![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
72 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are drugs? |
Drugs are chemicals of low molecular masses ( 100-500u). |
|
|
|
What are medicines? |
Drugs interact with macromolecular targets and produce a biological response. When the biological response is therapeutic and useful, these chemicals are called medicines. |
|
|
|
What is chemotherapy? |
Use of chemicals for therapeutic effect is called chemotherapy. |
|
|
|
What are various classifications of drugs? |
- on the basis of pharmacological effect - on the basis of drug action -on the basis of chemical structure - on the basis of molecular targets |
|
|
|
What are enzymes? What are receptors? |
Proteins which perform the role of biological catalysts in the body are called enzymes. Those which are crucial to communication system in the body are called receptors. |
|
|
|
Explain the term target molecules or drug targets as used in medicinal chemistry. |
Drugs with macromolecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, lipids and nuclear acids. Hence these are called drug targets.drugs possessing some common structural features may have the same mechanism of action on targets. |
|
|
|
What are the two major functions performed by enzymes during the catalytic activity? |
-The first function of an enzyme is to hold the substrate for a chemical reaction - The second function of an enzyme is to provide functional groups that will attack the substrate and carry out chemical reaction. |
|
|
|
How do substrates bind to the active site of the enzyme? |
Substrate bind to the active site of the enzyme through a variety of interactions such as ionic bonding hydrogen bonding van der Waals interactions or dipole dipole interaction. |
|
|
|
What are enzyme inhibitors? |
Drugs can block the binding site of the enzyme and prevent the binding of substrate, or can inhibit the catalytic activity of the enzyme. Such drugs are called enzyme inhibitors. |
|
|
|
What are allosteric site? |

Some drugs do not bind to the enzymes active site this bind to a different site of enzyme which is called allosteric site. |
|
|
|
How do allosteric site inhibit the attachment of substrate on active site of enzymes? |
The binding of inhibitor at allosteric site changes the shape of the active site in such a way that substrate cannot recognise it. If the bond formd between an enzyme and an inhibitor is a strong covalent bond and cannot be broken easily, then the enzyme is blocked permanently. The body that degrades enzyme inhibitor complex and synthesizes the new enzyme. |
|
|
|
What are chemical messengers? |
They are chemicals which communicate the messages between two neurons and that between neurons and muscles. |
|
|
|
What are receptors? |
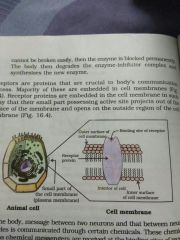
Receptors are proteins that are crucial to body's communication process. They are embedded in the cell membrane in such a way that their small part possessing active site projects out of the surface of the membrane and opens on the outside region of the cell membrane |
|
|
|
How do chemical messengers gives message to the cell? |
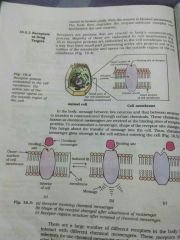
Chemical messengers are received at the binding sites of receptor proteins . To accommodate a messenger, shape of the receptor site changes. This brings about the transfer of message into the cell. Thus chemical messenger gives message to the cell without entering the cell. |
|
|
|
What are antagonists? |
Drugs that bind to the receptor site and inhibit its natural function are called antaginists. |
|
|
|
What are agonists? |
Drugs that mimic the natural messenger by switching on the receptor are called agonists. They are useful when there is lack of natural chemical messengers. |
|
|
|
What is histamine? |
Histamine is a chemical which stimulates the secretion of pepsin and hydrochloric acid in the stomach. |
|
|
|
Name the drug used to prevent the interaction of histamine with the receptors in the stomach wall. |
Cimetidine (tegamet) |
|
|
|
Another drug used as antacid? |
Rantidine (zantac) |
|
|
|
What are the various functions of histamines? |
Histamine is a potent vasodilator. It contracts the smooth muscles in the bronchi and gut and relaxes other muscles, such as those in the walls of the fine blood vessels. It is also responsible for the nasal congestion associated with common cold and allergic response to pollen. |
|
|
|
Name some antihistamines |
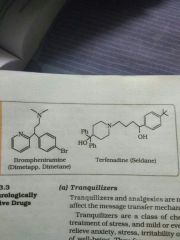
Brimpheniramine(dimetapp) and terfenadine (seldane) |
|
|
|
Why do above mentioned antihistamines not affect the secretion of acid in the stomach? |
