![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
26 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Systematic Error |
A "constant" error associated with an experimental system itself |
|
|
|
Random Error |
Error caused by uncontrollable variables in an experiment |
|
|
|
Precision |
Indicator of how close a series of measurments on the same object are to each other |
Each other |
|
|
Accuracy |
Indicator of how close a measurement (or average) comes to the true accepted value |
|
|
|
Significant Figures |
All the digits of certainty plus on of uncertainty |
|
|
|
Mass |
Total quantity of matter in an object |
|
|
|
Weight |
The measurement of the force exerted on an object by gravitational forces |
|
|
|
Density Equation |
D=m/v |
|
|
|
Intensive Property |
Property that is independent of the amount of substajce present |
Temperature, Color, Melting Point, and Density |
|
|
Extensive Properties |
Property that depends on the amount of the substance present |
Mass, Length, and Volume |
|
|
Heterogeneous Mixture |
Contains 2 or more visually distinguishable parts, each of which has different properties |
Sand and Sugar |
|
|
Homogeneous Mixture |
Contains only 1 visually distinguishable part, which has uniform properties throughout |
|
|
|
Element |
Pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler pure substances using ordinary chemical means |
|
|
|
Compound |
Pure substances that can be broken down into 2 or more simpler pure substances using chemical means |
|
|
|
Atom |
Smallest particle of an element that's exist and still have the properties of an element |
|
|
|
Molecule |
A group of 2 or more atoms that function as a unit because the atoms are tightly bound together |
|
|
|
Diatomic Molecule |

Molecule that contains 2 atoms |
|
|
|
Triatomic Molecule |
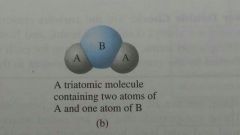
A molecule that contains 3 atoms |
|
|
|
Tetratomic Molecule |
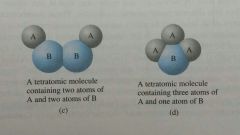
A molecule containing 4 atoms |
|
|
|
Homoatomic Molecule |
A molecule in which all atoms present are the same kind |
Must be an element |
|
|
Heteroatomic Molecule |
A molecule in which 2 or more different kinds of atoms are present |
Must be a compound |
|
|
Molecular Compound |
Compounds that have heteroatomic molecules as their basis structural unit |
|
|
|
Ions |
Extended 3D assembly of positively and negatively charged particles |
|
|
|
Ionic Compound |
Compounds that contain ions |
|
|
|
What is the limit of physical subdivision? |
Molecule |
|
|
|
What is the limit of chemical subdivision? |
Atom |
|

