![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
30 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Intro to sound |
- the heart & soul of Multimedia - presentation will be dull - like a silent movie - sound travels in waves |
|
|
|
How sound travels |
- vibrations that travels through air particles & other materials (like waves travels through water particle & we can see the effect in water) vibrate your eardrum & you perceive this as sound - sound waves vary in sound pressure level (amplitude) & in frequency or pitch - sound pressure levels (loudness / volume) measured in decibels (dB) |
|
|
|
Multimedia sound system |
multimedia sound is either digitally recorded audio / MIDI (Musical Instrument Digital Interface) music |
|
|
|
Digital Audio |
- digital audio data is the actual representation of sound, stored in the form of samples - samples represent the amplitude (or loudness) of sound at a discreet point in time - a digital sound is not a natural sound but produced by electronic equipment that an only manage information in binary form (1 & 0) - a digital sound imitates a wave by means of new characteristics which are the sampling rate & sound resolution |
|
|
|
Sample rate |
- the rate which the samples are captured / played back, measured in Hertz (Hz), or samples per second - audio CD has a sample rate of 44,100 Hz, often written as 44.1 KHz for short |
|
|
|
Sample / sound resolution |
- number of digits in the digital representation of each sample - think of the sample rate as the horizontal precision of the digital waveform & the sample size as the vertical precision - audio CD has a precision of 16 bits, which corresponds to about 216 or 65536 different audio levels |
|
|
|
Quality of digital recording |
- depends on the sampling rate (/ frequency) that is, the number of samples taken per sec & also how any numbers are used to represent the value of each sample (bit depth, sound resolution) - since its based on the quality of recording & not the device that will play the audio, digital audio is said to be device independent |

|
|

|
- 1 Hz ave is sampled at two differet sampling rates and sampling resolutions - first cycle (blue) uses a sampling rate of 50 Hz & a sampling resolution of 25 or 32 bits. - second cycle is sampled at 25 Hz with a 2 or 4-bit samping resolution - based on the graph, blue samples are more accurate in both the time & amplitude domains than the red sample |
|
|
|
Sampling frequencies |
most used in multimedia - 48 kHz, 88.2 kHz or 96 kHz - CD-quality 44.1 kHz (44100 Hz) - FM-radio quality 22.05 kHz - telephone quality 11.025 kHz |
|
|
|
How does audio get digitized on computer |
- comps hv soundcard = it could be separate card, like a SoundBlaster, or it could be built-in to your comp - soundcards comes with an Analog to Digital Converter (ADC) for recording, & a Digital to Analog Converter (DAC) for playing audio - OS (ex. Windows) talks to the soundcard to actually handle the recording & playback, & your sound recording software like Sound Forge talks to your operating system so that you can capture sounds to a file - you then can edit them, & mix multiple tracks while playing |
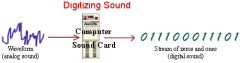
|
|
|
Digital audio file size |
varies according to four parameters - the duration / length (time) in seconds - the sampling rate in Hertz (Hz) - the bit resolution (÷ 8 in byte) - numer of tracks /cahnnel (Mono =1, Stereo = 2) |
|
|
|
File size of monophonic digital recording |
sampling rate duration of recording in seconds x ( bit resolution/8) x 1 |
|
|
|
File size of stereo recording |
sampling rate x duration of recording i seconds x ( bit resolution/8) x 2 |
|
|
|
Calculating digital audio file size |
Ex : Find the file size of a 3 minutes 20 seconds sound of CD-quality, coded in 16 bits, stereo. use formula file size for a sound file = sampling rate x duration of recording in secs x (bit resolution/8) x (1 mono or 2 stereo) |
|
|
|
MIDI audio |
- stands for Musical Instruments Digital Interface - MIDI is shorthand representation of music stored in numeric form - not digitized sound - sequencer software & sound synthesizer is required in order to create MIDI scores - MIDI is device dependent |
|
|
|
Working with MIDI audio |
- since they are small, MIDI files embedded in web pages load & play promptly - length of a MIDI file can be changed without affecting the pitch of th emusic / degrading audio quality - working with MIDI requires knowledge of music theory |
|
|
|
How musical MIDI works |
when a note is playing on a MIDI - aware instrument, it transmit MIDI messages - all notes that a musical instrument is capable of playing are assigned specific MIDI messages according to what the note & octave are - in MIDI, instruments are selected by number (0 - 127) using the Program Change message - which MIDI message & which binary digits will be transmitted upon playing of a certain note are defined in the MIDI specification & this comprises the core of the MIDI standard |
|
|
|
MIDI |
- analogous to structured of vector graphics - device dependent - smaller - sounds better - difficult to playback spoken dialog - doesn't hv consistent playback quality - requires knowledge of music theory in order to run MIDI |
|
|
|
Digital audio |
- digitized audio is analogous to bitmapped images - device independent - bigger size - can playback spoken dialog easily - provides consistent playback quality - doesn't need to hv music knowledge |
|
|
|
Audio file formats |

|

|
|
|
Wave (.wav) |
- wave is the standard form for uncompressed audio on a PC - since a wave file is uncompressed data, as close a copy to the original analog data is possible - it is therefore much larger than the same file would b ein a compressed format such as mp3 or RealAudio |
|
|
|
MP3 (.mp3) |
- popular compressed audio format widely used to transfer music over the internet - created by taking wave audio data & processing it with a special algorithm which removes parts of the audio that theoretically cannot be detected with the human ear, in actuality, there will be some degradation of quality |
|
|
|
RealAudio (.ra) |
- streaming audio format often used by Internet radio station & for posting sound files on websites - smaller even than MP3 files around 500 Kb a song - but lower quality if compressed enough to play over a slow connection (such as a 56 kbps modem) |
|
|
|
Windows Media (.wma) |
- similar to MP3 - competing format created y Microsoft & used primarily in Windows Media Player & other compatible programs - Microsoft claims that Windows Media files are still much more prevalent on the internet |
|
|
|
MIDI (.mid) |
- not compressed audio - a kind of language that allows computers & certain musical instruments to communicate consist of instructions telling the instrument (or MIDI synthesizer in the sound card) which notes to play, with what instrument, & when - MIDI can be used entirely within a computer, with no external instrument - hv synthesized sound, & are quite small, aroun 30-60 kB for your average song |
|
|
|
Audio programs |
compatible with most common audio format |
- wave (extension,wav) - audio interchange file format (extension : AIFF) - Audio-µLaw (extension. AU) - MIDI (extension .mid) |
|
|
Sound Editing Software |
- open source (Audacity) - Sony Creative Software (Sound Forge) - Adobe (Soundbooth/Audition) - Apple (GarageBand/Soundtrack) |
|
|
|
Adding sound to Multimedia project |
- file format compatible with multimedia authoring software being used along with delivery mediums, must be determined - sound playback capabilities offered by end user's system must be studied - the type of sound, whether background music, special sound effects / spoken dialog must be decided |
|
|
|
Production tips |
- the speed at which most animation & computer-based videos play, depends on the use's CPU - sound's RAM requirements as well as the users' playback setup must be evaluated - copyrighted material should not be recorded / used without securing appropriate rights from owner or publisher |
|
|
|
Copyright consideration |
- safest way to adhere to copyright requirements is to either generate original music & sound yourself - packaging should clearly state that you hv royalty-free permission to reuse the content |
|

