![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What are 3 different types of particles that make up matter? |
Atoms, Molecules, Ions |
|
|
What are atoms? |
Atoms are the smallest units of a chemical element which have all the characteristics of the element. |
|
|
What are molecules? |
Molecules are groups of two or more atoms bonded together and which can exist on their own. Molecules may be made up of atoms of the same element. |
|
|
What are ions? |
Ions are electrically charged particles. Ions may be formed from a single atom. |
|
|
SUBTOPIC |
The three states of matter |
|
|
What are the usual properties of solids? |
•Fixed Shape •Fixed Volume •Usually highly dense •Difficult to compress •Arranged in a tightly packed (rectangular) way. •Strong force of attraction •Low amount of kinetic energy possessed within •Moves (vibrates) in a fixed position |
|
|
What are the usual properties of liquids? |
•Varies in Shape (takes the form of the container it is in and always have a horizontal surface)•Fixed Volume •Less dense than solids but more dense than gases•Can be slightly compressed by adding pressure•Arranged randomly as they are small spaces between them •Weaker force of attraction in comparison to a solid but more stronger than a gas•Possess more kinetic energy than a solid but less than a gas•Moves slowly past each other |
|
|
What are are the usual properties of Gas? |
•Varies in Shape (takes the form of the container it is in entirely)•Varied Volume (Expands to fill container it is in)•Low Density •Very easy to compress •Arranged randomly as they are spaces between them•Weak force of attraction •Particles have large amounts of kinetic energy •Moves freely and rapidly |
|
|
SUBTOPIC |
Changing states |
|
|
What is the result when a gas is heated? |
• When a solid is heated, it usually changes state to a liquid and then to a gas. This occurs because the particles gain kinetic energy, move increasingly faster and further apart, and the forces of attraction between them become increasingly weaker. |
|
|
What is the result when a gas is cooled? |
• When a gas is cooled, it usually changes state to a liquid and then to a solid. This occurs because the particles lose kinetic energy, move more and more slowly and closer together, and the forces of attraction between them become increasingly stronger. |
|
|
State change diagram |
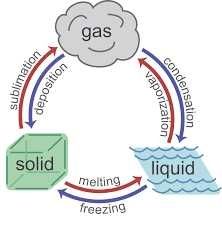
|
|
|
Evaporation Vs Boiling |
Evaporation and boiling are different in the following ways: • Evaporation can take place at any temperature, whereas boiling occurs at a specific temperature. • Evaporation takes place at the surface of the liquid only, whereas boiling takes place throughout the liquid. |
|
|
What is sublimation? |
Substances which sublimate (or sublime) change directly from a solid to a gas. Examples of substances that sublimate include carbon dioxide ('dry ice'), iodine and naphthalene (moth balls). |
|
|
What is deposition? |
The reverse of sublimation in which a gas changes directly to a solid. |
|
|
What is a heating curve? |
• A heating curve is drawn when the temperature of a solid is measured at intervals as it is heated and changes state to a liquid and then to a gas, and the temperature is then plotted against time. |
|
|
What is a cooling curve? |
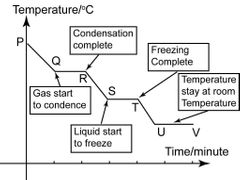
• A cooling curve is drawn when the temperature of a gas is measured at intervals as it is cooled and changes state to a liquid and then to a solid, and the temperature is then plotted against time time |
|
|
What is the melting point? |
The melting point is the constant temperature at which a solid changes into a liquid. |
|
|
What is the boiling point? |
The boiling point is the constant temperature at which a liquid changes into a gas. |
|
|
What is the freezing point? |
The freezing point is the constant temperature at which a liquid changes into a solid. |

