![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
92 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Definition of COPD: Reversible? Airflow limitation? Inflammation? What contributes to overall severity in individual patients? |
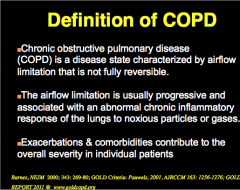
|
|
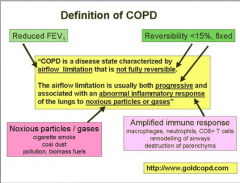
Note CD8 lymphocytes (different from asthma) |
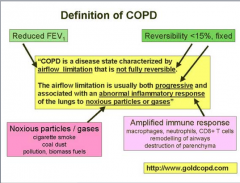
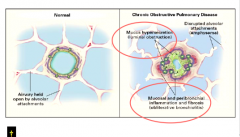
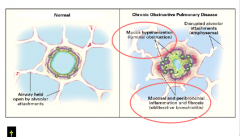
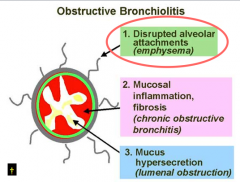
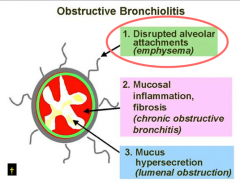
Destruction of alveoli = emphysema Remodling of airways = chronic bronchitis |
|
|
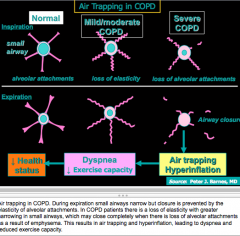
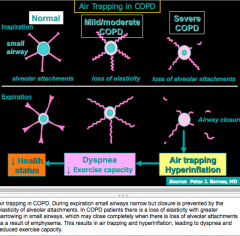
What to mechanisms lead to airflow limitation in COPD? |
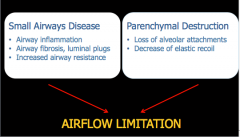
|
|
|
Has COPD increased or decreased since 1965? |
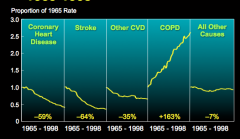
|
|
|
Who have the highest death rates from COPD? |
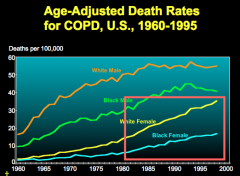
|
|
|
Men or women have higher COPD death rates? |
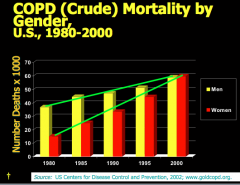
|
|
|
What is the third leading cause of death in the US and worldwide? What percent of population is affected each year? |

|
|
|
How many adults in the US have COPD? |
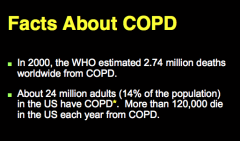
|
|
|
Primary cause of COPD? |

|
|
|
Does FEV1 decrease naturally with age? How does this change with smoking? |
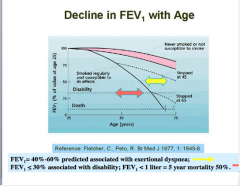
|
|

|

|
|
|
What are the risk factors for COPD? |
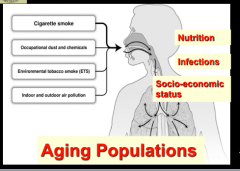
|
|
|
Which smokers develop COPD? When does it become symptomatic? When does dyspnea develop? |

|
|
|
Presence of __________ due to chronic bronchitis and/or emphysema. What is required to make diagnosis? May also include what? Will some patients with a long history of asthma go on to develop irresistible airflow obstruction indistinguishable from COPD? |

|
|
|
What are the symptoms of COPD? Exposure to risk factors? Required to establish diagnosis? |
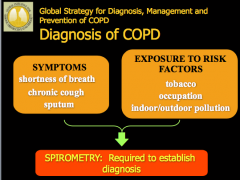
|
|
|
Describe the cough: Timing, contents, advanced cases of COPD? |

|
|
|
Describe the sputum production: Timing, contents, color changes, definition of chronic bronchitis? |

|
|
|
Describe the dyspnea: Timing, when it occurs, causes, how is it quantified? |

|
|

|

|
|
|
Physical examination: Signs of each Airflow limitation Hyperfinflation Impairment of mechanics of breathing |
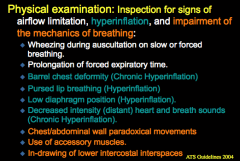
|
|
|
Systemic signs on the physical examination: Heart, muscle, color, liver, distention |

|
|
|
How do you test airflow limitation? When should bronchodilator reversibility be performed? |

