![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is diffusion? |
Spreading out of a gas to fill space |
Spreading |
|
|
Example of diffusion with HCl + Ammonia solution (just need to note a thing formed) |

Note ammonium chloride ring |
Ring? |
|
|
1. What happens when a gas increases in temp. 2. What happens when pressure is increased on a gas |
1. Expands, Volume increases 2. Compressed, Volume decreaaes |
Expa Compr |
|
|
What is Boyle's Law? (4 MAIN POINTS) |
When a fixed mass of gas is kept at a constant temperature, its volume multiplied by its pressure is constant. |
Temp. pV |
|
|
Example equation of Boyle's Law (p1, V1) |

|
|
|
|
Relationship between pressure and volume |
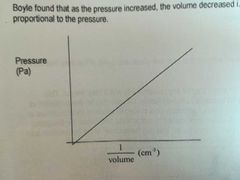
They are inversely proportional to each other. (P increase <-> V decrease) |
|
|
|
For how many gases does Boyle's Law is true for, for all units of pressure and volume, as long as they are of the same units |
All gases |
|
|
|
How does the value of pV change with p? |

It doesn't |
HA! , you thought |
|
|
What is Charles' Law? (3 MAIN POINTS) |
The volume of a fixed mass of gas, kept at constant pressure, is directly proportional to the absolute temperature (KELVINS) |
Volume Constant Absolute |
|
|
What is 100 Degrees Celsius in Kelvins? |
373.15 Kelvins (100 + 273.15) |
|
|
|
1. Formula for Charles' Law 2. Also, what is constant about the formula |

ᵛ⁄ₜ is constant |
|
|
|
What is Gay-Lussac's Law of combining volumes? (4 MAIN PARTS) |
Gases always react with each other in simple whole number ratios when volumes are measured at the same temperature and pressure |
Gases Ratio Volumes Same |
|

Q. Calculate how much H2 and NH3 is produced with 5g of N2?
|
H2 - 15g NH3 - 10g |
|
|
|
What is the name of the process in the previous picture? |
The Haber Bosch process for manufacture of ammonia |
HB |
|
|
What is Avogadro's Law? (3 MAIN POINTS) |
Equal volumes of gases, measured at the same temperature and pressure, contain equal numbers of molecules |
Gases Molecules |
|
|
Examples of Avogadro's Law in play (just looking is fine) |

|
|
|
|
What is the Combined Gas Law? (or the General Gas Law) |

Combining Boyle's and Charles' Law
|
|
|

|

|
|
|

|

|
|
|
|
What idea is the Kinetic Theory of Gases based on? |
Gases consist of particles that are in constant random motion |
Constant random motion |
|
|
List 5 Assumptions made about gas laws And also state whether they are true or not |
1. Gases consist of particles widely separated in space => volume of gas mostly empty space, gas don't occupy too much space either 2. Gas particles are in constant random motion colliding with each other + container walls 3. Collisions are elastic (no loss of energy from collisions) 4. There are no attractive forces between gas particles (independent) 5. Average kinetic energy of particles is proportional to absolute temp. (K) |
Consist of particles widely..... Colliding..... Elastic..... Attractive forces...... Ek ~ to K |
|
|
What is an ideal gas? |
A gas that obeys all gas laws at all temperatures and pressure |
All law at all |
|
|
Why can't there be an actual ideal gas? (3 PARTS) |
1. There are forces of attraction between molecules 2. The amount of space that gaseous particles occupy is significant under high pressures 3. Collisions are not entirely elastic (energy can be lost to surroundings) |
1. Forces 2. Space and pressure 3. Not entirely |
|
|
In what case would a real gas come closest to ideal behaviour? (2) |
At low pressures and high temperatures |
Low + High |
|
|
What is the Equation of State For An Ideal Gas? |

|
Rearrange with nR? |
|

|

|
|
|
|
Diagram for to determine the Relative Molecular Mass of a Volatile Liquid Using A Gas Syringe *Just look is fine |

|
|
|
|
Method to determineRelative Molecular Mass of a Volatile Liquid Using A Gas Syringe |
1. 5cm3 of air drawn in graduated syringe + rubber cap placed on 2. Steam passed through container until volume + temp. reading became steady (note values) 3. Propanone drawn into hypodermic syringe + weighed 4. Hypodermic syringe pushed through rubber cap + SOME injected 5. Plunger moves out from vaporised propanone, note volume 6. Hype syringe reweighed 7. Barometer checked for atmospheric pressure |
Graduated syringe steam passed propanone drawn some injected vaporised propanone reweighed barometer |
|
|
Why do you measure for atmospheric pressure? |
It's the same pressure acting on gas in syringe -plunger will move until pressure inside + outside is equal |
Same In + out |

