![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
139 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
autotroph |
makes own food |
|
|
heterotroph |
eats other animals for food |
|
|
prokaryotic |
no nucleus |
|
|
eukaryotic |
has a nucleus |
|
|
genetics |
the study of heredity, the way in which hereditary traits are passed from parents to offspring |
|
|
heredity |
transmission of traits from parents to their offspring |
|
|
species characterisitics |
traits that all members of a species have,
for example, (why the organism such as a dog looks like a dog, they all have 4 legs, certain hair types, etc.) |
|
|
individual characterisitics |
specific traits (long hair, spotted fur, pointed noise, stripes) |
|
|
two things that influence individual characteristics |
1. heredity - traits (genes) from parents Heredity determines what the individual is 2. environment - nutrition, experiences(childhood) environment influences what kind of individual it becomes |
|
|
Gregor Mendel |
given credit for beginning geneteics |
|
|
Mendel's three principles of heredity |
1. principle of dominance - because of dominance, the effects of the recessive genes are not observed when the dominant gene is present. 2. principles of segregation - alleles for the same trait separate (segregate) during the formation of gametes 3. Principle of independent assortment - genes for different traits are distributed to the reproductive cells independently. |
|
|
chromosome theory |
genes are located on all the chromosomes and each gene occupies a specific place on a chromosome.
A gene may exist in several forms (alleles) and each chromosome contains one allele for each gene. |
|
|
P1 generation |
parental generation |
|
|
principal of domiance
|
because of dominance, the effects of the recessive genes are not observed when the dominant gene is present. |
|
|
principle of segregation |
alleles for the same trait separate (segregate) during the formation of gametes |
|
|
principle of independent assortment |
genes for different traits are distributed to the reproductive cells independently. |
|
|
F1 generation |
offspring of the P1 generation |
|
|
F2 generation |
offspring of the F1 generation |
|
|
trait |
specific characteristic or quality |
|
|
genes |
segment of DNA on the chromosome that controls a particular hereditary trait. |
|
|
alleles |
each alternate form of a gene |
|
|
Dominant alleles |
Shown by using a capital letter, the trait is expressed instead of recessive alleles |
|
|
recessive alleles |
shown by using a lowercase letter, the trait is expressed when there are two recessive alleles. |
|
|
dominant trait |
covers the other trait |
|
|
recessive alleles |
trait that is covered by the dominant trait |
|
|
Homozygous |
recessive traits will always be homozygous (rr) |
|
|
heterozygous |
two alleles that are not the same (Tt) or (Rr) |
|
|
purebred |
homozygous (only one form of a trait) |
|
|
hybrid |
heterozygous ( two different alleles for a trait) Bb |
|
|
chromosomes and their relation to DNA |
cell structures that contain the genetic information(DNA) that is passed from one generation to the next. *Found in the nucleus |
|
|
genes and their relation to DNA |
segment of DNA that codes for a particular protein that carry out cellular functions * controls hereditary traits #Genes are on the chromosomes |
|
|
meiosis, products of meiosis, when it occurs |
division of the cell nucleus in which the parent cell divides twice forming four genetically different haploid cells (1N) each with half the number of chromosomes (46--->23) * occurs in sex cells (gametes) *cell division in sex cells (egg)(sperm) *part of sexual reproduction |
|
|
gamete |
sex cells (male - sperm) (female- egg) |
|
|
zygote |
diploid 2n, fertilized egg (divides many times forming a ball of cells called an embryo) *embryos are early stages of development of organisms |
|
|
fertilization, two types |
1. Internal fertilizations - occurs inside the female body of mammals, birds, and reptiles 2. External fertilization - occurs outside the female body, occurs in fish and amphibians |
|
|
Differences between mitosis and meiosis, which one is for genetics |
meiosis - two phases, 2 nuclear divisons, produces 4 genetically different haploid cells, part of sexual reproduction, half the chromosome number, used in genetics Mitosis- part of asexual reproduction, produces two genetically identical diploid cells, 1 nuclear divison, same chromosome number |
