![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
19 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Bohr's Atomic Model |
Different energy levels , absorb energy they move up ( the rings ) and opposite when they go down |
Rings |
|
|
Quantum Model |
The atoms nucleus is sorrounded by a cloud of electrons |
Nimbus |
|
|
Arnold Sommerfield |
Suggested / Discovered "l" and "m" quantum # s |
|
|
|
Louis de Broglie |
Electrons behave like waves |
|
|
|
Heisenberg |
"Impossible" to tell where the electrons are at a certain point in time |
|
|
|
Schrodinger |
Possible to have an estimate of where the electron is at a certain point |
|
|
|
Paul Dirac |
Better equation than schrodinger but relativley same effect |
|
|
|
Quantum # s |
N = Main energy level (prd table row) L = Shape of orbitals ( sublevel ) M = Magnetic quantum # ( orientation of orbitals S = Spin ( + 1/2 or - 1/2 ) |
Abdefg... |
|
|
Electronic Configuration |
Best way to organize an atoms electrons where the valence electrons are always named last ( last ones take place in all bonding and shiz ) |
|
|
|
Kernel Notation |
Abbreviated electronic configuration |
[ ] |
|
|
Periodic Table ( what is where ) Blocks , families etc |

|
|
|
|
Atomic Radius |
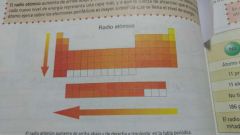
Distance from NUCLEUS to valence ring , increases in the table as you move up and left |
|
|
|
Ionic Radius |
Take out electrons ( negative particles ) and it becomes positive , and vice versa . The closer to the nucleus the valence ring is , the harder it is for the electrons to be removed |
|
|
|
Electron Negativity |

Used to compare atom behavior with other ones , Higher as you go up and right |
|
|
|
Octet Rule |
When a bond is formed atoms will give away , take in , or share their valence electrons to get as close to 8 in their valence shell as possible |
|
|
|
Lewis structure |

|
Beep boop boop |
|
|
Ionic / Covalent Bonds |

Ionic = One gives to the other leaving two OPPOSITELY charged atoms Covalent = 2 atoms of the same one share their with the other atom |
|
|
|
Intramolecular Forces |
Dipole -Dipole = --> < -- Attracted (POLAR POLAR molecules Dipole Induced = (Polar- NON Polar ) Momentarily active attraction. ---> ---> Dispersion = ( Non Polar ) < --- --- > |
|
|
|
Hydrogen Bonds |
Bridges , easily breakable , nitrogen , sulfur , oxygen , flouride . |
|

