![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
170 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Virulence |
Ability to grow and multiply |
|
|
Infectivity |
Ability to enter tissue |
|
|
Pathogenicity |
Ability to cause disease |
|
|
Duration of exposure |
Length of time person exposed |
|
|
Size of inoculum |
Number of organisms needed to cause disease |
|
|
India ink positive. Low glucose csf and predominant lymphocytes. Meningitis Light sensitivity |
Cryptococcosis Not communicable |
|
|
Meningitis Normal glucose Predom neutrophils |
Bacterial meningitis |
|
|
Meningitis Stain neg Normal glucose |
Viral meningitis |
|
|
Gram positive clusters |
Staphylococcus |
|
|
Gram positive chains |
Streptococcus |
|
|
Frequency distribution for intervals |
Histogram |
|
|
Line graph providing same data as histogram |
Frequency polygon |
|
|
Finger lesion |
Herpetic whitlow Restrict from work |
|
|
Confidence interval |
Large sample size=narrower and more precise. Quadruple sample size to halve margin of error |
|
|
Gram -, oxidase positive. Csf |
N. Meningitis is |
|
|
Diarrhea most often linked to contam seafood |
Vibrio |
|
|
Bronchoscopy AAIR |
12 ach. Neg pressure. |
|
|
Suspect bed bugs |
Bag belongings. Declutter. Vacuum with hepa filter |
|
|
SRP Ach |
Ach of 10. Neg air |
|
|
Hep A |
Not blood borne. Not spread person to person |
|
|
Floor Area in or needing to be cleaned |
3x4 foot around table |
|
|
Varicella exposure response |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Bed bug survival time with no feeding |
1 year |
|
|
During outbreaks, no. times in day that high touch surfaces should be cleaned |
3 times/day |
|
|
Droplet precaution termination for N.meningitidis |
After 24hrs of therapy |
|
|
Process measure |
Used to measure compliance with desired care or support practices or to monitor variation in these practices. Opposite is outcome measures |
|
|
Scarlet fever incubation period |
1-7 days. GAS. Symptoms 3 days after exposure. Rash. Throat |
|
|
High sensitivity |
Most who have disease will have positive test result. Few people who have disease will have a negative test result…number false negatives will be low |
|
|
Cdiff spore survival time |
5 months |
|
|
Rapid neurodegeneration. +csf. mri abnormalities in caudate nucleus. Typical eeg. |
Creutzfeldt- Jakob prion disease |
|
|
Patient HBeAg positive |
Patient is infectious |
|
|
Patient is Anti-HBc and Anti-HBs positive. |
Patient previously infected and now immune |
|
|
Gluteraldehyde, hydrogen peroxide, peracetic acid, chlorine, orthophthaldehyde |
HLD disinfectants needed for semi critical items |
|
|
Meningitis and CSF results |
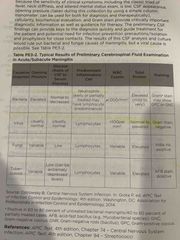
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Chart showing single line of data with upper and lower control limit |
Control chart |
|
|
Incidence exposed/incidence unexposed |
Relative risk |
|
|
Neuroparalytic. Blurred vision, dysphasia, paralysis, respiratory failure |
Botulism |
|
|
Cryptosporidium parvum |
Protozoa resistant to many disinfectants. Only hydrogen peroxide known to be effective |
|
|
Cat 1a recommendation |
Sterilization of instruments that will come into contact with sterile tissue |
|
|
Bacteria passed from mother to baby during birth |
Streptococcus agalactiae/ group b strep |
|
|
Why chg recommended? |
Dries in 30 sec and low risk for allergy. No rinsing required. Not for those under 2 months |
|
|
Immunoglobulin not available for what? |
Pertussis |
|
|
Dialysis HBsAg patient precautions |
Seperate equipment and separate room |
|
|
Hep c |
Low risk transmission by sex |
|
|
Special cause variation |
Variation more than 3 std deviations outside mean |
|
|
Measles |
Culture and transport on ice. Culture immediately or store at -70 |
|
|
HBsAg |
Detected in high levels in serum during acute or chronic HBV infection. HBsAg positive 7-30 days after vaccination |
|
|
Weil-Felix agglutination |
Test to differentiate rickettsia antibodies in serum. Used for Rocky Mountain spotted fever diagnosis |
|
|
Human factors engineering |
Studies human characteristics and is concerned with design of tools, machines and systems that take into account human capabilities |
|
|
Viral load of HIV patient |
Once during antiretroviral phase, decr during asymptomatic hiv infection, incr as progresses to aids |
|
|
Empiric |
Broad spectrum prior to culture results |
|
|
Job enrichment |
Giving employees more responsibilities and variety in work |
|
|
Propagated source of infection |
No single source |
|
|
Hills criteria for causation |
See chapter 10. Epi general principles |
|
|
Body piercing infections |