|
|
phenotype |
external appearance of an organism , color size, etc, black short curly |
|
|
Genotype |
the genetic makeup of an organism, the letters that represent traits (AaBb) or (Bb) |
|
|
Monohybrid |
cross between individuals that involve one pair of contrasting traits |
|
|
Dihybrid Cross |
cross involving two pairs of contrasting traits |
|
|
one factor cross |
Red X Orange birds (Rr x rr) = 4 boxes |
|
|
Two factor cross |
Blood types: ABRh+RH- X AARH-RH- = 16 boxes |
|
|
punnet squares, know how to use and what it shows |
diagram to predict genetic crosses |
|
|
incomplete dominance |
the active allele does not compensate for the inactive allele (Crossing Red and white = pink) (RR x WW = RW, RW = pink) or Redish White |
|
|
codominance |
both alleles of a gene are expressed, both are dominant (BB X WW = BW) Black crossed with white is black and white. |
|
|
polygenic traits |
traits controlled by two or more genes *it means having many genes *genes interact for different outcomes ex: skin color, weight, body size |
|
|
Multiple alleles |
more than two alleles for a gene exist in a population, each individual still only carries two alleles. ex: for blood types, IA IB iO |
|
|
test cross |
procedure in which an individual of an unknown genotype is crossed with a homologous recessive individual. |
|
|
crossingover |
occurs when the chromosomes that make up the tetrad exchange portions of their chromatids, resulting in an exchange of genes |
|
|
Antigen |
a substance that causes the body to produce an antibody |
|
|
antibody |
a separate protein that binds to an antigen on the surface of a pathogen (or foreign body) and helps to destroy it |
|
|
Four blood types |
A Blood, B Blood, AB Blood, O Blood, then all 4 can be positive or negative (RH+RH- or RH-RH-) |
|
|
Universal blood donor |
O negative is the universal donor, iOiORH-RH- |
|
|
blood type genotypes |
Heterozygous IA IB RH+ RH- = AB Hetero pos Homozygous IA IA RH+ RH+ = Homo A pos You get the idea... Type a and b can be homo or hetero, they will say heterozygous type A and heterozygous positive = IA iO RH= RH-
|
|
|
Linkage Groups |
genes on chromosomes linked together and inherited together *does not undergo independent assortment * the crhomosomes assort independently, not individual genes * crossing over can separate genes |
|
|
gene maps |
diagram that shows relative location of each gene on a chromosome |
|
|
Somatic Cells |
body cells with the exact same number ( 2n) and chromosomes, basically, all the cells in the body except those directly involved with reproduction. Most cells in multicellular plants and animals are somatic cells. They reproduce by mitosis and have a diploid number of chromosomes |
|
|
sex chromosomes |
XX - female, XY- male, sex chromosomes = X and Y, 23rd pair of chromosomes (22 pairs of autosomes, 1 pair of sex cells) |
|
|
autosomes |
body chromosomes, 22 pairs, |
|
|
sex linked genes |
genes for a certain trait that are located on the sex chromosome (X) ex: color blindness/ Hemophilia |
|
|
Sex Influenced genes |
caused by a gene whose expression differs in males and females
Like baldness, males even with heterozygous will express the trait, females only if both recessive Male = Bb or bb = bald Female Bb= not bald Female bb= bald |
|
|
carrier |
Females are carriers when they dont express it but carry it in their genes, ex: for baldness Bb, for colorblindness = XHXh |
|
|
Karyotype And what it tells you |
display of chromosomes, Tells you number of chromosomes, sex of individual, and any disorders or missing/extra chromsomes karyotypes are written as 46XY- normal male 46 XX - normal female Disorders are shown - 47XY +4, extra chromosome on the 4th one
|
|
|
Mutations |
changes in the genetic materials |
|
|
Two kinds of mutations |
point mutations and frameshift mutations |
|
|
point mutations |
occur at a single point in the dna sequence |
|
|
frameshift mutations |
mutations in which there are shifts the reading frame |
|
|
deletion |
loss of all or part of a chromosome |
|
|
inversion |
reverse the directions of parts of chromosomes |
|
|
translocations |
occur when part of one chromosome breaks off and attaches to another |
|
|
duplications |
produce extra copies of parts of a chromosome |
|
|
nondisjunction |
abnormal numbers of chromosomes find their way into gametes and a disorder of chromosome numbers may result |
