![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Data |
~Raw material. ~Not organised & has little value. ~Types of data: text, numbers, image, audio & video. |
Definition |
|
|
Information |
~Organised data. ~Valuable & meaningful. |
Definition |
|
|
Information System |
~A set of a related components that collects data, process data and provides information. |
Definition |
|
|
Usage of IS in 3 fields |
~Education ~Business ~Management |
|
|
|
Usage of IS in Education |
~Keep track of students statistic & grades. ~Help students & teacher in online learning & discussion. ~Store subject content. |
|
|
|
Usage of IS in business |
~Carry out online buying & selling. ~Help plan the delivery of goods & services. ~Make room bookings and checking the best rate. |
|
|
|
Usage of IS in management |
~See employee records (human resource management). ~Analyse products, services & products prices (marketing management). ~Process customer orders, organise production times and keep track of product inventory (manufacturing management) |
|
|
|
5 information system components |
~Data ~Hardware ~Software ~People ~Procedures |
|
|
|
The interrelation between information system components. |
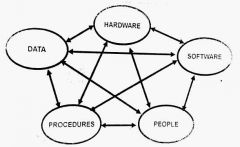
|
Diagram |
|
|
Types of information system |
~Management Information System (MIS) ~Transaction Processing System (TPS) ~Decision Support System (DSS) ~Executive Information System (EIS) ~Expert System (ES) |
5 types |
|
|
The hierarchy of data |
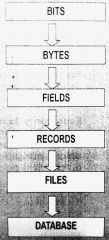
|
6 levels |
|
|
BIT |
~ Binary Digit ~0 for OFF, 1 for NO ~smallest unit of data |
|
|
|
Byte |
~ 1 byte = 8 bits ~ 1 byte = 1 character ~ examples: g, K, 7, #, & |
|
|
|
Field |
~ consists 1 or more character (bytes) ~smallest unit of meaningful information in DB. ~ each field has a field name ~ a column in a table represents a field. |
|
|
|
Record |
~A collection of related field. ~ A row of field in the table. |
|
|
|
File |
~A collection of related record. ~All record in a table. ~ file name is the table name. |
|
|
|
Database |
~ structured collection of information on specific subject. ~ consists of 1 or more tables (files). ~ is an electronic filing system. ~A DB allows its contents to be easily accessed, updated, stored and retrieved. |
|
|
|
Database Management System (DBMS) |
~ A program that accesses information form a database. ~provide an interface between database and user. ~DBMS enables you to extract, modify and store information form a DB. ~Example: Oracle, SQL Server, Microsoft Access. |
|
|
|
Benefits of using database |
1. Minimises data redundancy. 2. Data integrity is assured 3. Data can be shared 4. Information can be accessed easily |
|
|
|
Minimises data redundancy |
~ most data item store in only 1 file. ~ no repeat recording the same data. |
|
|
|
Data integrity is assured |
~ when a user modifies data in one of the files in DB, the same data will change automatically in all the files. ~this is called data integrity. |
|
|
|
Data can be shared |
~ DB allows the ease of sharing data. Data can be shared over a network by a whole organisations. |
|
|
|
Information can be accessed easily |
~ DB makes information access easy ~ everyone can access and manage data in a DB. |
|
|
|
Primary key |
~A field that uniquely represents each record in A table. ~ must not have null value. ~ each table must have at least 1 primary key. ~ also call unique identifier. ~ can set unique field as PK or add a special field (studentID , memberID ) ~ PK ensures data integrity by uniquely identifying each record. (Avoid duplicating and null record). |
|
|
|
Foreign key |
~ A field that matches the PK in another table. ~FK may have duplicate values. ~ PK and FK will create a relationship between 2 tables, mentally 1:M relation. |
|
|
|
Differences between primary key and foreign key |
1. PK must have unique value while FK may have duplicate values. 2. PK links data in a record (A row) while FK links PK in another table (same value). |
|
|
|
Types of Primary keys |
1. AutoNumber (automatically enter by MS Access) 2. Single -field (1 unique field) 3. Multiple-field ( 2 or more field combine and the combination is unique) |
|
|
|
The Database Objects |
1. Table 2. Query 3. Form 4. Report |
|
|
|
Table (DB object) |
A collection of data that is organised as rows and columns. |
|
|
|
Query (DB object) |
~to retrieve information base on the the criteria or request by user. ~ use for data manipulation. |
|
|
|
Form (DB object) |
1. A user friendly user interface. 2. Is an organised and formatted view of selected field form selected Taables or Queries. 3. User are allowed to add, delete, modify and view information. |
|
|
|
Report (DB object) |
1. Summaries information form DB. 2. Present selected information form tables or Queries for printing. |
|
|
|
What is Data Manipulation? |
1. Operation of accessing, locating, organising, modifying & managing data in DB. 2. Basic operations: update, insert, delete, retrieve, sort, filter, search. |
|
|
|
Function of each operations of data manipulation. |
1. Update: changing data in a DB table. 2. Insert: adding records to table. 3. Delete: removing records form table. 4. Retrieve: retrieving records form table. 5. Sort: sorting records 6. Filter: filtering records (needed) form table. 7. Search: finding records form table. |
|
|
|
Phases of System Development |
1. Analysis phase 2. Design phase 3. Implementation phase 4. Testing phase 5. Documentation phase 6. Maintenance phase |
|
|
|
Analysis phase |
Activities: A) interview target user. B) collecting printing documents for input & output. Purposes: 1. Problem analysis : finding out the needs of target user. 2. Identify the input, process & output (IPO) for new system. |
Activities and purpose. |
|
|
Design phase |
1. Tool used: Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD). 2. Guidelines: ~ Choose entity (item) to create table. ~ identify attributes (data) needed for each entity (table). ~ identify the types of relationship between 2 or more tables, then set PK and FK. ~ Choose data types for each field. |
Tools use, & steps to identify entity, attributes and relationship use. |
|
|
Implementation phase |
1. Create database using database system. 2. Convert technical plan & design plan into a computer program. 3. Steps: creating table, assigning table relationship. Creating queries, creating form, creating report. 4. Types of relationships ~ 1:1 ~ 1: M |
|
|
|
Testing phase |
Purpose: To ensure the system runs correctly and is error free. Done by 1. Tested by target users. 2. Detect errors & fix it. Activities ~ test data entry ~ test on DB objects ~ test on functionality of the system. |
Activities |
|
|
Documentation phase |
Important: 1. When the system requires changes in the future. 2. Reduce the amount of time for a new system developer in studying the existing program. 2 important documents: 1. User manual 2. Technical Documentation. |
|
|
|
The user manual |
1. Help user to use the system. 2. Written in simple language. Content: How to 1. run the system 2. Enter data 3. Modify data 4 Save & print report 5 Ways to overcome errors. |
|
|
|
Technical Documentation |
1. As system developer reference. 2. Useful for system improvements. 3. Written in technical language. |
|
|
|
Maintenance phase |
System developer: ~including checking, changing & enhancing to improve IS performance. |
|
|
|
3 types of IS maintenance |
1. Corrective maintenance 2. Perfective maintenance 3. Preventive maintenance |
|
|
|
Corrective maintenance |
To repair an error in system design. |
|
|
|
Perfective maintenance |
To improve IS. |
|
|
|
Preventive maintenance |
Prevention of future breakdown. |
|
|
|
Web-based Applications |
~ applications and data store in web server. ~user access applications through websites. ~ Example of web applications : Google calendar, Yahoo mail. ~Example of DB: Oracle, MS SQL Server. |
|