|
|
|
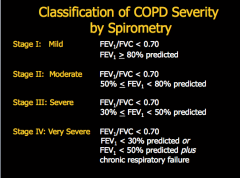
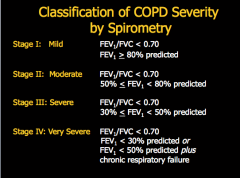
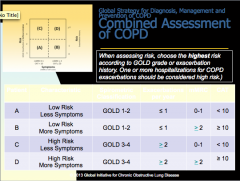
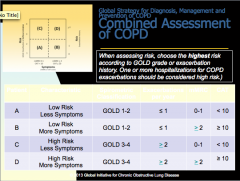
What are the GOLD classifications of severity of airflow limitation? Based on what ratio? |
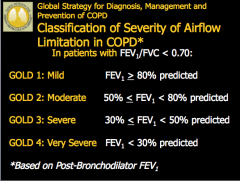
|
|
|
How do you assess lung volumes and gas exchange? Are lung volumes increased or decreased in COPD? |

DLCO (tests alveoli) REDUCED IN EMPHYSEMA = NORMAL IN ASTHMA AND BRONCHITIS |
|
|
How do you access exacerbations? What indicates high risk? |

|
|
|
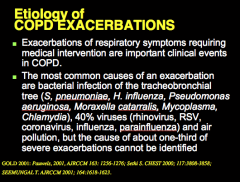
What is an exacerbation of COPD? |

|
|
|
What do exacerbations affect? Life, function, economy, death |
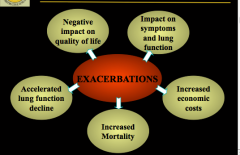
|
|
|
When should you do CXR? What can be used to evaluate a patient's oxygen saturation and need for supplemental oxygen therapy? When should you do an alpha-1 antitrypsin deficiency screening? |

|
|
|
What accounts for <1% of all COPD cases? What is the normal alpha-1-anti-trypsin allele? Location? Most deficient individuals are homozygous for what allele? Other forms? |

Alpha 1 def = PANACINAR emphysema |
|
|
In what populations are the alpha-1-antitrypsin deficiencies seen? Do patients develop COPD without smoking? What is treatment? |

|
|
|
Define mixed pattern: |

|
|
|
Define blue boaters: |

|
|
|
Define pink puffers: |

|
|
|
Components of Type A or "Pink Puffer" Respiratory drive, dyspnea, age, sputum volume, CHF, blood gas volumes, disease predominant |
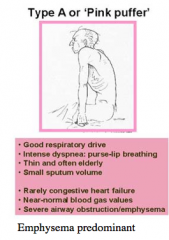
|
|
|
Components of Type B or "Blue Bloater" Respiratory drive, dyspnea, weight, sputum volume, CHF, respiratory failure components |
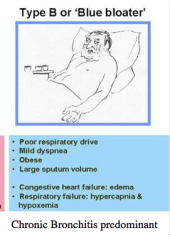
|
|
|
What is chronic bronchitis (smurf) characterized by? What is the hypoxemia and hypercapnia due to? What controls ventilation that changes WOB? |
|
|
|
What is increased in the hypoventilation of chronic bronchitis? What does the longterm hypoxemia cause? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
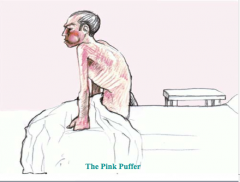
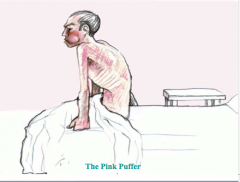
What is the pink puffer characterized by? What is hypoxemia due to? How do patients maintain PCO2? |
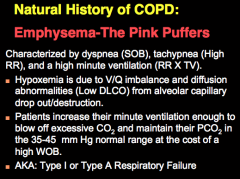
|
|
|
Pink puffer: High or low WOB? Why are they known as pink puffers? When does the victim usually die? |

|
|
|
COPD patients are also at increased risk for what? |

|
|
|
Extrapulmonary (systemic effects of COPD): |

|
|
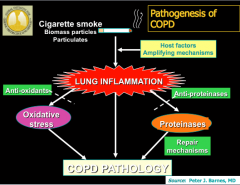
|
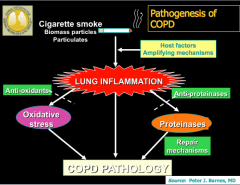
|
|
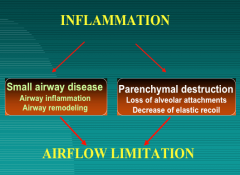
|
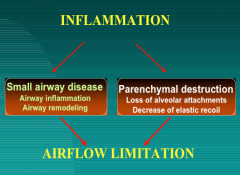
|
|
|
Compare asthma and COPD: |
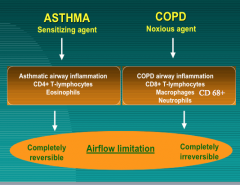
KNOW THIS!! TEST QUESTION! |
|
|
Is pure bronchitis or emphysema rare? Do they often overlap? What does develops because of V/Q mismatch? |