|
|
mutagen |
a mutagen is a physical or chemical agent that changes the genetic material, usually DNA, in an organism and thus increases the frequency of mutations |
|
|
polyploidy |
a condition in which an organism has extra sets of chromosomes |
|
|
pedigree |
a chart that shows the relationships within a family Circle = female Square = male shaded in = has the recessive trait |
|
|
controlled breeding |
manipulation of heredity, characteristics of offspring by selecting parents with specific phenotypic traits. |
|
|
mass selection (selective breeding) |
process of choosing a few individuals as parents from a large group of individuals (select only cows that produce the most milk to breed with a certain bull) |
|
|
Inbreeding (line breeding) |
crossing closely related individuals with similar characteristics (phenotype) so that the offspring will have similar phenotypes and genotypes. (breeding certain types of dogs to produce favorable characteristics, father to daughter ) |
|
|
Hybridizations |
crossing dissimilar individuals - two different but related species (crossing a donkey with a horse = a mule) Then the offspring are sterile |
|
|
hybrids |
offspring of dissimilar organisms |
|
|
hybrid vigor |
quality displayed by hybrids that makes the individuals hardier than parents |
|
|
Genetic Engineering |
technique that directly alters an organisms DNA. Altering DNA structure by substituting genes from other DNA Molecules |
|
|
DNA Recombination |
combining segments of DNA from at least two different organisms (Recumbent DNA - Combined DNA) |
|
|
DNA insertion |
recumbent DNA is inserted into living cells |
|
|
Cloning |
technique in which a large population of genetically identical cells are derived from one original cell. |
|
|
DNA sequencing |
gene sequences, a process of determining the exact order of bases in a fragment of DNA |
|
|
Transgenic |
1.
organism that has genes from other species |
|
|
HUGO |
human genome organization, an international organization of scientists that work to identify the base sequences of every gene on the 23 pairs of human chromosomes. 30,000 genes |
|
|
sickle cell anemia |
Sickle cell anemia is the most common form of sickle cell disease, |
|
|
huntingtons disease |
causes by dominant alleles, mental deterioration and uncontrollable movements, symptom sappear when you are middle aged |
|
|
downs syndrome |
trisomy 21, 47XX +21 |
|
|
turner syndrome |
45 X, (one x nothing else) Turner syndrome is typically caused by what is called nondisjunction. Turner syndrome is caused by a missing or incomplete X chromosome. |
|
|
klinefelter syndrome |
47 XXY, extra sex chromosome |
|
|
Duchenne muscular dystrophy |
It is caused by an alteration (mutation) in a gene, called the DMD gene that can be inherited in families in an X-linked recessive fashion |
|
|
cyctic fibrosis |
47 XY+21 excess in mucus in lungs, digestive tract, liver , increased susceptibility to infections, |
|
|
cri du chat syndrome |
, it involves a deletion on the 5th pair of chromosomes (Cri-du-chat is caused by a deletion on the short arm of chromosome 5.) |
|
|
monosomy |
the presence of only one chromosome (instead of the typical two in humans) from a pair. * |
|
|
Trisomy - |
the presence an extra chromosome (instead of the typical two in humans) from a pair giving 3. |
|
|
hemophilia |
sex linked disease, Changes in the F8 gene are responsible for hemophilia , hemophilia prevents or slows blood clotting, once you are cut you bleed to death. |
|
|
who determines sex of child? |
the male or heterozygous parent, either XY or ZW. |
|
|
Identical twins vs fraternal twins |
identical twins develop from a single egg and sperm so they have the same genetic makeup, while fraternal twins develop from different eggs and sperm and are no more alike than other brothers and sisters. |
|
|
Cell division |
mitosis, cell divides into two daughter cells, cell division occurs in stomach and skin, as well as after injury |
|
|
chromosomes |
structures in the cell that contain genetic information that is passed on from one generation to the next, found in the nucleus |
|
|
chromatin |
material in chromosomes, made of DNA and protein. *DNA in chromatin exists as thin uncoiled strands |
|
|
chromatid |
two identical strands that make up each chromosome |
|
|
centromemre |
structure that holds pairs of chromatids together |
|
|
chromosomes numbers |
