![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
44 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What do the y and x intercepts on a lineweaver-burke plot represent? |
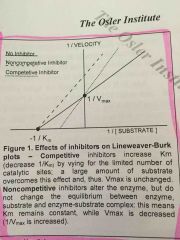
Y = 1/velocity X = -1/substrate |
|
|
How does a lineweaver-burke plot change with a noncompetitive enzyme? |
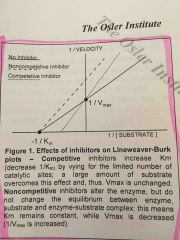
The y intercept is changed, and the x intercept is unchanged |
|
|
How does a lineweaver-burke plot change with a competitive enzyme? |
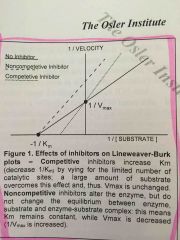
The Y intercept is unchanged, while the slope, which equals Km is decreased |
|
|
What is an IU?
|
1 IU = the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 1 micromole of substrate per minute
|
|
|
What is a Katal?
|
1 katal = the amount of enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of 1 mole of substrate per second
|
|
|
How many katals in an IU
|
1 IU = 16.7 nanokatals
|
|
|
Where are AST and ALT located in the cell?
|
AST mostly mitochondrial, ALT is cytoplasmic
|
|
|
How does renal failure affect AST and ALT?
|
It lowers the values
|
|
|
Where are LD1 and LD2 traditionally found?
|
Red cells, heart, kidney (fast moving isoenzymes)
|
|
|
Where is LD4 and LD5 found?
|
Liver and skeletal muscle
|
|
|
Where is LD3 found?
|
lung, spleen, lymphocytes, and pancreas
|
|
|
What are the comparative concentrations of LD isoenzymes in normal serum?
|
LD2>LD1>LD3>LD4>LD5
|
|
|
What three possibilites exist with an LD1>LD2?
|
Acute MI, hemolysis, and renal infarction
|
|
|
Elevated LD1 and LD5 points to what?
|
AMI with liver congestion or chronic alcoholism that has been complicated by liver damage and megaloblastic anemia
|
|
|
Where is alk phos produced?
|
Bone, bile ducts, intestine, placenta
|
|
|
How many isoenzymes of ALK phos are there?
|
4
|
|
|
How does heat inactivate the different alk phos isoenzymes?
|
Bone burns (90%) inactivation, liver lingers, intestine intermediate, placenta persists (0% inactivation of placental alk phos)
|
|
|
What is the most sensitive marker of hepatic masses?
|
Biliary alk phos
|
|
|
What cell in the bone produces alk phos?
|
Osteoblasts
|
|
|
What conditions display elevated 5' nucleotidase?
|
Cholestatic conditions
|
|
|
What are the characteristics of physiologic jaundice?
|
Noted from 2-3 days of neonatal life and rarely rises at a rate greater than 5mg/dl/day, usually peaks by day 4-5
|
|
|
AST > 3000 suggests what etiology?
|
Toxin in 90% of cases
|
|
|
How many serum amylases are there?
|
6, 3 salivary and 3 pancreatic
|
|
|
Where is CK-BB found and what is the migration pattern?
|
It is found primarily in the brain, most widely distributed, and is the fastest migrating on electrophoresis (CK1)
|
|
|
Where is CK-MM found and what is the migration pattern?
|
CM-MM (CK3) is found in skeletal and cardiac muscle. MM is the slowest migrating faction
|
|
|
Where is CK-MB found and what is the migration pattern?
|
CK-MB (CK2) is found in cardiac and skeletal muscle (30% in cardiac muscle). MB migrates between MM and BB on eletrophoresis.
|
|
|
What is Macro-CK?
|
it is a CK-Ig complex that migrates between MM and MB
|
|
|
What is mitochondrial CK?
|
It migrates close to MM. It is seen in patients with advanced, often disseminated malignancies and is assocatiated with a poor prognosis
|
|
|
Where is BNP stored?
|
Ventricular myocytes
|
|
|
what does the Km represent? |
net equilibrium coefficent. Represents the net likelihood of an enzyme substrate complex dissociating over the likelihood of the enzyme associating with its substrate. Also the probability that the enzyme catalyzed reaction will proceed. If Km is large - the likelihood that an enzyme substrate complex will dissociate is much greater than the likelihood that it will form in the first place and the reaction is not likely to occur. |
|
|
what is Vmax? |
maximum velocity for a particular enzyme concentration. If the amount of enzyme is increased, then the reaction will have a new, higher Vmax. |
|
|
what is the michaelis-mentin equation? |
V=Vmax * [S/(Km+S)] |
|
|
what is a zero order reaction? |
unrelated to the amount of substrate present. |
|
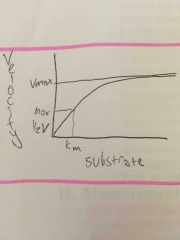
what is happening when the velocity of a reaction is equal to 1/2 the Vmax? |
The substrate concentration is equal to Km. Thus, the maximum concentration can be used to determine Km. |
|
|
how are the lineweaver-burk plots related to the michaelis-mentin equation? |
The lineweaver-burk plots are simply the inverse of the michaelis mentin equation |
|
|
Are most enzymes measured by activity or immunoassay? |
Most enzyme assays measure enzyme activity. Immunoassays for some enzymes are available (CK MB, pancreatic amylase and trypsin, PAP and PSA) |
|
|
how do you measure enzyme activity? |
kinetic assay. Measure rate of appearance of product or disappearance of substrate per unit time. Must perform at Vmax since the reaction is zero order (doesn't depend on amount of substrate present) and it is directly related to the amount of enzyme present. the change in absorbance per unit time time is measured and is then proprotional to the change in concentration. |
|
|
Describe the graph for determining enzyme activity |
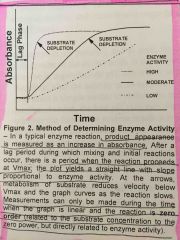
|
|
|
What # does NADH absorb at? Does NAD+ absorb at this? |
NADH often is used as an indicator in enzyme reactions. It absorbs at 340nm. NAD+ does not - which is why this can be used as an indicator |
|
|
An increase in temperature of _________ will approximately double the rate of reaction |
10 degrees!!! (know this!!) |
|
|
do kids or adults have a higher alk phos? |
kids |
|
|
where is acid phos found? which is tartrate resistant? which is tartrate inhibited? |
found in prostate (tartrate inhibited), bone/osteoclasts (tartrate resistant), RE system. |
|
|
how can acid phosphatase be used in prostate cancer? |
less sensitive than PSA but not affected by hormone treatment. with metabolic bone disease, bone isoenzyme reflects osteoclastic activity |
|
|
Where is ACE found and what can it be used for? |
found in macrophages, all endothelial cells, especially lung. can be used to follow sarcoidosis, related to number and activity of granulomas. Diabetes, autoimmune disease, AIDS. directly related to thyroid hormone levels. |

