![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
264 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Lewis structure oxygen |

|
|
|

What is this? |
Erlenmeyer flask - easy to swirl, low risk of spill. Used for titrations! |
|
|

What is this? |
Beaker! Not used for measuring - used for mixing and storing chemicals. |
|
|
|
What is centrifugation? |
Laboratory machine that spins a liquid to separate parts from one another. Example - centrifuge that separates blood components. |
|
|
|
Law of conservation of matter |
Matter can neither be created or destroyed (reason why equations must be balanced!) |
|
|
|
Law of conservation of matter |
Matter can neither be created or destroyed (reason why equations must be balanced!) |
|
|
|
Examples of physical changes? |
Cutting something, phase change (liquid,solid,gas), take something apart. |
|
|
|
Law of conservation of matter |
Matter can neither be created or destroyed (reason why equations must be balanced!) |
|
|
|
Examples of physical changes? |
Cutting something, phase change (liquid,solid,gas), take something apart. |
|
|
|
Indicators that a chemical change has occurred? |
Odor, formation of precipitate, color change, change in temperature, formation of new compound. |
|
|
|
Chromatography. |
Laboratory practice to separate mixtures of substances into different components. (Separated color dye) |
|
|
|
How to convert Celsius to Kelvin? |
+ 273 |
|
|
|
Heterogeneous solution? |
Not mixed evenly - can see differences in the solution - example - blood, soil, cereal |
|
|
|
Heterogeneous solution? |
Not mixed evenly - can see differences in the solution - example - blood, soil, cereal |
|
|
|
Homogeneous mixture? |
Evenly mixed and uniformly distributed. Example - salt water, lemonade. |
|
|
|
Exothermic and endothermic? |
Exo - gives off heat (heat is a product)
Endo - takes in heat (heat is a reactant) |
|
|
|
Direct relationship? |
As one variable increased, so does the other. Example -
V1 = V2 T1 T2 (Charles law) |
|
|
|
Direct relationship? |
As one variable increased, so does the other. Example -
V1 = V2 T1 T2 (Charles law) |
|
|
|
Inverse relationship? |
As one variable increases, the other decreases!
Example - Boyles law
P1V1 = P2V2 |
|
|
|
Equation for percent error? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
1 L = _______ mL |
1000 |
|
|
|
1 L = _______ mL |
1000 |
|
|
|
1 kg = ________ g |
1000 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
25.7 |
3 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
25.7 |
3 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
100.62 |
5 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
25.7 |
3 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
100.62 |
5 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
5.00 |
3 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
25.7 |
3 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
100.62 |
5 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
5.00 |
3 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
200 |
1 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
25.7 |
3 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
100.62 |
5 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
5.00 |
3 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs?
200 |
1 |
|
|
|
How many sig figs? 0.0050 |
2 |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Volumetric flask |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Mortal and pestel |
|
|

