![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
61 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Cubic Packing Equation |
N = V/d³
|
|
|
Close Packing Equation
|
N= V/d³ × 1.356 OR d= ³√ ( 1.356V/N)
|
|
|
Percent Error |
% Error= (|measured-true|/true) ×100%
|
|
|
Mega |
M (10⁶) |
|
|
Kilo |
K (10³) |
|
|
Deci |
d (10⁻¹) |
|
|
Milli |
m (10⁻³) |
|
|
Micro |
µ (10⁻⁶) |
|
|
Nano |
n (10⁻⁹) |
|
|
Volume= |
m ---- d |
|
|
Mass= |
d×v |
|
|
Density= |
m ----- v |
|
|
Volume(block)= |
l×w×h
|
|
|
Volume(cylinder)= |
πr²h |
|
|
Volume(sphere)= |
4/3 πr³ |
|
|
Crystalline Solid |
ordered |
|
|
Amorphic Solid |
random |
|
|
Pure Substance |
-1 component -composition doesn't change -element or compound |
|
|
Element |
-can't separated into particles
|
|
|
Compound |
-more than one kind of element/atom
|
|
|
Mixture |
Variable→multiple components heterogenous & homogeneous |
|
|
Homogeneous |
Uniform |
|
|
Heterogeneous |
Non-Uniform |
|
|
Intensive Properties |
-independent of the amount of material -gives idea about composition ex: melting pt, density
|
|
|
Extensive Properties |
-dependent of the amount of material ex: mass, volume |
|
|
Energy |
capacity to do work |
|
|
Work |
force acting over a distance |
|
|
Kinetic Energy |
Motion |
|
|
Potential Energy |
Position or composition |
|
|
Total Energy = |
Potential + Kinetic energy |
|
|
Speed= |
m/s |
|
|
Accuracy |
how close measurements are to "true value" |
|
|
Precision |
how close measurements are to each other |
|
|
Law of Definite Proportions |
all samples of a given compound have the same proportions of their constituent elements |
|
|
Law of Multiple Proportions |
When two elements (A+B) form 2 different compounds the masses of A+B that combine are in a ratio of small whole numbers. |
|
|
Dalton Atomic Theory |
-elements composed of small particles→atoms -all atoms of an element are identical -atoms are not charged by chemical reactions -Didn't theorize what atoms look like |
|
|
Thomson's Cathode Ray Tube |
discovery of electrons |
|
|
Millikan's Oil Drop Experiment |
Charge of electrons |
|
|
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment |
1) structure of atoms 2) discovery of protons
|
|
|
Atomic Number |
Z= #protons |
|
|
Mass number |
A= (#protons)+ (#neutrons) |
|
|
Isotopes |
atoms of the same element with different numbers of neutrons |
|
|
Ion |
atom that is charged |
|
|
Anions |
non-metals →each negative charge=1 added electron ending becomes: -ide |
|
|
Cations |
metals →each positive charge=1 less electron ending: stays same |
|
|
Metalloids |
properties of metals & nonmetals -used as semiconductors |
|
|
Alkali Metals |
1A soft, reactive form +1 ions |
|
|
Alkali Earth Metals |
2A harder, reactive form +2 ions |
|
|
Noble Gases |
Gases at room temp unreactive |
|
|
Halogens
|
7A (next to noble gases)
all 3 states diatomic (always come in pairs) very reactive form -1 ions |
|
|
Covalent Bond |
atoms share electrons bond between non-metals
|
|
|
Ionic Bond |
atoms transfer electrons →metal(cation) + nonmetal (anion) |
|
|
Chemical Formula |
which atoms what proportions |
|
|
Molecular Formula |
actual number & type of atoms in molecule |
|
|
Empirical Formula |
relative number of atoms |
|
|
Natural Abundance
|
a percent of element that is particular isotope
|
|
|
atom of a specific isotope
|
nuclide
|
|
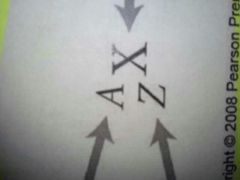
symbols
|

|
|
|
Chadwick Discovered... |
-neutrons in nucleus are NOT charged
-neutrons have similar mass to protons |
|
|
Diatomic Elements (list elements) |
H₂ N₂ F₂ O₂ I₂ Cl₂ Br₂ (Have No Fear Of Ice Cold Beer) |
|
|
Polyatomic Elements (list 3) |
P₄ S₈ Se₈ |

