermodice |
|
|
Phylum Arthropoda
|
jointed legs
exoskeleton that molts--made of chiton segmented body 84% of all described species |
|
|
Subphylum crustecea
|
head, thorax, and abodomen
head an thorax may fuse larval naupilus |
|

|
Phylum: Arthropoda
Subphylum: crustacea Genus: Stenopus Banded Coral Shrimp |
|

|
Phylum Arthropoda
Subphylum crustacea Genus Panulirus Species argus Caribbean Spiny Lobster |
|
|
Phylum Ectoprocta characteristics
|
bryozoans
zooids mouth and anus U shaped lobophore |
|
|
Phylum Mollusca characteristics
|
muscular foot
eyes shells radula (scraping to eat) mantle which produces shell veliger larvae |
|
|
class gastropoda
|
snails
|
|
|
class polyplacophora
|
chitons
|
|
|
class bivalvia
|
bivalves
|
|
|
class cephlopoda
|
octopus and squid
|
|

|
phylum: mollusca
class: gastropoda genus: strombus species: gigas queen conch |
|

|
phylum mollusca
class gastropoda genus cyphoma |
|

|
Phylum: mollusca
class: polyclacophora genus: acanthopleura fuzzy chiton |
|

|
phylum mollusca
class gastropoda genus elysia lettuce sea slug |
|

|
phylum: mollusca
class: bivalvia genus: lima rough fileclam |
|

|
Phylum mollusca
class bivalvia genus: pinna amber penshell |
|

|
Phylum: mollusca
class: cephalopoda genus: sepiotheuthis caribbean reef squid |
|
|
Phylum Echinodermata characteristics
|
water vascular system
podia used for fighting, movine, sitting 5 fold radial symmetry tube feet spine skeleton can regenerate |
|
|
pedicellariae
|
used in echinoderms for cleaning and defense
|
|
|
class crinoidea
|
feather stars
|
|
|
class asteroidea
|
sea stars
|
|
|
class echinoidea
|
sea urchins and sand dollars
|
|
|
class holothuroidea
|
sea cucumbers
|
|
|
class ophiuroidea
|
brittle stars
|
|

|
phylum echinodermata
class crinoidea crinoid/feather stars |
|
|
|
phylum: echinodermata
class: asteroidea genus: oreaster cushion sea star |
|

|
phylum: echinodermata
class: asteroidea genus: oreaster cushion sea star |
|

|
phylum: echinodermata
class: echinoidea diadema antillarum |
|

|
phylum: echinodermata
class: ophiuroidea brittle stars |
|

|
phylum: echinodermata
class: echinoidae genus: echinometra rock boring urchin |
|