Atypical mycobacterium Staph species Pseudo species |
|
|
HVAC malfunction possible infections |
Increase in SSI Aspergillus Hai varicella outbreak |
|
|
Sensitivity |
Ability to detect true positives when applied to population with disease |
|
|
HSV ref range |
<1:10 neg 1:10 or greater= pos |
|
|
Point of care instruments with lumen |
Wash with water. Never saline |
|
|
P value of 0.1 means |
1 in 10 chance of making type 1 error |
|
|
Type 1 error |
Occurs when rejecting null hypothesis when it is true |
|
|
4 principles of EM |
Mitigation, preparedness, response and recovery |
|
|
Most common pneumonia in kids |
Mycoplasma pneumoniae |
|
|
Hep B exposure |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Gram -ve bacilli. Aerobic. |
Acineyobacter baumanii |
|
|
Safe cold food temp storage |
Below 5c |
|
|
Malassezia furfur fungal infection often associated with.. |
Intravenous lipid infusions |
|
|
Which level of equipment must be processed by HLD |
Semi-critical |
|
|
Blood collection time |
Less than 2hrs room temp |
|
|
Amount of water needed to be stored for emergency situation |
25gallons per patient per day |
|
|
Mycoplasma pneumonia isolation |
Droplet |
|
|
Mycobacterium chelonae potential source of infection |
Bronchoscope and hydrotherapy pool |
|
|
Cat B bioterrorism |
Moderate ease in spread, moderate morbidity, low mortality. Eg typhus |
|
|
Relative humidity limit to prevent fungal growth |
60% |
|
|
Dialysis infection risk reduced with |
AV fistula rather than dialysis catheter Tunneled cuffed catheter Femoral only short time and bed bound |
|
|
Cryptosporidium resistant to what disinfectant? |
Chlorine |
|
|
Bleach used at what conc? |
5.25-6.15% |
|
|
Pareto chart |
Bars and lines present |
|
|
Meningococcal meningitis incubation period |
2-10 days |
|
|
Recommendations for mop heads |
Launder daily Change mop water after use in 3-4 rooms or no ore than 1 hr of use |
|
|
Measles isolation period |
7 days after rash appears |
|
|
Iatrogenic CJD |
Develops as a result of medical treatment |
|
|
Positive predictive value |
True positive/(true positive+false positive) |
|
|
Ethylene oxide sterilization affected by what parameters |
Gas conc Temp Relative humidity Exposure time |
|
|
Positive TST |
Indicates past exposure to TB. Detects latent Tb. No current infection |
|
|
IgM |
Primary immune response |
|
|
Hepatitis A IgM detectable after how many days? |
5-10 days after exposure. Ab detectable within 3 weeks. Ab not detectable after 6-12months |
|
|
Pertussis incubation period |
7-10 days |
|
|
Scabies incubation period |
4-6weeks. Minimal 10days. Discontinue contact isolation after 24hrs of treatment |
|
|
What does TST induration mean |
10mm= positive |
|
|
Csf interpretation |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Flu incubation period |
1-4 days |
|
|
Flu shedding |
Adults:Day before symptoms begin through 5-10 days after |
|
|
Immunocompromised def |
Neutropenia, HIV with CD4 <200, less than 1 yr BMT, steroid, chemo |
|
|
Paroxysmal stage of whooping cough |
1-6 weeks |
|
|
Lyme disease not found where? |
Southeast |
|
|
Bacteria that can penetrate conjunctiva |
Neisseria gonorrhea/meningitidis Strep pneumoniae Listeria monocytogenes Corynebacterium diphtheria |
|
|
Scabies presentation |
Pruritic lesions on hands, webs of fingers, wrists, elbows, knees, outer surface of feet, armpits, buttocks and waist |
|
|
Not known to contaminate TPN |
Mycobacterium fortuitum |
|
|
ESBL resistance to what Ab? |
Ceftazidime, cefotaxime, ceftriaxone |
|
|
Koplik spots |
Measles. Prodromal fever, conjunctivitis, cough, small spots with white center |
|
|
Pneumonic plague isolation |
From inhaled aerosolized bacteria. Incubation period 1-6 days. Flu like symptoms. Resp droplet spread. Mask. Cohorted. 3ft. Iso disc 48hrs after therapy. |
|
|
SSI risk score |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Anthrax |
Bioterrorism agent. Mediastinal widening. Gram+ box car shaped bacilli. |
|
|
Measles symptom onset |
Cough: lasts 2-4 days Rash appears day 3-7, lasting 5-6 days |
|
|
Vaccination |
Federal regulations do not require informed consent |
|
|
Disinfectant |
More microbes, greater amount of time needed |
|
|
Transtheoretical model/ stage theory stages |
Precontemplation, contemplation, preparation(planning for behavior change), action and maintenance |
|
|
Water management plan |
Disinfect when distal sites is 30% |
|
|
OPA benefit |
Does not require activation |
|
|
Room temp to treat bed bugs |
118 for 1 hr |
|
|
Negative predictive value |
True negative/(false + true neg) |
|
|
Higher specificity than sensitivity |
TN/(TN+FP) Neg result more accurate than positive |
|