|
|
|
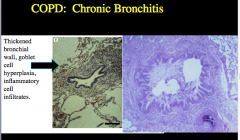
What is chronic bronchitis characterized by? Clinical definition? Pathology? |

|
|
|
What leads to excessive mucous production or chronic bronchitis? Airway wall changes? What is the inflammatory infiltrate? |

|
|
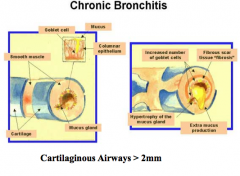
|
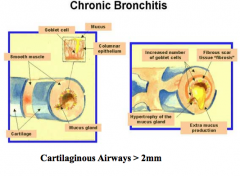
|
|
|
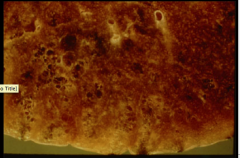
Pathology of chronic bronchitis in central airways: Age present Goblet cells Inflammatory infiltrate Fibrosis? Major site of airflow limitation? |

|
|
|
|
|
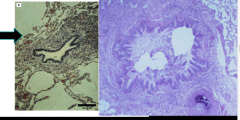
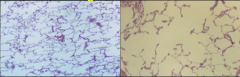
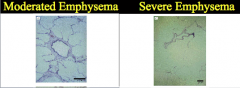
What is shown here? |
|
|
|
What enlarges in emphysema? Difference between centrolobular and pan lobular emphysema? |

|
|
|
What are bulllae? Emphysema results in a significant loss of what? What are the inflammatory infiltrates? |

|
|
|
|
|
Left and right |
|
|

|
|
|
|
Emphysema |
|
|
What are the three causes of IRREVERSIBLE airflow limitation? |

|
|
|
What are the causes or REVERSIBLE airflow limitation? |

|
|
Look over |
|
|
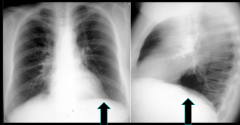
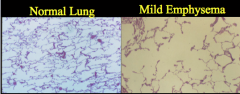
What is shown? |
Emphysema: A1 AT deficiency Arrows: hyperinflation with flat diaphragms |
|
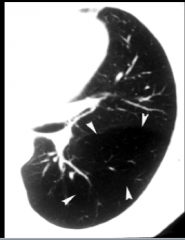
Shown here? |

A1AT def. |
|
|
|
|
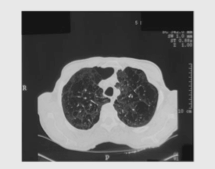
|
Bullous emphysema |
|
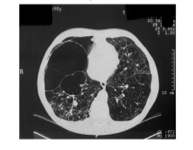
|
Bullous emphysema with parenchymal destruction |
|
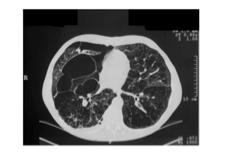
|
Severe bullous emphyseam and secondary spontaneous pneumothorax |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
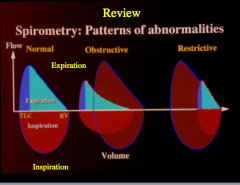
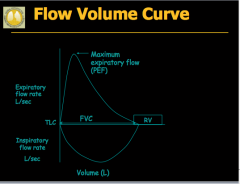
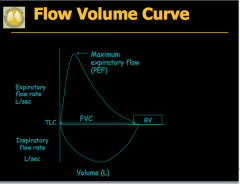
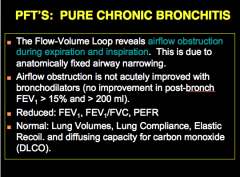
PURE CHRONIC BRONCHITIS: What does the flow-volume loop reveal? What is this due to? In PURE CHRONIC BRONCHITIS, will airflow obstruction be acutely improve with bronchodilators? What three components are reduced? What is normal? |
|
|
|
PURE EMPHYSEMA: When does the flow-volume loop reveal airflow obstruction? What is this due to? Is airflow obstruction acutely improved with bronchodilators? What three components are reduced? |

