![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
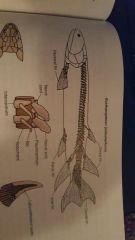
|
Osteolepiforms |
|
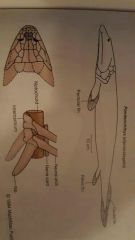
|
Elpistostegalids |
|

|
Crassigyrinus |
|

|
Sirenidae - salamander lacking 4 limbs, only has two |
|

|
Cryptobranchidae - known as hidden gills and part of the giant salamanders |
|

|
Proteidae - includes mudpuppies and european olm |
|
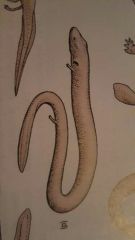
|
Congo eel - aquatic and only adults have developed lungs |
|

|
Mole salamander |
|

|
Plethodontidae - the lungless salamander using cutaneous respiration, some can drop tail |
|

|
Toad (spadefoot) |
|
|
Toad |
|

|
African clawed frog (Xenopus) |
|

|
Caecilian |
|
|
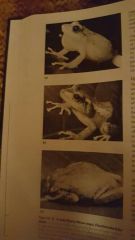
Puerto Rican Coqui - posture of a water conserving tree frog |
|

|
Australian snake necked turtle (bends neck horizontally to retract head) |
|
|
South American Matamata (turtle) [that bends neck horizontally to retract] |
|

|
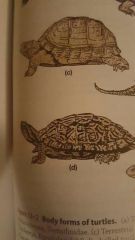
Tortoise (bends neck in S shape) |
|
|
Box & Pond Turtles (bend neck in S shape to retract) |
|
|
Snapping Turtle |
|

|
Soft Shelled Turtle (has webbed feet) |
|

|
Loggerhead and Green Turtles (sea turtles) |
|

|
Leatherback turtle (largest existant turtle, sea turtle and can dive up to 1000m) |
|
|
Turtle Heart |
|

|
Tuatara - had spines on back |
|

|
Green and Black Iguanas |
|
|
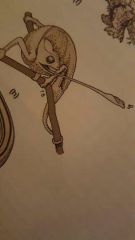
Chameleon (Chameleonidae - grasped tail and digits in pairs) |
|
|
Legless lizard |
|

|
Mososaur - Komodo Dragon is related to them |
|

|
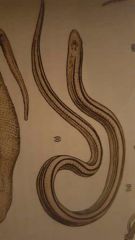
Thread Snake (blind snakes) |
|
|
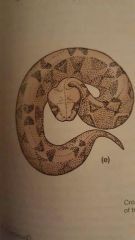
Puff Adder (Viper that has a blunt head for burrowing) |
|

|
King snake and Milk Snake (crawl slowly and rely on chemoreception) |
|

|
Whip Snake and Racers (move quickly and are visual predators) |
|

|
Parrot Snake (have large eyes) |
|
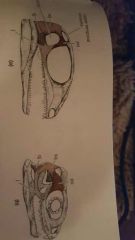
|
Ancestral Diapsid Condition (Tuatara) has 2 complete temporal arches |
|
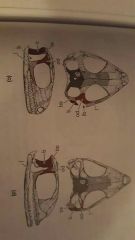
|
Reduction and eventual loss of lower temporal arch |
|
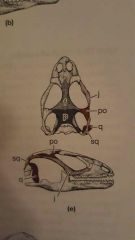
|
Lizards with loss of lower temporal arch |
|
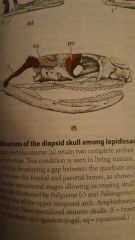
|
Snakes (and some lizards) have a further loss of their upper temporal arch |
|

|
Amphisbaenian Skull |
|
|
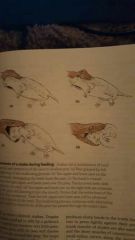
Snakes usually swallow prey head first |
|

|
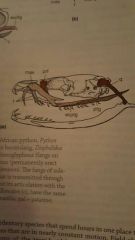
Opisthoglyphous - fangs near rear of maxille and solid or groove on surface of fang |
|
|
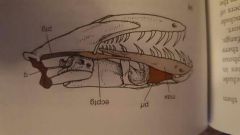
Protoglyphous - hollow fangs at front of maxille, permanently erect and short |
|

|
Solenoglyphous - have long hollow teeth that can strike forward quickly |
|
|
Aglyphous - Snakes without fangs |
|

|
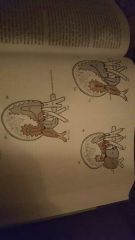
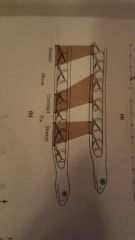
Lateral Undulation |
|
|
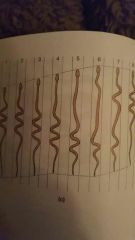
Rectilinear locomotion (straight line) |
|
|
Concertina |
|

|
Sidewinding |
|

|
Chuckwalla - lives in rocky foothills of Mojave Desert |
|
|
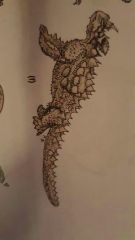
Thorny Devil (collects dew on body) |