Front (Term) |
Watch glass |
|
|
|
Scientist came up with atomic theory that said atoms were indivisible building blocks of matter. |
Dalton |
|
|
|
Scientist came up with atomic theory that said atoms were indivisible building blocks of matter. |
Dalton |
|
|
|
Scientist did gold foil experiment? |
Rutherford |
|
|
|
Scientist came up with atomic theory that said atoms were indivisible building blocks of matter. |
Dalton |
|
|
|
Scientist did gold foil experiment? |
Rutherford |
|
|
|
Scientist created visual that showed electrons occupying fixed energy levels that circle the nucleus. |
Bohr |
|
|
|
Scientist came up with atomic theory that said atoms were indivisible building blocks of matter. |
Dalton |
|
|
|
Scientist did gold foil experiment? |
Rutherford |
|
|
|
Scientist created visual that showed electrons occupying fixed energy levels that circle the nucleus. |
Bohr |
|
|
|
Created first periodic table. |
Mendeleev |
|
|
|
Atomic number = number of ________ |
Protons |
|
|
|
Mass number = ___________ |
Protons + neutrons |
|
|
|
What is an ion? |
When a neutral atomic gains or loses electrons. |
|
|
|
What is an ion? |
When a neutral atomic gains or loses electrons. |
|
|
|
Cation |
Loses electrons and had a positive charge. |
|
|
|
What is an ion? |
When a neutral atomic gains or loses electrons. |
|
|
|
Cation |
Loses electrons and had a positive charge. |
|
|
|
Anion |
Gains electrons and has a negative charge |
|
|
|
What is an isotope? |
Same number of protons, different number of neutrons. |
|
|
|
What is Pauli exclusion principle? |
No more than two electrons in each orbital! |
|
|
|
What is Pauli exclusion principle? |
No more than two electrons in each orbital! |
|
|
|
What is Hund's rule? |
When a sublevel has more than one orbital.... Always put electrons ONE AT A TIME into each orbital before doubling up. |
|
|
|
What is Pauli exclusion principle? |
No more than two electrons in each orbital! |
|
|
|
What is Hund's rule? |
When a sublevel has more than one orbital.... Always put electrons ONE AT A TIME into each orbital before doubling up. |
|
|
|
What is the Aufbau rule? |
electrons orbiting one or more atoms fill the lowest available energy levels before filling higher levels (e.g., 1s before 2s) |
|
|
|
Electron configuration for carbon? |
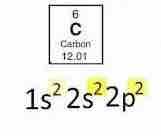
|
|
|
|
Electron configuration for calcium? |
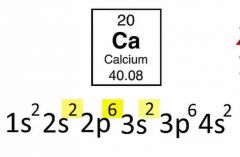
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Arrow diagram for oxygen? |
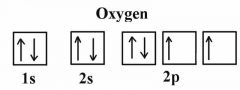
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Arrow orbital nitrogen? |
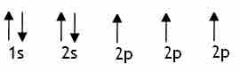
Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
What is a valence electron? |
# of electrons in last shell.
Group 13 has 3 Group 18 has 8 |
|
|
|
What is a valence electron? |
# of electrons in last shell.
Group 13 has 3 Group 18 has 8 |
|
|
|
Valence electrons in neon? |
8 |
|
|
|
What is a valence electron? |
# of electrons in last shell.
Group 13 has 3 Group 18 has 8 |
|
|
|
Valence electrons in neon? |
8 |
|
|
|
Valence electrons in H? |
1 |
|
|
|
What is a valence electron? |
# of electrons in last shell.
Group 13 has 3 Group 18 has 8 |
|
|
|
Valence electrons in neon? |
8 |
|
|
|
Valence electrons in H? |
1 |
|
|
|
Oxidation number of oxygen? |
-2 |
|
|
|
What is a valence electron? |
# of electrons in last shell.
Group 13 has 3 Group 18 has 8 |
|
|
|
Valence electrons in neon? |
8 |
|
|
|
Valence electrons in H? |
1 |
|
|
|
Oxidation number of oxygen? |
-2 |
|
|
|
Oxidation number of aluminum? |
+3 |
|
|
|
Horizontal rows of periodic table? |
Periods |
|
|
|
Horizontal rows of periodic table? |
Periods |
|
|
|
Columns of periodic table |
Groups!
Aka families - elements in same group/family have similar chemical characteristics. |
|
|
|
What are the diatomic elements? |
There are seven -
H2 O2 N2 F2 Cl2 Br2 I2 |
|
|
|
Group 18 = |
Noble gases |
|
|
|
Group 18 = |
Noble gases |
|
|
|
Group 1 = |
Alkali metals |
|
|
|
Group 18 = |
Noble gases |
|
|
|
Group 1 = |
Alkali metals |
|
|
|
Groups 3-12 = |
Transition metals |
|
|
|
Group 18 = |
Noble gases |
|
|
|
Group 1 = |
Alkali metals |
|
|
|
Groups 3-12 = |
Transition metals |
|
|
|
Group 2 |
Alkaline earth metals |
|
|
|
Group 18 = |
Noble gases |
|
|
|
Group 1 = |
Alkali metals |
|
|
|
Groups 3-12 = |
Transition metals |
|
|
|
Group 2 |
Alkaline earth metals |
|
|
|
Group 17= |
Halogens |
|
|
|
What is the trend line for ATOMIC RADIUS? |

|
|
|
|
What is the trend line for Ionization energy and electro negativity? |
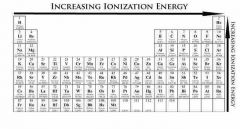
|
|
|
|
Lewis structure lithium? |

