![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Control |
Any process that directs the activities of individuals toward the achievement of organizational goals |
|
|
|
Symptoms of an Out-of-Control Company |

7 Symptoms |
|
|
|
Managerial control |

1. Bureaucratic control 2. Market control 3. Clan control |

|
|
|
Bureaucratic control |
The use of rules, regulations, and authority to guide performance |
|
|
|
Market control |

Control based on the use of pricing mechanisms and economic information to regulate activities within organizations |
|
|
|
Clan control |
Control based on the norms, values, shared goals, and trust among group members. |
|
|
|
Control Cycle |
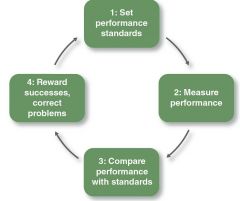
1. Setting performance standards. 2. Measuring performance. 3. Comparing performance against the standards and determining deviations. 4. Taking action to correct problems and reinforce successes. |
|
|
|
Setting performance Standard |
Expected performance for a given goal: a target that establishes a desired performance level, motivates performance, and serves as a benchmark against which actual performance is assessed. |
|
|
|
Principle of exception |
A managerial principle stating that control is enhanced by concentrating on the exceptions to or significant deviations from the expected result or standard. |
|
|
|
After-action review |

A frank and open-minded discussion of four basic questions aimed at continuous improvement. |
|
|
|
Approaches to Bureaucratic Control |
1. Feedforward control 2. Concurrent control 3. Feedback control |
|
|
|
Feedforward control |
The control process used before operations begin, including policies, procedures, and rules designed to ensure that planned activities are carried out properly. |
|
|
|
Concurrent control |
The control process used while plans are being carried out, including directing, monitoring, and fine-tuning activities as they are performed. |
|
|
|
Feedback control |
Control that focuses on the use of information about previous results to correct deviations from the acceptable standard. |
|
|
|
Role of Six Sigma |
-At a six-sigma level, a process is producing fewer than 3.4 defects per million, which means it is operating at a 99.99966 percent level of accuracy -Six Sigma companies have not only close to zero product or service defects but also substantially lower production costs and cycle times and much higher levels of customer satisfaction |
|
|
|
Management audit |
-An evaluation of the effectiveness and efficiency of various systems within an organization
1. External audit 2. Internal audit |
|
|
|
External audit |
1. Investigates other organizations for possible merger or acquisition 2. Determines the soundness of a company that will be used as a major supplier 3. Discovers the strengths and weaknesses of a competitor to maintain or better exploit the competitive advantage of the investigating organization |
An evaluation conducted by one organization, such as a CPA firm, on another. |
|
|
Internal audit |
1. Assesses what the company has done for itself 2. What it has done for its customers or other recipients of its goods or services. |
A periodic assessment of a company’s own planning, organizing, leading, and controlling processes. |
|
|
Budgeting |
The process of investigating what is being done and comparing the results with the corresponding budget data to verify accomplishments or remedy differencesalso called budgetary controlling. |
|
|
|
Types of budgets |
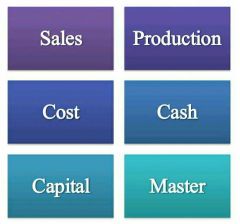
6 types |
SPM 3C |
|
|
Accounting audits |
Procedures used to verify accounting reports and statements. |
|
|
|
Activity-based costing (ABC) |
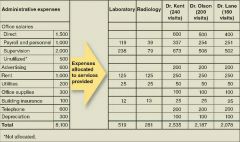
A method of cost accounting designed to identify streams of activity and then to allocate costs across particular business processes according to the amount of time employees devote to particular activities |
|
|
|
Financial Controls |
-Balance sheet -Assets -Liabilities -Stockholders’ equity -Profit and loss statement |
|
|
|
Balance sheet |
A report that shows the financial picture of a company at a given time and itemizes assets, liabilities, and stockholders’ equity. |
|
|
|
Assets |
The values of the various items the corporation owns. |
|
|
|
Liabilities |
The amounts a corporation owes to various creditors |
|
|
|
Stockholders’ equity |
The amount accruing to the corporation’s owners. |
|
|
|
Profit and loss statement |

An itemized financial statement of the income and expenses of a company’s operations |
|
|
|
Financial Ratios |
1. Current ratio 2. Debt-equity ratio 3. Return on investment (ROI) |
|
|
|
Current ratio |
A liquidity ratio that indicates the extent to which short term assets can decline and still be adequate to pay short-term liabilities |
|
|
|
Debt-equity ratio |
A leverage ratio that indicates the company’s ability to meet its long-term financial obligations |
|
|
|
Return on investment (ROI) |
A ratio of profit to capital used, or a rate of return from capital |
|
|
|
Management myopia |
Focusing on short-term earnings and profits at the expense of longer-term strategic obligations. |
How to use financial ratios |
|
|
Downside of Bureaucratic Control |

3 downside |
|
|
|
Designing Effective Control Systems |
1. Establish valid performance standards. 2. Provide adequate information to employees. 3. Ensure acceptability to employees. 4. Maintain open communication. 5. Use multiple approaches. |
|
|
|
Balanced scorecard |
Control system combining four sets of performance measures: financial, customer, business process, and learning and growth |
|

