![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
90 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
energy required to separate one mole of an ionic compound into gaseous ions
|
lattice energy
|
|
|
What is the trend in electronegativity?
|
increases left to right decreases with increasing atomic number |
|
|
Arrange the following according to electronegativity: H, C, N, O, P, S, Cl.
|
O > N > Cl > C > S > P,H
|
|
|
difference between number of valence electrons and the number of electrons assigned to the same atom in a Lewis structure
|
formal charge
|
|
|
What is true about first row elements?
|
Octet Rule
|
|
|
explanation that accounts for observations and reflects our inability to draw an accurate picture of molecules with dots and lines
|
resonance
|
|
|
What type of arrows are used to display resonance?
|
double-headed (<--->)
|
|
|
Electrostatic forces quite strong. (Ionic or covalent?)
|
ionic
|
|
|
Typically solids with high melting points. (Ionic or covalent?)
|
ionic
|
|
|
Many are water soluble and result in aqueous solutions that conduct electricity. (Ionic or covalent?)
|
ionic
|
|
|
Bond energies quite strong relative to intermolecular forces. (Ionic or covalent?)
|
covalent
|
|
|
Typically gases, liquids, or low melting solids. (Ionic or covalent?) |
covalent
|
|
|
Generally insoluble in water but if soluble, do not result in solutions that conduct electricity. (Ionic or covalent?)
|
covalent
|
|
|
predicts shapes bases simply on counting the number of atoms and electron pairs about a central atom and placing them in an idealized geometry
|
VSPER model
|
|
|
explains differences in bond lengths and bond energies |
not VSPER
|
|
|
accounts for stability of covalent bond in terms of overlapping atomic orbitals
|
valence bond theory
|
|
|
accounts for different bond types
|
valence bond theory
|
|
|
with hybridization, accounts for molecular geometry
|
valence bond theory
|
|
|
describes covalent bonds in terms of orbitals formed from the interaction of the atomic orbitals of all bonding atoms in the entire molecule
|
molecular orbital theory
|
|
|
What does molecular orbital theory say about orbitals?
|
They often spread over a number of atoms.
|
|
|
provides the best picture of bonding in molecules and molecular properties
|
molecular orbital theory
|
|
|
cylindrical and provide electron density between the nuclei
|
sigma bonds
|
|
|
lie above and below a plane containing the nuclei and provide electron density between the nuclei |
pi bonds
|
|
|
carbon forms polymeric or chain-like structures with itself
|
catenation
|
|
|
collection of atoms that define the shape, physical properties, type and strength of intermolecular forces, and chemical reactivity of a molecule
|
function groups
|
|
|
What do structures with the same functional groups have? (Three plus examples.) |
similar physical properties (odor, color, melting points and boiling points) similar chemical reactivity (acid/base reactions and redox reactions) similar spectroscopic properties (absorption of electromagnetic radiation of different wavelengths) |
|
|
What are the four broad families of functional groups?
|
carbons and hydrogens (no polar bonds) polar C-Z bond polar C=Z bond combinations of the above |
|
|
hydrocarbons consisting exclusively of carbon and hydrogen in saturated sigma C-C and C-H bonds
|
alkanes
|
|
|
What is the chemical formula of all alkanes? |
CnH(2n+2)
|
|
|
Name CH4
|
methane
|
|
|
Name C2H5 |
ethyl
|
|
|
Name C3H8 |
propane
|
|
|
Name C4H9 |
butyl
|
|
|
Name C5H12 |
pentane
|
|
|
Name C6H13 |
hexyl |
|
|
Name C7H16 |
heptane
|
|
|
NameC8H17
|
octyl
|
|
|
Name C9H20 |
nonane
|
|
|
Name C10H21 |
decyl
|
|
|
hydrocarbons consisting exclusively of carbon and hydrogen in saturated sigma C-C and C-H bonds and possessing one or more carbocyclic rings
|
cycloalkanes
|
|
|
What is the chemical formula of all cycloalkanes?