|
|
|
|
Lewis structure carbon |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Lewis structure carbon |

|
|
|
|
Lewis structure argon |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
|
Lewis structure carbon |

|
|
|
|
What is NH4+ |
Ammonium |
|
|
|
Lewis structure oxygen |

|
|
|
|
What is hydroxide? |
OH- |
|
|
|
What is SO4 -2 |
Sulfate |
|
|
|
What is phosphate |
PO4 -3 |
|
|
|
NO3 - |
Nitrate |
|
|
|
What is NaNO3 |
Sodium nitrate |
|
|
|
Iron (III) sulfate |
Fe2 (SO4)3 |
|
|
|
NH4Cl |
Ammonium chloride |
|
|
|
Calcium hydroxide |
Ca(OH)2 |
|
|
|
Lewis structure argon |

|
|
|
|
K2CO3 |
Potassium carbonate |
|
|
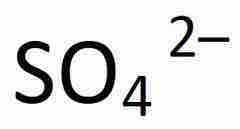
|
Sulfate |
|
|
|
What is phosphate |

|
|
|

|
Nitrate |
|
|
|
How to name covalent? |
Use prefixes!!!! Mono 1 Di 2 Tri 3 Tetra 4 Penta 5 Hexa 6 |
|
|
|
What is CCl4 |
Carbon tetrachloride |
|
|
|
What is PBr3 |
Phosphorus tribromide |
|
|
|
How to write sulfur hexafluoride |
SF6 |
|
|
|
How to write P2O3 |
Diphosphorus trioxide |
|
|
|
What is CS2 |
Carbon disulfide |
|
|
|
Lewis structure oxygen |

|
|
|
|
Acids ALWAYS start with... |
H |
|
|
|
Bases ALWAYS end in... |
OH (hydroxide) |
|
|
|
What is HCl? |
Hydrochloric acid |
|
|
|
What is HNO3 |
Nitric acid |
|
|
|
What is H2SO4 |
Sulfuric acid |
|
|
|
Phosphoric acid? |
H3PO4 |
|
|
|
Carbonic acid? |
H2CO3 |
|
|
|
Aluminum hydroxide |
Al(OH)3 |
|
|
|
Magnesium hydroxide |
Mg(OH)2 |
|
|
|
NaOH Is... |
Sodium hydroxide |
|
|
|
Compound name ?
Na2S |
Sodium sulfide |
|
|
|
Acid is a H+...
Donor or acceptor? |
DONOR |
|
|
|
Bases accept OR donate H+? |
Accept! |
|
|
|
pH of an acid and of a base? |
Acid is less than 7 Bases are more than 7 |
|
|
|
Difference between molecular and empirical formulas? |
Molecular - tells how many of each atom
Empirical - lowest whole number ratio of atoms |
|
|
|
What is empirical formula of C6H12 |
CH2 |
|
|
|
Empirical formula of...
C10H20O2 ? |
C5H10O |
|
|
|
Formula for magnesium chloride? |
MgCl2 |
|
|
|
Formula for lithium nitride? |
Li3N |
|
|
|
Chemical name? K3P |
Potassium phosphide |
|
|
|
Copper (I) bromide |
CuBr |
|
|
|
Copper (ii) bromide |
CuBr2 |
|
|
|
Iron (iii) oxide? |
Fe2O3 |
|
|
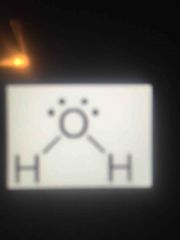
Lewis structure type? |
BENT (polar - because of extra electrons around centra atom) |
|
|

Lewis structure type? |
Tetrahedral - nonpolar! |
|
|
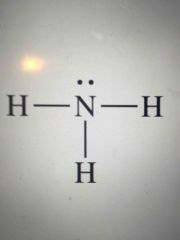
Lewis structure type? |
Pyramidal - polar (extra electrons around central atom) |
|
|