Becoz antiallergic and antacid drugs work on different receptors. |
|
|
|
What are tranquilizers? |
They are neurologically active drugs they are used for the treatment of stress and mild or even severe mental diseases. These relieve anxiety, stress, irritability or excitement by inducing a sense of well being |
|
|
|
What is noradrenaline? |
This is one of the neurotransmitters that plays a role in mood changes. If the level of adrenaline is low then the signal sending activity becomes low and the person suffers from depression. |
|
|
|
Name some antidepressant drugs. |
Iproniazid and phenelzine. |
|
|
|
Name some tranquilizers. |
Chlordiazepoxide and meprobamate. |
|
|
|
Name a drug used in controlling depression and hypertension. |
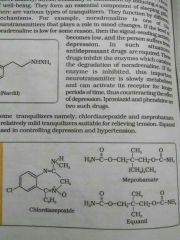
Equanil. |
|
|
|
Name some barbiturates which constitute an important class of tranquilizers. |
Veronal, amytal, Nembutal, luminal, and seconal. Barbiturates are hypnotic i.e. sleep producing agents. Some other substances used as tranquilizers are valium and serotonin. |
|
|
|
What are analgesics? |
Analgesics reduce or abolish pain without causing impairment of consciousness, mental confusio, incoordination or pyrolysis or some other disturbances of nervous system. |
|
|
|
What are the two types of analgesics? |
Narcotic and non narcotic analgesics which differ in the terms of addictiveness. |
|
|
|
What are some examples of non narcotic drugs? |
Aspirin and Paracetamol belong to the class non narcotic analgesics (non addictive). Aspirin inhibits the synthesis of chemicals known as prostaglandins which stimulate inflammation in the tissue and cause pain. These drugs are effective in relieving skeletal pain such as that due to arthritis. They also have many other effects such as reducing fever (antipyretic effect) and preventing platlate coagulation. Because of its anti blood clotting action aspirin find use in prevention of heart attacks. |
|
|
|
Give some examples and uses of narcotic analgesics. |
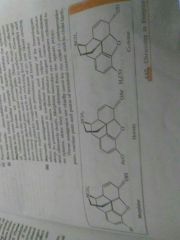
Morphine and many of its homologues when administered in medicinal doses, relieve pain and produce sleep. In poisonous doses, is produce stupor, convulsions and ultimately death. Morphine narcotics are sometimes referred to as opiates since they are obtained from the opium poppy. These are chiefly used for the relief of postoperative pain, cardiac pain and pains of terminal cancer, and in childbirth. |
|
|
|
What is the definition of an antibiotic? |
Antibiotic now refers to a substance produced wholly or partly by Chemical synthesis which in low concentrations inhibits the growth or destroy micro organisms by intervening in the metabolic processes. |
|
|
|
Which scientist conceived the idea of searching for chemicals that word adversely affect invading bacteria but not the host? |
Paul Ehrlich, a German bacteriologist, was the genius who conceived this idea. |
|
|
|
What is arsphenamine? |
Asrphenamine is a medicine which was used in the treatment of syphilis. Paul Ehrlich discovered this while investigating arsenic based structures to produce less toxic substances for treatment is syphilis. This medicine was known as salvarsan. He got a Nobel Prize for medicine for this discovery. It was the first effective treatment which while being toxic to human beings was still useful as its effect on the bacteria spirochete was greater. |
|
|
|
What is prontosil used for? |
Ehrlich was working on azodyes also and noticed a similarity in structures of salvarsan and azodyes. The -As=As- linkage in the former was similar to the -N=N- linkage in the latter. He also noticed tissues getting coloured by dyes selectively. Before he began to search for compounds which resemble in structure to azodyes and selectively bind to bacteria and succeeded in preparing the first effective antibacterial agent prontosil which resembles in structure to the compound which he developed earlier. Soon it was discovered the in the body prontosil is converted to a compound called sulphanilamide which is the real active compound. The sulpha drugs were discovered. Large range of sulphonamide analogues was synthesized. |
|
|
|
Which is the most effective sulpha drug? |
One of the most effective is sulphapyridine. |
|
|
|
Which was the real revolution in antibacterial therapy? |
The real revolution in antibacterial therapy begin with the discovery of Alexander Fleming, of the antibacterial properties of a Penicillium fungus. Isolation and purification of active compound to accumulates sufficient material for clinical trials took 13 years. |
|
|
|
What are the two types of effects that antibiotics can have? Give a few examples of each. |