|
|
|
What is increase in PURE EMPHYSEMA? What is decreased? What is the decrease in DLCO due to? |
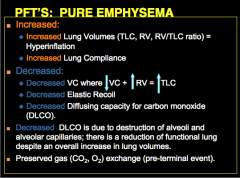
|
|
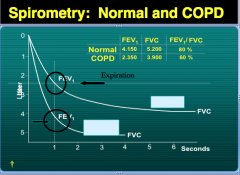
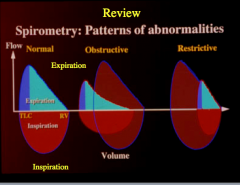
Which line is normal and which is COPD? How do you know? |
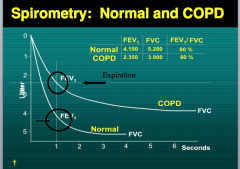
|
|
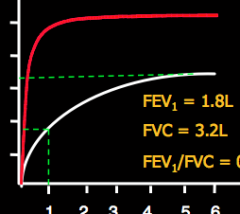
What does the red line indicate? White line? |
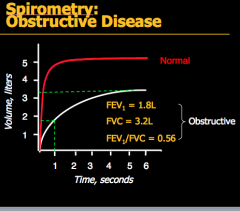
|
|
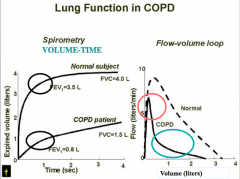
Look over |
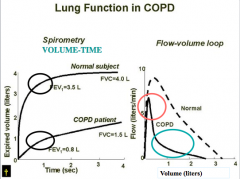
Look over |
|
|
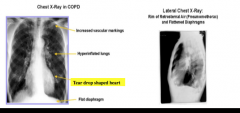
What are the symptoms of COPD? What are some exposure risk factors? What results would you see on spirometry (reversible, FEV1 post bronchodilator, FEV1/FVC)? |
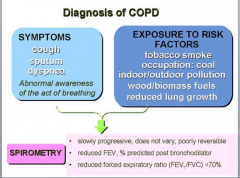
|
|
|
|
|

|

|
|
|
What are important clinical events in COPD? What are the most common causes of exacerbation of COPD? |
|
|
|
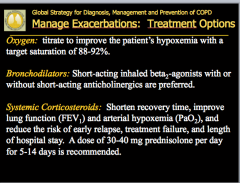
How do you manage exacerbations? Drugs? What can shorten recovery time, improve lung function (FEV1), and arterial hypoxemia (PaO2), and reduce the risk of early relapse, treatment failure, and length of hospital stay? Can exacerbations be prevented? |

|
|
|
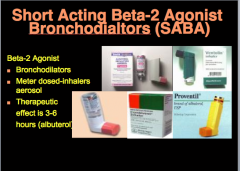
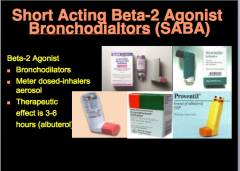
Three treatment options for exacerbations: |
|
|
|
Antibiotics should be given when you see which three cardinal symptoms? What additional groups should receive antibiotics? |

|
|

|

|
|
|
Management of stable COPD includes all of the following except: 1. Smoking cessation and avoidance of noxious agents. 2. Influenza vaccination 3. Pneumococcal vaccination 4. Long term oxygen therapy in selected patients 5. Oral systemic glucocorticoid therapy in patients with mild COPD. 6. Pulmonary rehabilitation. 7. Nutritional therapy. |
5. Oral systemic glucocorticoid therapy in patients with mild COPD. |
|
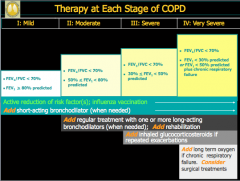
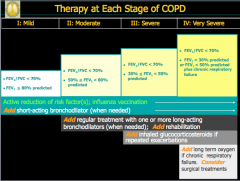
Look over: |
|
|
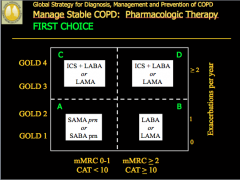
|
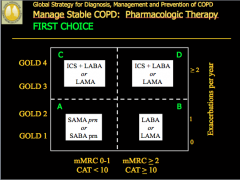
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
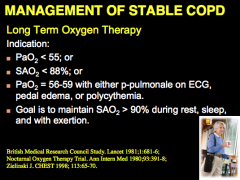
Long term oxygen therapy: 1. Most important drug in hypoxic patients is what? 2. What does oxygen improve? 4. What should you try to raise the PaO2 to 60 and SaO2 5. How long should it be worn? 6. What are some delivery methods? |

|
|
|
Indications for long term O2 therapy: PaO2 level SaO2 level PaO2 with p-pulmonale on ECG, pedal edema, polycythemia What is the goal to maintain SAO2 during rest, sleep, and with exertion? |
|