Lewis structure type? |
Linear! Nonpolar |
|
|
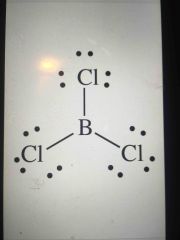
Lewis structure type? |
Trigonal planar - nonpolar - no unpaired electrons around central atom |
|
|
|
What type of reaction?
N2 + 3H2 --> 2 NH3 |
Synthesis |
|
|
|
What type of reaction?
2 KClO3 --> 2 KCl + 3O2 |
Decomposition |
|
|
|
What type of reaction?
Mg + 2 HCl --> MgCl2 + H2 |
Single replacement |
|
|
|
What type of reaction?
AgNO3 + NaCl --> AgCl + NaNO3 |
Double replacement |
|
|
|
What type of reaction?
CH3COCH3 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O |
Combustion |
|
|
|
What type of reaction?
CH3COCH3 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O |
Combustion |
|
|
|
What type of reaction?
HCl + NaOH ---> H2O + NaCl |
Neutralization |
|
|
|
What type of reaction?
CH3COCH3 + O2 ---> CO2 + H2O |
Combustion |
|
|
|
What type of reaction?
HCl + NaOH ---> H2O + NaCl |
Neutralization |
|
|
|
What are the products and reactants of a neutralization reaction?
|
Reactants - acid and base Products - salt and water |
|
|
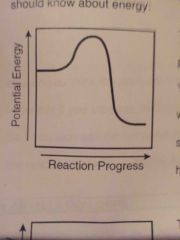
What type of reaction?? Endo exo? |
EXOTHERMIC - energy is released (products energy lower than reactants) |
|
|
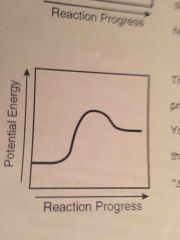
Endo or exo? |
ENDOTHERMIC! Energy is absorbed! Products energy higher than reactants! |
|
|
|
What does a catalyst do? |
LOWERS activation energy so that the reaction occurs faster! |
|
|
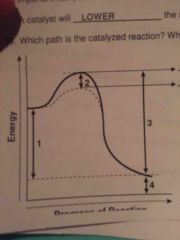
Which path (1 or 2) is catalyze a reaction? |
Path 2 - lower energy required to start reaction. |
|
|
|
How does temperature affect a reaction? |
INCREASES speed of molecules colliding so... Reaction rate also INCREASES |
|
|
|
1 mole = ________ molecules |
6.02 x 10^23 |
|
|
|
1 mole = ________ molecules |
6.02 x 10^23 |
|
|
|
1 mole = ______ liters |
22.4 |
|
|
|
Convert 3.58 x 10^24 atoms of Fe into moles Fe |
5.95 miles Fe |
|
|
|
Convert 2.25 moles of KNO3 into grams of KNO3 |
227 g KNO3 |
Find molar mass of KNO3 |
|
|
How much heat is required to raise the temperature of a 100.0g piece of copper metal from 25*C to 175*C? The specific heat of copper is 0.385J/g*C? |
Use q=mcT(change in T!)
5775 J |
|
|
|
When 435 J of heat is added to 3.4g of olive oil at 21*C, the temperature increases to 85*C. What is the specific heat of olive oil? |
Use q=mcT(change in T)
2.0 is answer |
|
|
|
Balance the following equation:
___ Mg + ____ O2 --> ____ MgO |
2,1,2 |
|
|
|
When magnesium metal is burned, it produces magnesium oxide (MgO) how many miles of oxygen has are needed to burn 10 moles of Mg? |
Set up equation:
2 Mg + O2 --> 2 MgO
Use molar ratio!
Answer: 5 mil O2 |
|
|
|
Given following equation,
2 C2H6 + 7 O2 --> 4 CO2 + 6 H2O
If 5.2 moles of ethane (C2H6) is burned, how many moles of O2 are required? |
Answer - 18.2 mol O2 |
|
|
|
Given the following equation, if 3.4 moles of aluminum reacts with excess hydrochloric acid, how many moles of H2 will be produced?
2 Al + 6 HCl --> 2 AlCl3 + 3 H2 |
Answer 5.1 moles H2 |
|
|
|
2 KOH + H2SO4 --> 2 H2O + K2SO4
What mass of potassium hydroxide is required to react completely with 2.70 g of sulfuric acid to produce potassium sulfate and water? |
Answer - 3.09 g KOH |
|
|
|
How many grams of KCl are required to prepare 500 mL of a 0.125 M solution? |
Molarity!
M= mol/L
Then convert moles to grams like in the question!
Answer - 4.66 g KCl |
|
|
|
How to find molarity? |
M = mol/L |
|
|
|
What is molarity of a solution that is prepared by dissolving 75.0 g of C6H12O6 in enough water to prepare 500.0 mL of solution? |
First convert grams to liters. Convert mL to liters.
Then, mol/L
Answer - 0.833 M |
|
|
|
Equation for dilution? |
M1V1 = M2V2 |
|
|
|
Equation for dilution? |
M1V1 = M2V2 |
|
|
|
A 15 mL sample of 4.0 M NaOH was diluted to a volume of 250 mL. What is the new concentration of the solution? |
0.24 M |
|
|
|
750 mL of 0.50 M HCl is required for a lab experiment. How many milliliters of 6.00 M HCl should be used? |
62.5 mL |
|
|
|
Charles Law?? |

