![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
63 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
The molecular ion is both a free radical and an ion. |
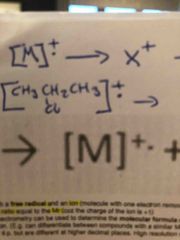
Breaking C-C bonds in alkanes
|
|
|
Thermal cracking produces a high percentage of ...? |
Alkenes |
|
|
Conditions of thermal cracking? |
• high temp • high pressure |
|
|
Catalytic cracking produces mainly ...? |
• cyclic alkanes • aromatic hydrocarbons (Used as motor fuels) |
|
|
Conditions of catalytic cracking? |
• slight pressure • high temp • zeolite catalyst |
|
|
Cracking general equation: |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Write two equations to show incomplete combustion of an alkane? |
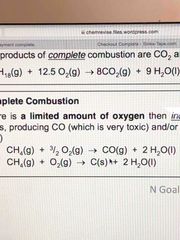
Back (Definition) |
|
|
Equation to show how sulfur dioxide is removed from glue gases? |
SO2 + CaO -> CaSO3 (Can also use CaCO3) • calcium sulfite is used to make calcium sulfate for plasterboard |
|
|
Halogenoalkanes contain a polar bond |
• |
|
|
The carbon-halogen bond enthalpy decides reactivity. Fluoroalkanes undergo nucleophilic substitution more slowly than iodoalkanes. |
• |
|
|
NO and NO2 effects: |
NO • toxic • can form NO2 NO2 • toxic • acidic • form acid rain |
|
|
The two reactions in catalytic converters: |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Ozone is formed naturally in the upper atmosphere |
• |
|
|
Why is ozone beneficial? |
Absorbs UV |
|
|
Equation to show the formation of ozone naturally (in the upper atmosphere) ? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
How are chlorine free radicals formed in the upper atmosphere? |
UV radiation causes C-Cl bonds in chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) to break |
|
|
What is a chlorofluorocarbon? |

A halogenoalkane molecule where all of the hydrogen atoms have been replaced by chlorine and fluorine atoms |
|
|
The formation of major and minor products in addition reactions of unsymmetrical alkenes. |
• |
|
|
How to IUPAC name an addition polymer? |
• write the name of the alkene monomer e.g. chloroethene • put brackets around it e.g. (chloroethene) • put poly in front E.g. poly(chloroethene) |
|
|
Draw the repeating unit of an addition polymer? |

(Make sure to include trailing bonds) |
|
|
For addition polymers, repeating units are always two carbons long |
• |
|
|
Addition polymers are unreactive. |
• |
|
|
Plasticised PVC is much more flexible than rigid PVC |
• |
|
|
What allows yeast to produce ethanol? |
They have an enzyme (Consider optimum rate and denaturation) |
|
|
The industrial production of ethanol by fermentation of glucose uses renewable resources |
• |
|
|
Conditions for the hydration of ethene? |
• steam (gaseous water) • 330°C • pressure (70 atm) • solid phosphoric (V) acid catalyst |
|
|
Arguments for and against biofuels? |
For • renewable energy source -> sustainable • usually classed as carbon neutral Against • to be used as fuels -> engine modification • problems where countries grow biofuel instead of feeding people |
|
|
Addition polymers can be produced without using monomers derived from crude oil |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
The principle behind infrared spectroscopy |
Bonds in a molecule absorb infrared radiation at characteristic wavenumbers (characteristic frequencies) |
|
|
Infrared spectroscopy can be used to find out how pure a compound is. How? |
Impurities produce extra peaks in the fingerprint region. |
|
|
Global warming is caused by a very similar mechanism to infrared spectroscopy. How? |
• CO2, methane, water vapour (greenhouse gases) obviously all have bonds • these bonds absorb infrared radiation • they re-emit some infrared radiation back towards earth • more greenhouse gases in the atmosphere is amplifying this effect |
|
|
Write an equation for the reduction of propanal to propan-1-ol? |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Write an equation for the reaction of propanone with HCN? (Name the product) Write an equation for the reaction of ethanal with HCN? (Name the product) |