There are two effects on microbes, cidal (killing) and static (inhibitory). Penicillin,aminoglycoside, ofloxacin are some bactericidal examples and Erythromycin, tetracycline, chloramphenicol are bacteriostatic examples. |
|
|
|
What are broad spectrum and narrow spectrum antibiotics? |
Those antibiotics which kill or inhibit a wide range of Gram Positive and Gram Negative bacteria are said to be broad spectrum while those effective mainly against gram positive and Gram Negative bacteria are narrow spectrum antibiotics. |
|
|
|
What are limited spectrum antibiotics? |
They are effective against a single organism or disease. |
|
|
|
Name some examples of broad spectrum and narrow spectrum antibiotics. |
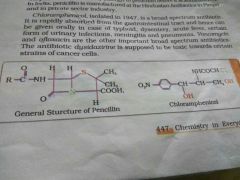
Penicillin G has a narrow spectrum. Ampicillin and amoxicillin are synthetic modifications of penicillins and these have broad spectrum. It is absolutely essential to test the patience for sensitivity or allergy to penicillin before it is administered. Chloramphenicol, vancomycin and ofloxacin are broad spectrum antibiotics. |
|
|
|
Where is Penicillin manufactured in India? |
Penicillin is manufactured at the Hindustan Antibiotics in Pimpri and in private sector industry. |
|
|
|
Which diseases is chloramphenicol used to treat? |
Chloramphenicol is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and hence can be given orally in case of typhoid, dysentery, acute fever, certain form of urinary infections, meningitis and pneumonia. |
|
|
|
What is the antibiotic dysidazirine used for? |
It is supposed to be toxic towards certain strains of cancer cells. |
|
|
|
What are some examples of antiseptics? |
Some examples of antiseptics are furacine, soframycine and so on. Dettol is also a commonly used antiseptic which is a mixture of chloroxylenol and terpineol. Biothionol/Bithional is added to soaps to import antiseptic properties. Iodine is a powerful antiseptic. Its 2 to 3% solution in alcohol water mixture is known as tincture of Iodine. Idoform is also used as an antiseptic for wounds. Boric acid in dilute aqueous solution is weak antiseptic for eyes. |
|
|
|
What are some examples of disinfectants? |
Chlorine in the concentration of 0.2 to 0.4 ppm in aqueous solution and Sulphur dioxide in very low concentrations are disinfectants. 1% phenol is disinfectant. |
|
|
|
Which is one substance which can act as an antiseptic as well as a disinfectant? |
Phenol. Phenol 0.2% solution is an antiseptic while its 1% solution is disinfectant. |
|
|
|
What do birth control pills essentially consist of? |
Birth control pills essentially contains a mixture of synthetic estrogen and progesterone derivatives. Both of these compounds are hormones and it is known that progestrone suppresses ovulation. It is known that progestrone derivatives are more potent than progestrone. Norethindrone is an example of synthetic progesterone derivative most widely used as antifertility drug. The estrogen derivative which is used in combination with progestrone derivative is ethynylestradiol (novestrol). |
|
|
|
Which is the first popular artificial sweetening agent? |
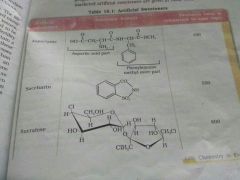
Ortho sulphobenzimide, also called saccharin, is the first popular artificial sweetening agent. It is 550 times sweeter than cane sugar. It appears to be completely inert and harmless when taken and is excreted from the urine unchanged. Its use is of great value to diabetic people and people to need to control intake of calories. |

|
|
|
Which is the most successful and widely used artificial sweetener? |
Aspertame is the most successful and widely used artificial sweetener. What is roughly hundred times as sweet as cane sugar. It is methyl ester of the peptide fromed from aspartic acid and phenylalanine. Use of this is limited to cold foods and soft drinks because it is unstable at cooking temperature. |
|
|
|
Which is a high potency sweetener? |
Allitame is high potency sweetener, although it is more stable than aspertame, the control of sweetness of food is difficult while using it. |
|
|
|
What is sucralose? |
Sucralose is the trichloro derivative of sucrose. Its appearance and taste are like sugar. It is stable at cooking temperature and it does not provide calories. |
|
|
|
Which are some commonly used food preservatives? |
Common preservatives include table salt, sugar, vegetable oils and sodium benzoate, C6H5COONa. Sodium benzoate is used in limited quantities and is metabolized in the body. Salts of sorbic acid and propanoic acid are also used as preservatives. |
|
|
|
What is saponification? |