As temperature increases, volume increases... This is DIRECT! |
|
|
|
Boyles Law? |

As pressure increases, volume decreases... Or... As pressure decreases, volume increases |
|
|
|
A sample of oxygen gas is collected over water at 98.67 kPa. If partial pressure of water is 2.67 kPa, the partial pressure of oxygen is...
|
98.67 - 2.00= 96.67 kPa |
|
|
|
A sample of gas occupies a volume of 5.00 L at 25*C. This gas was heated at constant pressure and the volume increased to 6.00 L. What is the new temperature?? |
*** always convert to Kelvin when doing gas laws.
358 K (85*C) |
|
|
|
A sample of gas occupies a volume of 10.0 liters at 10*C. What would be the volume of this gas at 50*C if the pressure remains constant? |
Use Charles Law!
*Always convert to kelvins for gas laws.
11.4L |
|
|
|
What is ideal gas law? |
PV = nRT
R=0.0821 P pressure V volume n number of moles t temperature |
|
|
|
Solid to liquid? |
Melting!! |
|
|
|
Solid to liquid? |
Melting!! |
|
|
|
What is another term for melting? |
Fusion |
|
|
|
Solid to liquid? |
Melting!! |
|
|
|
What is another term for melting? |
Fusion |
|
|
|
Liquid to solid? |
Freezing! |
|
|
|
Solid to liquid? |
Melting!! |
|
|
|
What is another term for melting? |
Fusion |
|
|
|
Liquid to solid? |
Freezing! |
|
|
|
Solid to gas? |
Sublimation! |
|
|
|
Solid to liquid? |
Melting!! |
|
|
|
What is another term for melting? |
Fusion |
|
|
|
Liquid to solid? |
Freezing! |
|
|
|
Solid to gas? |
Sublimation! |
|
|
|
Gas to liquid? |
Condensation! |
|
|
|
Liquid to gas? |
Evaporation |
|
|
|
Liquid to gas? |
Evaporation |
|
|
|
Gas to solid? |
Deposition |
|
|
|
Three phase changes that are endothermic? |
Melting, evaporation, sublimation |
|
|
|
Three phase changes that are endothermic? |
Melting, evaporation, sublimation |
|
|
|
Three phase changes that are exothermic? |
Condensation, freezing, deposition |
|
|
|
What is a calorie? |
Amount it takes to raise the temperature of ONE GRAM Of water by ONE DEGREE CELSIUS |
|
|
|
Why does water have such a high boiling point or high heat capacity? |
Hydrogen bonding!!!! (Very strong intermolecular forces) |
|
|
|
What does "like dissolves like" mean? |
Must be the same to dissolve... So...
Polar dissolves polar and nonpolar dissolves nonpolar.
Nonpolar and polar do NOT mix (oil and water) |
|
|
|
You should know that...
If a substance has a high melting point or boiling point... |
It will have strong attractive forces!! |
|
|
|
Independent and dependent variable definitions? |
Independent - x axis - the one the scientist changes
Dependent - y axis - the one that changes as a result |
|
|
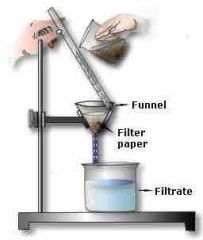
What is this? |
Filtering |
|
|
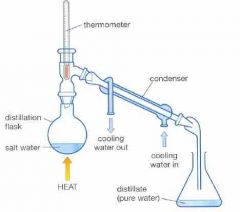
What is this? |
Distillation - separates the pure substance out of a mixture |
|
|
|
What is density? |
Mass/volume |
|
|
|
Covalent bonds ___________ electrons |
