![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are abnormalities that can lead to cholestasis?
|
Impaired bile formation (hepatocytes)
Impaired bile flow (bile ducts/ductules) |
|
|
What are the consequences of cholestasis?
|
Build up in blood of the substances normally excreted in bile
Synthesis/release of apical membrane proteins (Alk-phos) |
|
|
Does an obstruction in the neck of the gall bladder cause jaundice?
|
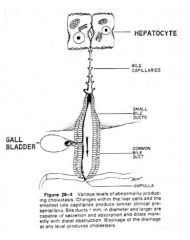
NO!
The gall bladder just hangs off the side...the liver isn't cholestatic unless the common bile duct is blocked |
|
|
What are the different classes of cholestatic diseases?
|
Functional impairment in bile formation at the level of the hepatocyte
A structural interference with normal bile secretion and flow at the level of the small intrahepatic bile ducts Structural interference with normal bile flow at the level of the large and extrahepatic ducts |
|
|
What are some biochemical signs ofl cholestasis?
|
Increased serum bilirubin
Increased serum alk-phos |
|
|
What are some pathologic signs of cholestasis?
|
Bile ducts in dilated canaliculi
Increased bile pigment in hepatocytes Bile lakes/infarcts Biliary infection |
|
|
What are clinical signs of cholestasis? What does this mean?
|
Jaundice
Dark urine/clay-colored feces Puritis It needs to be advanced to see this. |
|
|
What are some tests that you can do to look for cholestasis?
|
Liver biopsy
CT of the ducts, etc. Direct visualization by MRI, endoscopy |
|
|
What is another cause for orange skin?
|
Hypercarotenemia
|
|
|
What are some causes of decreased bile formation? What kind of cholestasis will this occur?
|
Sepsis
Estrogens Intrahepatic |
|
|
What are some causes of alterations of the intrahepatic bile ducts?
|
Primary biliary cirrhosis
Infiltration of liver with tumor/ganulomas |
|
|
What are some causes of impaired cholestasis due to liver disease?
|
Viral hepatitis
|
|
|
What are some causes of extrahepatic bile duct obstruction?
|
Tumor
Gallstones Strictures Primary sclerosing cholangitis |
|
|
What are factors that act on transporters to reduce the transport of bile?
|
Estrogens
Endotoxin/TNF |
|
|
What transporters do estrogens inhibit?
|
Bile acids
Bilirubin |
|
|
What transporters do TNF impact?
|
Turn off the bilirubin transporter
|
|
|
What's the course of primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
Chronic, slowly evolving cholestatic disorder
|
|
|
Who gets primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
Midle-aged women
|
|
|
What kind of destruction takes place in primary biliary cirrhosis? How does it happen?
|
Destruction of the intrahepatic bile ducts
T-cells |
|
|
What happens to liver function in people with primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
The function stays in tact.
|
|
|
What are the laboratory abnormalities in primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
MARKEDLY elevated Alk-Phos
Slightly elevated: bilirubin, AST/ALT Elevated cholesterol |
|
|
What's the diagnostic test in primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
Anti-mitochondril antibody
|
|
|
What are the findings in primary biliary cirrhosis?
|
Jaundice
Puritis Xanthomas/xanthalasmas |
|
|
Where do xanthomas take place? What is it?
|
Tendons and joints
Cholesterol tumors due to an obstruction of biliary outflow |
|
|
How do granulomas cause cholestasis?
|
Granulomas compress small, intrahepatic bile ducts
|
|
|
What are the types of diseases that cause granulomas in the liver/
|
TB
Sarcoid |
|
|
What are conditions that can cause an isolated elevated Alk-Phos?
|
Sarcoid
Tb Lymphomas in the liver Cancers |
|
|
What types of cells are found in granulomas in the liver?
|
GIANT CELLS!
|
|
|
What's the most common kind of cholestasis?
|
Blockage
Primary biliary cirrhosis and sarcoid aren't common |
|
|
What is a requirement for jaundice?
|
Complete blockage of the biliary tract outflow from the liver
|
|
|
What do you do to visualize the biliary tract?
|
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatoraphy
You put in an endoscope into the duodenum and inject dye retrogade through the ampulla of vater and then take a plainfilm |
|
|
What are some common causes of intrinsic obstruction of the gall bladder?
|
Gallstones
Biliary strictures (POST SURGICAL - DON'T TOUCH IT!) Primary sclerosing cholangitis Worms/parasites Clots, hemobilia |
|
|
What are some causes of extrinsic obstruction of the bile tract?
|
Tumors
Acute/chronic pancreatitis Congenital diseass |
|
|
What are some kinds of tumors that can extrinsically obstruct the biliary tract?
|
Pancreatic
Cholangiocarcinoma Periampullary lymphoma/mets |
|
|
What are some congenital diseases that can obstruct the biliary tract?
|
Biliary atresia
Choledochal cyst |
|
|
What kind of a tumor most commonly causes bile duct obstruction?
|
Pancreatic...
|
|
|
Who gets primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
MEN with IBD, mostly UC
|
|
|
What are complications of primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
Complete obstruction'
Jaundice Biliary infection Puritis Cholangiocarcinoma |
|
|
What happens tot he hepatocytes in primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
Hepatocytes are preserved
|
|
|
What are the abnormal lab findings in primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
Markedly elevated alk phos
Slightly elevated AST/ALT Slightly elevated bilirubin |
|
|
What are the clinical findings in primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
Bile duct obstruction
Jaundice and dilated bile ducts if complete obstruction occurs On biopsy: bile lakes, plugs, infarcts Cirrhosis if end-stage |
|
|
What are the histologic findings of sclerosing cholangitis?
|
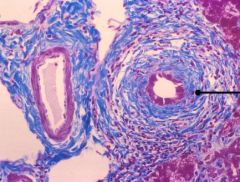
Onion-skinning fibrosis around the bile ducts
|
|
|
What is the most common way we look for primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
ERCP
|
|
|
What does ERCP look like in primary sclerosing cholangitis?
|
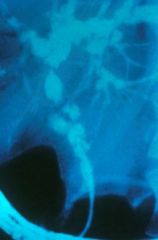
"Band of lakes appearance"
You need multiple strictures in multiple areas for a diagnosis of PSC |
|
|
What do you see in bile ducts in acute cholangitis?
|
PMNs in the bile duct
|
|
|
What's the management for an acute cholangitis?
|
Abs right away!!!
They can get septic! |
|
|
Where do gallstones typically obstruct?
|
Right below the sphincter of Odii
|
|
|
What can compress the bile duct?
|
Malignant proximal strictures due to cancerous lymph nodes
Cancer at the pancreas Post-inflammatory stricture due to surgery Choledocholithiasis |
|
|
What's the treatment of a narrowed bile duct?
|
STENTS!
You've got to keep the flow going so they're not yellow and itchy. |
|
|
What is a very common cause of bile duct narrowing? Uncommon/
|
Common: stones
Uncommon: ascoriasis |
|
|
What are some complications of cholestasis?
|
Secondary liver damage: cirrhosis
Failure of substances secreted in bile to reach the intestine |
|
|
What are some consequences of a failure of substances secreted in bile to reach the intestine>
|
Bile acid deficiency in the gut
Fat malabsorption/fat-soluble vitamin malabsorption |