Back (Definition) |
|
|
Racemic mixture |
• a mixture of equal amounts of enantiomers |
|
|
Bond length c-c > c-c (In benzene) > c=c |
• |
|
|
Benzene ring -> planar |
• |
|
|
Condensation polymers are generally stronger and more rigid than addition polymers. Why? |

• condensation polymers are made up of chains containing polar bonds e.g. C-N and C-O. So as well as VDWs, they have permanent dipole-dipole forces and hydrogen bonds between polymer chains |
|
|
Uses of Nylon 6,6? |
• clothing • carpet • rope |
|
|
What is Kevlar used for? |
• Bulletproof vests • lightweight sports equipment |
|
|
What is Terylene used for? |
• Plastic bottles • clothing |
|

What are aromatic amines used for? |
• making dyes |
|
|
Amino acids can be separated and identified by thin-layer chromatography. |
• |
|
|
Describe 2 ways of locating amino acids on a chromatogram? |
Use locating agents, either: • spray with ninhydrin • ultraviolet light |
|
|
On a chromatogram, amino acids are identified by their ...? |
Rf values |
|
|
Enzymes have stereospecific active sites. |
• |
|
|
Chemists aim to design processes/pathways that: |
• do not require a solvent • use non-hazardous starting materials • have fewer steps • have a high percentage atom economy |
|
|
What can chromatography be used for? |
To separate and identify components in a mixture. |
|
|
Types of chromatography? |
• Thin-layer (TLC) • Column chromatography (CC) • Gas chromatography (GC) |
|
|
Explain simply what TLC involves? |
A plate is coated with a solid and a solvent moves up the plate |
|
|
Explain simply what Column chromatography involves? |
A column is packed with a solid and a solvent moves down the column |
|
|
Explain simply what gas chromatography involves? |
A column is packed with a solid (or solid coated by a liquid) and a gas is passed through the column under high pressure at high temperature |
|
|
Separation depends on the balance between solubility in the stationary phase and retention by the stationary phase |
• |
|
|
In the different types of chromatography, retention times and Rf values are used to identify different substances |
• |
|
|
A mass spectrometer can be used to analyse the components separated by gas chromatography. |
• |
|
|
Give the advantages and disadvantages of different methods of disposal of polymers? |
Landfill • pros: cheap and easy, useful when the plastic is difficult to separate from other waste/not in sufficient quantities to make separation financially worthwhile/too difficult technically to recycle • cons: requires lots of land, as the waste decomposes it can release methane a greenhouse gas, leaks can contaminate water supplies Incineration • pros: the heat released can generate electricity • cons: the process needs to be carefully controlled to reduce the release of toxic gases (polymers containing chlorine can produce HCl when burnt), produces CO2 (contributes to global warming) Recycle • pros: reduces amount of waste going into landfill, it saves raw materials (oil), the cost of recycling plastics is lower than making the plastics from scratch), produces less CO2 than burning the plastic • cons: technically difficult, more expensive than burning/landfill, you often can’t remake the plastic you started with, the plastic can be easily contaminated during the recycling process |
|
|
Describe the process of recycling polymers? |
1) the polymers are separated and sorted Then there are two types: • some plastics can be melted and remoulded • some plastics can be cracked into monomers -> can be used to make more plastics or other chemicals |
|
|
Amino acids are amphoteric. Have both acidic and basic properties. Basic amino group Acidic carboxyl group |
• |
|
|
Define - isoelectric point (of an amino acid)? |
The pH where the average overall charge on the amino acid is zero |
|
|
Equation for the hydration of ethene? |
CH2=CH2(g) + H2O(g) -> CH3CH2OH(l) |
|
|
In a condenser, water goes against the force of gravity. Why? |
• provides more efficient cooling • prevents back flow of water |
|
|
Equation to show how tollens reagent and equation to show how Fehling’s solution work. |
Look up |
|
|
What will you observe in the Fehling’s solution test? |
Blue Cu2+ solution -> red Cu2O ppt |
|
|
What happens if air is present in fermentation of glucose by yeast? |
Ethanol oxidised to ethanoic acid |

