![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
37 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Identify General Uses of Life Insurance |
Create an estate pay in estate taxes fund a business transfer or continuation pay off a home mortgage provide an education fund, protect a business from loss of a person, create a retirement fund, comply with a court order, make a gift, to reward and retain valuable employees, equalize inheritances, use cash value as an emergency phone, replace lost income, and final expenses |
|
|
|
List and describe the legal elements of a life insurance contract |
Agreement which is the offer and acceptance, consideration which is the premium, competent parties, legal purpose so someone will suffer a financial loss |
4 elements |
|
|
Explain the features of three types of term insurance level term annual renewable term and decreasing term |
Level term the premium and face amount remain level but only for a number of years. Annual renewable term insurance art the face amount remains level as the premium annual increases. Decreasing term the face amount decreases as the premium remains level used for mortgage insurance |
|
|
|
Identify the characteristics of whole life insurance |
Paid on the death of the insured whenever the death occurs and will remain in force until death it's guaranteed. Face amount will be paid regardless of age at the death of the insured comma continuous or limited premium. Use for permanent protection for College Planning for estate protection and for retirement planning |
|
|
|
Advantages of whole life insurance |
The premium Remains the Same throughout the contract, in case of a lapse of policy may stay and Forest via the APL the automatic premium loan, and the cash value grows tax-deferred and available for loans or emergency use. |
|
|
|
Disadvantages of whole life insurance |
Initial cost is higher than term insurance, the cash value not paid is not paid in addition to the death benefit but it can be, lost investment opportunities. |
|
|
|
List the six components of universal life insurance |
Cash, mortality charge, policy expenses (fixed), cash value, Interest, death benefit. |
|
|
|
Identify the flexibility choices afforded by the universal life insurance policy |
1. Premiums can be skipped. 2. The increase or decrease the face amount 3. Lengthen or shorten protection period 4. Increase or decrease level of premiums 5. Lengthen or shorten the premium paying period. 6. Contribute or withdraw lump sums of money and the ability to have either partial surrenders or loans |
|
|
|
Comparison chart universal life vs. Whole life |
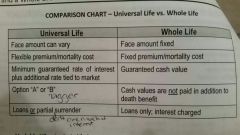
|
|
|
|
Explain the tax considerations for life insurance as it relates to the premium, cash value and death benefit |
1. Life insurance premiums are not tax deductible 2. Death proceeds are not subject to federal income tax 3. The proceeds will be included in the estate of the owner for federal estate tax purposes |

|
|
|
List some riders in life insurance policies |
Guaranteed insurability rider the Gir , waiver of premium rider rider, accidental death rider, payor benefit, accelerated death benefit. |
|
|
|
Briefly explain a guaranteed insurability rider |
Attached to a whole life in, endowment, or universal life contract the policyholder is guaranteed the right without medical or occupational examination to make periodic additions to their life insurance at standard rates |
|
|
|
Briefly explain the benefits of the waiver of premium Rider in a life insurance policy |
Should be insured become totally disabled by bodily injury or disease the payment of subsequent premium is waived by the insurer there is normally a 90 or 180 day waiting. Before the company waives the premium this insures the insurance such as an auto accident where the insured cannot work |
|
|
|
Briefly explain the accidental death benefit Rider on a life insurance |
Provides for the payment of a multiple of the face amount in the event of an accidental death. Accidental death is usually defined as a death resulting directly and independently of all other causes of injuries solely through external violent or accidental means and occurs within 90 days from the date of such accidents such as an airplane taxi train and it triples the value on a public transportation |
|
|
|
Briefly explain the payor benefit Rider |
Waves the premium should the payor usually a parent die or be totally disabled while paying the premiums of an insured their child this usually terminates when the insured child reaches the age of 25. This is used on juveniles policy |
|
|
|
Briefly explain accelerated death benefit Rider in a insurance policy |
This is a free rider that the insured can collect on their own life policy if they are diagnosed with a terminal illness and must be certified by attending a position of an individual that has one year or less to live some companies will pay up to 90% of the face amount this is money to use while you're still alive it is not taxed even if you don't die. This can be used for home renovations for a disability accommodation |
|
|
|
The standard provisions of a life insurance contract |
1. Incontestable clause - planes cannot be denied after 2 years from the date of issue 2. Grace period - a. In which premium must be paid to prevent the policy from lapsing. 3. Miss statement of age or sex 4. Suicide 5. Entire contract clause - the application becomes part of the policy so the insured has a copy. 6. Reinstatement Dash allows for reinstatement after lapse of policy generally up to two to three years it does require the owner to pay back all the premiums plus interest and prove to be insurable. 7. Right to examine - the free-look provision that allows the applicant number of days following physical receipt of the policy to examine it and return the contract for a full refund 8. Exclusions such as a war clause or cause of death exclusion Ownership's rights / crabs |
|
|
|
Identify dividend options of participating life insurance policies |
Return of excess premiums. Carpo. 1. C - cash not subject to income tax 2. A - accumulation of Interest which is taxable 3. R- reduce premium 4. P - paid up additional insurance 5. O - 1 year level term |
C.a.r.p.o. |
|
|
The following policy Provisions are commonly found in most major medical insurance policies: a. Co-insurance Clause, b Deductible. Describe each provision |
A. The co-insurance Clause requires that the insured pay a portion of each dollar loss after deductible has been exceeded. B. A deductible is an amount of money paid by the insured it must be satisfied before the insurance contract responds |
|
|
|
One of the standard Provisions found in most life insurance policies is the reinstatement provision. Explain the reinstatement provision and list the requirements needed to reinstate a policy. |
After the expiration of the grace period, the insured May request the reinstatement of the contract. Requirements Requirements: proof of insurability , payment of all back premiums, interests, and policy loans. |
|
|
|
Beneficiary designations |

