![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
14 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Name the Topoisomerase II and Topoisomerase I inhibiting drugs
|
Topoisomerase II:
DAUNOMYCIN, DOXORUBICIN mitoxantrone, dactinomycin Topoisomerase I: topotecan, IRINOTECAN |
|
|
How do Topoisomerase I and II work, what is the MOA of Topoisomerase inhibitors?
|
Topoisomerase II introduces transient protein bridged DNA breaks in BOTH strands of DNA
Topoisomerase I introduces DNA breaks in ONE strand of DNA. TII inhibitors are intercalators and lead to strand breaks |
|
|
Explain the concept of MDR and how cells become resistant to topoisomerase inhibitors
|
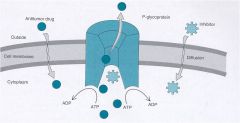
Cells can develop cross resistance to chemotherapy agents via the P-glycoprotein membrane efflux pump.
Continous infusions may downregulate P-glycoprotein or Quinine/verapamil/cyclosporin may block the efflux pump |
|
|
Describe the side effects of doxorubicin and daunorubicin
|
Daunorubicin and doxorubicin cause nausea, vomiting, hairloss and myelosuppression (10-14 days after administration). They also have a cumulative cardiac toxicity and patients should NOT be given more than 400 mg/m2 because of the high risk of CHF
|
|
|
What are the benefits of giving doxorubicin at 60mg/m2 over 96 hours vs 20mg/m2 over 20 minutes?
|
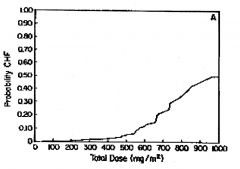
Giving doxorubicin over 96 hours shifts this curve FAR to the right when compared with giving it over 20 min. HOWEVER, it does NOT change the lifetime dose meaning that 400mg/m2 is NEVER to be exceeded
|
|
|
True or False. Doxirubicin is more cardiotoxic than daunorubicin
|
True
|
|
|
Describe the MOA of Irinotecan
|
Irinotecan is a topoisomerase I inhibitor and is a prodrug, as such requiring bioactivation (to SN38) in the liver to become more effective.
|
|
|
Explain how doxorubicin manifests schedule dependent cardiac toxicity but also demonstrates schedule independent cytotoxicity
|
Infusing doxorubicin over a prolonged period delays cardiac toxicity by maintaining low levels of free radical (vs giving it at high quick doses)
Prolonging the administration time does not alter the antitumor effect of the drug which is why it has schedule independent cytotoxicity. |
|
|
What must one be cautious of when giving irinotecan?
|
Irintocean requires significant hepatic metabolism and a dose reduction is required in jaundiced people.
UGTIAI mutations (the enzyme responsible for clearing irinotecan and bilirubin) are present in 9% of both black and white populations |
|
|
What is Irinotecan used for?
|
Irinotecan is a topoisomerase I inhibitor (single strand breaks) and is useful in colorectal cancer when used with 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin
|
|
|
What is bleomycin?
|
Bleomycin causes free radical production and leads to single and double strand DNA breaks.
It is NOT myelosuppressive however it has cumulative pulmonary toxicity and patients should NOT be administered more than 400 units |
|
|
What is the MOA of tamoxifen
|
Tamoxifen - estrogen receptor in breast, can cause endometrial cancer and thrombosis
remember we already had this... its an anti-cancer hormonal agent |
|
|
Describe the MOA of Flutamide
|
Flutamide inhibits uptake and binding of testosterone to specific receptors in hormonally sensitive prostate cancer cells
|
|
|
Which drug is a vesicant?
|
Doxorubicin is a vesicant (a substance that causes tissue blistering
|