46 in humans, 23 pairs dog - 78 gorilla - 44 horse 64 |
|
|
homologus chromosomes |
the two members of each pair of chromomes, same size and shape |
|
|
diploid |
2n,a cell that contains both chromosomes, diploid number of humans is 2n, 46 chromosomes |
|
|
haploid |
haploid number is 1n, for humans sperm or egg is 23, no homologus chromosomes |
|
|
cell cycle and interphase - 4 phases, what happens in each |
1. G1 phase - cell growth, normal state 2. S- phase - DNA replication 3. G2 phase- preparation for mitosis 4. Mitosis = M- Phase |
|
|
Binary Fission |
the division of a prokaryotic cell into two offspring cells |
|
|
3 phases of the cell cycle |
interphase, mitosis, cytokinesis |
|
|
interphase, 3 phases |
resting phase, dna replicates, contains the G1, S, and G2 phases. G1 phase - proteins are made S phase - ATP is made and used G2 phase- longest phase |
|
|
mitosis |
processes by which the nuclei of cells divide into two nuclei each with the same number and kinds of chromosomes as the parent cell |
|
|
cytokinesis |
cytoplasm splits and forms two new cells, organelles separate, cell membrane forms between the two cells and pinches in |
|
|
Four stages of mitosis and what happens in each |
prophase - nuclear membrane disappears, chromatin forms chromosomes, centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell, asters form, spindle fibers develop
metaphase- chromosomes (2 chromatids) line up in the middle of the cell
Anaphase- chromatids separate (centromeres divide) and move to opposite ends of cell
Telophase- centrioles and spindle fibers disappear, nucleolus and nuclear membrane form, chromatids form into chromatin- threadlike DNA |
|
|
cell plate |
1. cell plate. (in plant cells) a plate that develops at the midpoint between the two groups of chromosomes in a dividing cell and that is involved in forming the wall between the two new daughter cells. |
|
|
aster |
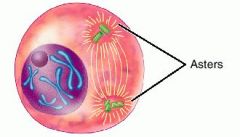
system of microtubules arranged in starlike rays around each pair of centrioles during mitosis |
|
|
stages of meiosis 1 and 2 |
1. Prophase I 2. Metaphase I 3. Anaphase I 4. Telophase I 5. Cytokinesis Then Meiosis II Prophase II Metaphase II Anaphase II Telophase II |
|
|
prophase of mitosis |
nuclear membrane disappears, chromatin forms chromosomes, centrioles move to opposite ends of the cell, asters form, spindle fibers develop |
|
|
metaphase of mitosis |
chromosomes (2 chromatids) line up in the middle of the cell on the cell plate
|
|
|
anaphase of mitosis |
chromatids separate (centromeres divide) and move to opposite ends of cell |
|
|
telophase of mitosis |
centrioles and spindle fibers disappear, nucleolus and nuclear membrane form, chromatids form into chromatin- threadlike DNA |
|
|
meiosis 2 |
chromatids of each chromosome are segregated into separate cells |
|
|
Prophase I |
Dna strands of chromatin from chromosomes, spindle fibers appear, nucleolus, nuclear membrane disappears, chromosomes line up next to its homologous chromosome, homologue |
|
|
Metaphase I |
tetrads move to the center of the cell, homologous pairs of chromosomes stay together |
|
|
Anaphase I |
homologous pairs of chromosomes separate and move to opposite ends, each chromosome is still composed of two chromatids |
|
|
Telophase I |
spindle fibers disappear, cytoplasm divides forming 2 daughter cells, each new cell has one of each pair of homologous chromosome, cytokineses occurs right after |
|
|
prophase II |
new spindle fiber forms, etc same as other prophase
|
|
|
metaphase II |
chromosomes line up in middle |
|
|
anaphase II |
centromeres divide and each chromatid separates moving to opposite ends of cell |
|
|
telophase II |
4 daughter cells form from a single parent each with half the number of chromosomes as the parent (1n) (Gametes) |
|
|
synapsis |
process in which the pairing of homologous chromosomes occurs |
|
|
tetrad |
a group of two homologous chromosomes, (4 chromatids) |
|
|
crossing over |
occurs when the chromosomes that make up the tetrad exchange portions of their chromatids, resulting in an exchange of genes |
|
|
ootid |
egg cell receives almost all the cytoplasm, it is the one haploid egg that survives, the other 3 are polar bodies |
|
|
polar bodies |
little or no cytoplasm, usually dissolves |
|
|
3 differences between plant an animal cells |
1) plants have cell walls
1. animals have centrioles, only a cell membrane, small vacuole. |