|

|
|
|
Describe the function of a conditional receipt |
It's itchy by the agent after completing the application and receiving money. Coverage is enforced as in the application date or medical exam date if later. We have a death occurs during underwriting the face amount is payable if the risk would have been accepted by the company. The amount paid under a conditional receipt is limited to the face amount. Conditional receipt wording is non-standard. Look for when coverage begins and what amount would be paid |
|
|
|
Seven life insurance settlement options |
1 cash or lump sum buy a debit card or check book the most common. 2 fixed amount payments for example $1,000 a month. 3. 6. Payments for example over 15 or 20 years. 4. Interest payments for example paying only the interest but it's unusual. 5 period life income for example the death benefit percentage of life expectancy was the money per month. Life in come with. Certain guarantees someone will get paid over a period of time 7. And installment with refund |
|
|

Determine how much will be paid |

|
|
|
|
Examples of Cost Containment requirements for health insurance |
Pre-admission certification Kama secure a required second surgical opinion, notification within 24 hours of an emergency admission, discharge from the hospital by a preset schedule date, pre-approved Hospital stay extension deemed necessary, concurrent review, retrospective review, ambulatory services use so, one day surgery units. |
|
|
|
Three types of tax advantaged accounts in health insurance |
Fsa, hra, hsa |
|
|
|
requirements of a health savings account HSA |
Must purchase a qualified high-deductible health insurance plan and hdhp, must be a written document using an approved HSA trustee. Oh, fun with cash contributions to cover unreimbursed claims optional |
|
|
|
Hsa features |
Tax-deferred growth Ira, not subject to use it or lose it as an FSA, withdrawals have a penalty if taken early the max contributions are 3350 for a single + 6750 for family |
|
|
|
What is part a of Medicare |
Hospital care. Inpatient hospital care after The Upfront deductable a hospital stay for the first 60 days this is for someone who is getting better. Skilled Nursing Facility to qualify the patient must be hospitalized for at least 3 days / night's |
|
|
|
What is Part B of Medicare |
Part B is medical insurance it is optional it's up for a person who fails to qualify for part I can still receive Part B benefits generally provided on a $166 deductible basis with an 80/20 coinsurance. There is only one deductible per calendar year. This covers medical expenses / dr. Services Kama Home Health Care, Outpatient Care. The premium is based on income other than Social Security there is no max out of pocket |
|
|
|
What is Part C of Medicare |
Part C is the advantage plan it replaces plant part A and Part B similar to an HMO plus additional coverages are available. |
|
|
|
What is Part D of Medicare |
Part D is the RX prescription drug plans that are government-sponsored insurance policies designed to help protect Medicare beneficiaries against the rising cost of prescription drugs. The premium will vary based on the drug plan purchase and one's income |
|
|
|
What are the three options available When selecting a benefit schedule in group life insurance |
1 flat schedule 2. earning schedule which is the most common 3 occupation or position schedule |
|
|
|
List the possible sources of funding and assistance for the issues of long-term care insurance |
Family, self-insure, Veterans Administration, Medicare , Medicaid, LTC insurance policy |
|
|
|
List of benefits typically provided by a long-term care policy |
In-home coverage, assisted living facility, nursing home, Adult Day Care, Hospice Care |
|
|
|
Common long-term care insurance policy provisions and options |
1. Bed reservation - provides 3250 days a year for daily room expenses at an assisted living facility or nursing home. 2. Daily /weekly / monthly benefit Dash most if you don't daily benefit pays to cover expenses but no more than the maximum limit preferred to get a monthly benefit. 3. Reimbursement versus Indemnity - most contract sold as reimbursement. 4. Guaranteed benefit increase inflation Rider increases the daily benefit on a systematic basis is usually annually.5. Joint waiver of premium purchase by couples is premium on both if one partner satisfies the coverage trigger. 6. Calls you sharing benefit - a benefit added by writer when contracts purchased by couples and benefit. Is less than a lifetime. Enter 7. The elimination period - the time frame the insured must wait before collecting benefits from the contract the longer the period the lower the premium waiting. Is the self-insured and her 8. Benefit period - the number of years benefit is payable once the claim is triggered answer 9. Premium discounts - carriers offer discounts |
|
|
|
Benefit triggers required to approve a claim in a long-term care insurance policy |
Inability to perform any two of the activities of daily living has to be medically certified by a physician. Or cognitive impairment. |
|