|
Diluted bleach storage time in open container |
24hrs |
|
|
Non immune hcp given vzig, isolation time |
28 days after exposure |
|
|
Bloom taxonomy analysis |
Compare, discriminate, differentiate |
|
|
Organisms most often associated with improper scope reprocessing |
TB and pseudomonas |
|
|
Sterilizer that forced steam into the chamber from top and push air out bottom |
Gravity displacement sterilizer |
|
|
Common urine contaminant |
Yeast |
|
|
Sterility assurance level for critical items |
10^-6 |
|
|
Case-control |
Use for rare outcomes |
|
|
Anthrax clean |
Standard terminal clean. No person to person transmission |
|
|
Discrete data |
Whole numbers. Can be categorical or noncategorical |
|
|
Time for IgM response to develop in measles |
Up to 72hrs |
|
|
Delphi technique |
Structured communication method to solicit opinion from experts by answering questionnaires in 2 or more rounds |
|
|
Passive immunity |
HepA IG given within 2 weeks after exposure |
|
|
Community acquired MRSA pneumonia symptoms |
Severe pneumonia, hemoptysis, mulitlobar infiltrate |
|
|
Hot water laundry temp |
160f |
|
|
MERV filtration minimum OR |
MERV 14 |
|
|
Airflow direction in OR |
Noninductional unidirectional infusion of air with a supply over the surgical table and an exhaust near floor at periphery of room. From clean to less clean |
|
|
Bleach dilution for non porous surface |
1:100 |
|
|
Airborne room requirement |
Must exhaust outside. Minimum 12 air changes/hr |
|
|
Water temp range to prevent legionella |
Hot water 124c and cold 68 |
|
|
When to use detergent |
Enviro friendlier. Can use to clean floors when not an isolation room |
|
|
Sterile storage parameters |
18 inch below ceiling, 8 inches above floor and 2 inches from wall |
|
|
Sterile supply room parameters |
Temp of 75. RH not to exceed 70%. |
|
|
Tuberculin rxn interpretation |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Food service worker hep a exclusion from work |
7 days after onset of jaundice |
|
|
Regulations about handling of infectious waste regulated at what level? |
State |
|
|
Incidence proportion used to measure frequency of new cases in a specific population during a limited time |
Attack rate |
|
|
Can inactivate disinfectants |
Blood and protein |
|
|
Rooms required to be negative pressure |
Janitor closet and ER waiting room |
|
|
Virulence factor common to Gram -ve |
Produce endotoxin |
|
|
Class of chemical indicator Bowie-Dick |
Class 2 |
|
|
Epi model consisting of hub(host) with inner core of genetic info. Outer enviro of physical, biological or social. |
Wheel model of Disease causation |
|
|
Critical, semi critical, non critical require what cleaning? |
Sterilization, HLD and low level disinfection respectively |
|
|
Flu vaccine storage rate |
2-8C |
|
|
3 domains of learning |
Cognitive Affective- emotions Psychomotor- manual/physical |
|
|
Bloom’s taxonomy |
Remembering Understanding Applying Analyzing Evaluating Creating |
|
|
TB risk assessment categories and annual screen |
<200. Low<3, Medium>3 (annual screen) |
|
|
Flu isolation |
5 days or until symptoms resolved(whichever is longest) |
|
|
Amount of time for multi dose vials |
28 days |
|
|
When does antibiotic timeout occur? |
Within 24-48hrs of results being available |
|
|
What method of disinfection & sterilization will kill all organisms and spores? |
Steam sterilization and ethylene oxide |
|
|
Negative airborne ach |
6-12 ach |
|
|
Smallpox mortality |
30% |
|
|
Tdap vaccine recommendations |
All >19yrs should get it |
|
|
When can chi- square test be used? |
To evaluate effect of variable on outcome, to calculate odds or relative risk, when each cell greater than 5. |
|
|
What test when data small? |
Fishers exact |
|
|
Specificity calculation |
No. true negatives/total persons without disease x100 |
|
|
Std deviation |
1std=68% 2std=95% 3std=99.7% |
|
|
Correlationl |
r closest to 1 means stronger positive correlation |
|
|
Kurtosis |
How flat a peak is. 0: mesokurtic. Bell shaped +: leptokurtosis. More peaked -:platykurtic. Flatter curve. |
|
|
Mode |
Number in a set occurring most frequently |
|
|
Extraneous variable that systematically varies with independent variable and influences dependent variable |
Confounding |
|
|
Kaposis sarcoma |
Caused by herpesvirus 8 |
|
|
Coccidioides |
Soil fungus. 50% of ppl in endemic areas exposed |
|
|
Avian flu found in what reservoir? |
Domestic poultry |
|
|
Prevalence of disease is low means… |
Positive predictive value of diagnostic test is lowered |
|
|
Attributable risk calc |
(No. exposed who get disease/total no. Exposed) - (no. Unexposed who get disease/total no. Who are not exposed) |