Share!!!
(Ionic give or take electrons ) |
|
|
|
What is activation energy? |
amount of energy needed to start a reaction |
|
|
|
Endothermic or exothermic?
C3H8 + 5 O2 --> 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + 2042kJ |
Exothermic (gives off heat) |
|
|
|
Endothermic or exothermic?
C3H8 + 5 O2 --> 3 CO2 + 4 H2O + 2042kJ |
Exothermic (gives off heat) |
|
|
|
Endothermic or exothermic?
C + H2O + 113kJ --> CO + H2 |
Endothermic (heat is absorbed) |
|
|
|
What is Avogadro's number? |
6.02 x 10^23 |
|
|
|
Solute vs solvent ? |
Solute - what is dissolved in solution
Solvent - what the "stuff" gets dissolves in |
|
|
|
Solute vs solvent ? |
Solute - what is dissolved in solution
Solvent - what the "stuff" gets dissolves in |
|
|
|
pH + pOH = |
14 |
|
|
|
What is pH? |
Percent H+ ion concentration |
|
|
|
What is pOH? |
Percent hydroxide ion (OH-) concentration |
|
|
|
What is pOH? |
Percent hydroxide ion (OH-) concentration |
|
|
|
What is an indicator? |
Something that changes color to show pH |
|
|
|
When converting moles and liters, what is the conversion factor? |
22.4 |
|
|
|
What is the limiting reactant? |
The substance that "runs out" in the reaction so the reaction stops |
|
|
|
Acid or base?
KOH |
Base (ends in OH) |
|
|
|
Acid or base?
KOH |
Base (ends in OH) |
|
|
|
Acid or base?
HCl |
acid (starts with H) |
|
|
|
Acid or base?
H2CO3 |
ACID (starts with H) |
|
|
|
Acid or base?
H2CO3 |
ACID (starts with H) |
|
|
|
Acid or base?
NaOH |
Base (ends in OH) |
|
|
|
What is titration? |
determination of the concentration of an acid or base by exactly neutralizing the acid or base with an acid or base of known concentration. |
|
|
|
Strong vs weak electrolyte?
|
Strong - completely disassociates in water - also emits more electricity
Weak - partially disassociates in water - emits little electricity |
|
|
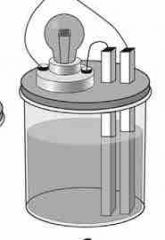
No light given off... |
NONELECTROLYTE |
|
|
|
Strong vs weak electrolyte?
|
Strong - completely disassociates in water - also emits more electricity
Weak - partially disassociates in water - emits little electricity |
|
|
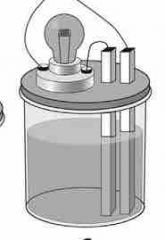
No light given off... |
NONELECTROLYTE |
|
|
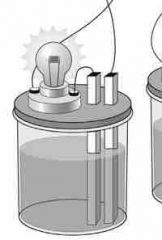
Dim light given off... |
Weak electrolyte ! |
|
|
|
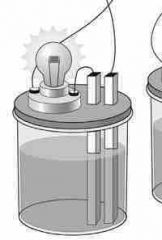
Strong vs weak electrolyte?
|
Strong - completely disassociates in water - also emits more electricity
Weak - partially disassociates in water - emits little electricity |
|
|
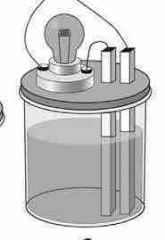
No light given off... |
NONELECTROLYTE |
|
|
Dim light given off... |
Weak electrolyte ! |
|
|
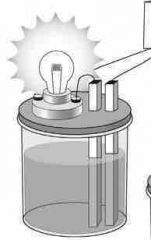
Bright light given off |
STRONG electrolyte |
|
|
|
Math equation for pH |
pH = - log (H+) |
|
|
|
Math equation for pH |
pH = - log (H+) |
|
|
|
Math equation for pOH |
pOH = - log (OH-) |
|