|
CnH2n
|
|
|
rings that share two adjoining atoms |
fused
|
|
|
rings that share two non-adjoining atoms |
bridged
|
|
|
rings that share one common atom
|
spiro
|
|
|
hydrocarbons consisting exclusively of carbon and hydrogen linked by sigma bonds and one or more unsaturated carbon-carbon double bonds (pi bonds) |
alkenes
|
|
|
What does each carbon-carbon double bond or pi bond reduce the number of hydrogens by? |
2
|
|
|
hydrocarbons consisting exclusively of carbon and hydrogen linked by sigma bonds and one or more unsaturated carbon-carbon triple bonds
|
alkynes
|
|
|
hydrocarbons possessing a benzene ring |
arenes
|
|
|
compounds containing a polar C-halogen bond |
alkyl halides
|
|
|
What are the halogens? |
F, Cl, Br, I
|
|
|
compounds containing a polar C-OH bond |
alcohols
|
|
|
What is a hydroxyl group?
|
-OH
|
|
|
compounds containing a polar C-OR bond where R is an alkyl group
|
ethers
|
|
|
What is an alkoxy group? |
-OR
|
|
|
What is "R"?
|
carbon bonded to other things (alkyl group)
|
|
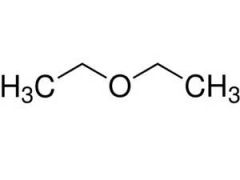
|
ether
|
|
|
compounds containing a polar C-SH bond |
thiols or mercaptans
|
|
|
What is a thiol group? |
-SH
|
|
|
compounds containing a polar C-SR bond |
sulfides or thioethers
|
|
|
What is a thioalkoxy group? |
-SR
|
|
|
compounds containing a polar C-amino group bond |
amines
|
|
|
What are amino groups? |
NH2 NHR NR2 |
|
|
What functional groups possess C=O?
|
aldehydes and ketones
|
|
|
What functional groups possess S=O? |
sulfoxides and sulfones
|
|
|
What functional groups possess P=O? |
phosphine oxides
|
|
|
What functional groups possess C=N? |
imines
|
|
|
What functional groups possess C=S? |
thiocarbonyl compounds (rare)
|
|
|
What have two hydroxyl groups?
|
diols
|
|
|
What have hydrocarbon and carboxylic acid functional groups? |
fatty acids
|
|
|
What are carbonyl compounds? |
C=O
|
|
|
What are proximal ether and alcohol functional groups called (OH group off R)?
|
hemiacetals
|
|
|
What are proximal ether functional groups called (share R)? |
acetals
|
|
|
What are proximal carbonyl and polar C-OH bonds called? |
carboxylic acid
|
|
|
What are proximal carbonyl and polar C-Cl bonds called? |
acid chloride
|
|
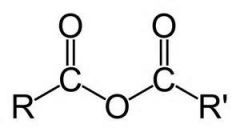
|
acid anhydride
|
|
|
What are proximal carbonyl and polar C-OR bonds called?
|
carboxylic ester
|
|
|
What are proximal carbonyl and polar C-SR bonds called? |
carboxylic thioester
|
|
|
What are proximal carbonyl and polar C-NR2 bonds called? |
carboxamide
|
|
|
What are proximal C=O carbonyl groups called? |
alpha-ketoacids
|
|
|
removal of electrons
|
oxidation
|
|
|
addition of elections |
reduction
|
|
|
What kind of reaction is a functional group interconversion?
|
redox
|
|
|
What are the five symmetry elements that are of particular importance in the study of chemistry? |
symmetry axis (Cn) plane of symmetry (sigma) center of symmetry (i) rotation-reflection axis (Sn) identity |
|
|
an axis around which a rotation produces a molecule that is indistinguishable from the original
|
symmetry axis or n-fold rotational axis (Cn)
|
|
|
a mirror plane through which an identical copy of the original molecule is obtained |
plane of symmetry (sigma)
|
|
|
for any atom in the molecule, an identical atom exists diametrically opposite this center an equal distance from it
|
center of symmetry or inversion center (i)
|
|
|
an axis around which a rotation followed by a reflection in a plane perpendicular to it, leaves the molecule unchanged |
rotation-reflection axis (Sn)
|
|
|
an apparently trivial symmetry element possessed by every molecule |
identity (example: chirality)
|
|
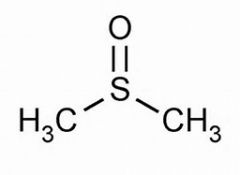
|
sulfoxide
|
|
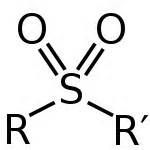
|
sulfone |