Soaps containing sodium salt are formed by heating fat i.e, glyceryl ester of fatty acid with aqueous sodium hydroxide solution. This reaction is known as saponification. (Soaps used for cleaning purposes are sodium or potassium salts of long chain fatty acids , e.g, stearic, oleic and palmitic acids). In this reaction esters of fatty acids are hydrolysed and soap obtained remains in colloidal form. It is precipitated from the solution by adding sodium chloride The solution left after removing the soap contains glycerol which can be recovered by fractional distillation. Only Sodium and potassium soaps are soluble in water and are used for cleaning purposes. |
|
|
|
Which soap is softer to the skin? |
Potassium soaps are softer to the skin. |
|
|
|
What are toilet soaps? |
They are prepared by using better grades of fats and oils and care is taken to remove excess alkali. Colour and perfumes are added to make these more attractive. |
|
|
|
How do they make soaps that float in water? |
These soaps are made by beating tiny air bubbles before their hardening. |
|
|
|
How are transparent soaps made? |
They are made by dissolving the soap in ethanol and then evaporating the excess solvent. |
|
|
|
How are medicated soaps made? |
Substances of medicinal value are added and in some soaps, deodorants are added. |
|
|
|
What are some special materials added in shaving soaps? |
Shaving soaps have glycerol to prevent rapid drying. A gum called rosin is added while making them. It forms sodium rosinate which lathers well. |
|
|
|
What do laundry soaps contain? |
They contain fillers like sodium rosinate, sodium silicate, borax and sodium carbonate. |
|
|
|
How are soap chips made? |
They are made by running a thin sheet of melted soap onto a cool cylinder and scraping off the soaps in small broken pieces. |
|
|
|
What are soap granules? |
They are dried miniature soap bubbles. |
|
|
|
What are some special additions to soap powders and scouring soaps? |
Soap powders and scouring soaps contain some soap, a scouring agent (abrasive) such as powdered pumice or finely divided sand, and builders like sodium carbonate and trisodium phosphate. Builders make the soaps act more rapidly. |
|
|
|
Why don't soaps work in hard water? |

They don't work because hard water contains calcium and magnesium ions. These ions form insoluble calcium and magnesium soaps in hard water which separate as scum and are useless as cleansing agent. In fact they are a hindrance to good washing because the precipitate adhered onto the fibre of the cloth as gummy mass. Hair washed with hard water looks dull because of sticky precipitate. Dye does not absorb evenly on cloth washed with soap using hard water, because of this gummy mass. |
|
|
|
What is an advantage of synthetic detergent over soap? |
Detergents can be used in hard and soft water both as they give foam even in hard water. Some detergents even give foam in ice cold water. |
|
|
|
What are three categories of detergents? |
Anionic detergents, cationic detergents 🐈, non-ionic detergents. |
|
|
|
What do anionic detergents consist of? |

They are sodium salts of sulphonated long chain alcohols or hydrocarbons. Alkylhydrogensulphates formed by treating long chain alcohols with concentrated sulphuric acid are neutralized with alkali to form anionic detergents. Similarly alkyl benzene sulphonates are obtained by neutralizing alkyl benzene sulphonic acids with alkali. Note: sodium salts of alkylbenzenesulphonates are an important class of anionic detergents. They are mostly used for household work. Anionic detergents are also used in toothpastes.
|
|
|
|
What are cationic detergents? |

They are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorines or bromides as anions. Cationic part possess a long hydrocarbon chain and a positive charge on nitrogen atom. Cetyltrimethylammonium bromide is a popular cationic detergent and is used in hair conditioners. They have germicidal properties and are expensive and hence of limited use. |
|
|
|
What are non ionic detergents? |

They are formed when there is no ion in their constitution. One such detergent is formed when stearic acid reacts with polyethyleneglycol. Liquid dishwashing detergents are non-ionic type. Mechanism of cleansing is same as soaps and they also remove grease and oil by micelle formation. |
|
|
|
What environmental problems are faced when using non ionic detergents? |
Main problem is that if hydrocarbon chain is highly branched, then bacteria cannot degrade them easily. Slow degradation leads to their accumulation. Effluents containing such detergents reach rivers, ponds, etc. These persist in water even after sewage treatment and cause foaming in rivers, ponds, and streams and their water gets polluted. These days branching is kept to a minimum. |
|