|
Phylum: echinodermata
class: holothuroidea genus: holothuria donky dung sea cuc |
|
|
Phylum Chordata Subphylum Urochordata Class Ascidieacea
|
Tunicates
trididemnun-overgrowing mat has soral notochord and nerve chord gill slits water enters and exits through siphons |
|
|
what ecological processes control algae
|
light
nutrients top down grazing recruitment |
|
|
Explain the physiolical difference between Eucidaris thouarsii in the E. pac and galapagos
|
E pac are small, nocturnal, sedentary, and feed on CCA
Galapagos are large, diurnal, mobile, and feed on coral as well the difference is becaseu E pac there is higher predation by triggerfish and pufferfish |
|
|
Acanthaster planci effects
|
COTS
corallivorous sea star witha large stomach that moves quickly 1st effects-low coral 2nd: increase algal cover 3rd: increase herbivorous fish |
|
|
why explosion of COTS
|
adult aggregation (a disturbance forces them shallow)
natural cycles terrestrial run off increases recruitment pollution reduces predators |
|
|
Effects of Echinometra mathaei on reefs in Kenya
|
in fish protected areas balistae kept them in control, which kept more cca, topographical complexity, etc
in unprotected areas there was more algal and sponge cover and lots of urchins |
|
|
Discuss the role of diadema as a keystone grazer
|
eats algae
1983-1984 die off lead to an increase in algae cover decrease in coral, zooxanthids, and CCA increased grazing by fish |
|
|
What are methods for underwater surveys
|
snorkel
sea scooter manta tow |
|
|
what are underwater surveys used for
|
archaeological findings
geological surveying biological/ecological (CR bleach) search and recover observing towed equipment |
|
|
hazards of sea scooters
|
caught in propelor
crashing into soething low buddy safety trouble popping ears deco |
|
|
manta tow hazards
|
line getting caught in propellor
feel like bait ears equalizing wrapped in line |
|
|
Reproductive structures in mammals evolved how for the marine environment
|
they moved to be within the body in order to be more streamlined
|
|
|
echolocation: use and development for marine environment
|
capture prey and comunicate
deblitate prey with pressure done from within the head |
|
|
what type of bone is used more in the marine environment
|
spongy bone because they have less impact
|
|
|
how did marine mammals evolve so they could dive
|
streamline-less energy when swim @ depth
blubber to stay warm greater red blood count 90% of O2 used alveoli compress at depth |
|
|
sensory systems of marine mammals
|
large auditory system
can taste little smell |
|
|
3 types of lactation strategies in marine mammals
|
fasting- not eat; rapid weaning; high fat content
forage-leave baby to get food; longer lactation period; moderate fat aquatic nursing; mom stay together during feeding; low fat; long lact period |
|
|
marine mammals eyes
|
see in air and water
more sensitive to blue and shorter wavelengths of light |
|
|
thermoregulation marine mammals
|
high SA:V to increase insulation
|
|
|
locomotion marine mammals
|
propulsive movement is easier
wave riding to save energy drafting |
|
|
osmoregulation in marine mammals
|
get from food and efficient kidneys
|
|
|
odontocenti social structure
|
matriline
|
|
|
dolphin social structure
|
schools within groups based on age, sex, and size
|
|
|
sperm whale social structure
|
matilinear
males leave and join later |
|
|
mutualism
|
both organisms benefit
|
|
|
commensalism
|
one benefits and the other is unaffected
|
|
|
parasitism
|
one is harmed and other benefits
|
|
|
ex of mutualism, commensalism, parasitism
|
mutual: coral/zoox
commensalite: secretary blennies and coral parasitism: isopods on creolefish |
|
|
Endosymbiotic theory
|
bacteria will become part of a cell and turn into mitochondria
chloroplast evolved from engulfing photosynthetic bacteria engulfing bacteria --> evolved |
|
|
Evidence that cleaning stations are parasitic
|
cleaners feed on mucus
client leaves if bit cleaners are punished cleaners will learn to eat flakes instead of a prawn if "punished" |
|
|
phoresy
|
org used for transport
|
|
|
inquilinism
|
used for housing
|
|
|
metabiosis
|
using something that was created by the first after it dies
ex: hermit crabs |
|
|
5 characteristics for mimcry
|
1. share same habitat and range
2. same size 3. mimic less abundant that model 4. alters behavior to appear more like model 5. must benefit from resemblance |
|
|
batesian mimicry
|
mimic resembles successful species but is not harmful
|
|
|
mullerian mimicry
|
mimic resembles and both cause harm
|
|
|
aggressive mimicry
|
mimic imitates the appearance and behavior of harmless species to approach prey
ex: yt snapper and goatfish |
|
|
co evolution
|
change in genetic composition of one species in response to a change in another
found in highly specified relationships |
|
|
ex of co evolution
|
grazers evolved along with algae
grazer; bite strength, gut length, microbes algae: chemical defense |
|
|
competition
|
rivalry between individual groups for limited resources
|
|
|
interference
|
interaction between individauls via aggression
physilca or chemical |
|
|
exploitation
|
indivudal affects all other competitors
|
|
|
r-selection
|
high fecundity
early maturity short generation time quick growth not good competitors |
|
|
k-selection
|
low fecundity
later maturity long life slow growth expert competitors large body size |
|
|
are coral brooders k or r?
|
r
|
|
|
amensalism
|
one sp hurts another w/o benefit
|
|
|
if you put a drop of hcl on sponge and it fizzes what type of sponge do you have
|
calcareous sponge
|

