![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
57 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
matter |
anything that has mass and takes up shape |
|
|
chemistry |
the study of matter and the changes it undergoes |
|
|
five branches of chemistry |
organic chemistry inorganic chemistry biochemistry analytical chemistry physical chemistry |
|
|
pure chemistry |
pursuit of chemical knowledge just for the sake of knowledge |
|
|
applied chemistry |
research dedicated towards a specific goal/application |
|
|
scientific method |
a logical, systematic approach to a scientific problem |
|
|
steps to scientific method |
make an observation form a hypothesis test hypothesis with an experiment |
|
|
theory |
well tested explanation of a set of observations (can change) |
|
|
scientific law |
concise statement that summarizes the results of many observations and experiments. it just describes relationships, doesnt explain |
|
|
measurement |
a quantity that has both a number and a unit |
|
|
1 cm cubed |
1 mL |
|
|
1 m cubed |
1000 L |
|
|
Kelvin conversion |
C+273 |
|
|
mole |
mol- amount of a substance |
|
|
candela |
cd- luminous intensity |
|
|
amperes |
A- electrical current |
|
|
mass |
amount of particles in a substance |
|
|
volume |
the amount of space it takes up |
|
|
physical properties |
characteristic of a substance that can change without the substance becoming a different substane |
|
|
qualitative properties |
describe using adjectives things you can observe |
|
|
quantitative properties |
things that involve numbers extensive or intensive |
|
|
solid |
fixed shape, fixed volume, closely packed particles, not easily compressed |
|
|
liquid |
indefinite shape, fixed volume, close particles (loosely packed), not easily compressed |
|
|
gas |
indefinite shape, indefinite volume, easily compressed, spread apart particles |
|
|
extensive properties |
depend on the amount of substance present mass, volume, enthalpy, entropy, energy |
|
|
intensive |
independent of the amount of substance present density temperature boiling point pressure ductility |
|
|
physical changes |
change in one or more physical properties, but no change in the fundamental components that make up the substance |
|
|
phase changes |
state of matter changes melting, condensation, vaporization, deposition, sublimation, freezing |
|
|
melting |
solid to liquid |
|
|
freezing |
liquid to solid |
|
|
vaporization |
liquid to gas |
|
|
condensation |
gas to liquid |
|
|
sublimation |
solid to gas |
|
|
desposition |
gas to solid |
|
|
phase diagram |
graph of pressure vs temperature that shows which phase a substance exists under different conditions of temperature and pressure |
|
|
triple point |
on a phase diagram where the matter is a solid, liquid, and gas at the same time equilibrium is reached |
|
|
heating curve |
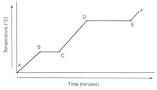
|
|
|
cooling curve |

|
|
|
matter can be... |
...substances or mixtures |
|
|
substances |
matter that has a uniform and unchanging composition elements and compounds |
|
|
elements |
the smallest form of a substance that has the properties of a substance can be combined with other elements cannot be stably be broken down represented with chemical symbols from the periodic table |
|
|
compounds |
substance that contains two or more elements chemically combined in a fixed proportion always have the same composition always contain at least two different elements can only be broken down through chemical means represented with chemical formulas |
|
|
mixtures |
material of variable composition that contains two or more substances can be separated into pure substance of either elements and or compounds |
|
|
homogeneous mixtures |
same throughout, also called solutions |
|
|
heterogeneous mixtures |
contain regions of different properties |
|
|
distilation |
method for separating the components of a liquid mixture by evaporation, that utilizes different boiling points |
|
|
filtration |
method for separating components of a mixture containing a solid and liquid using a filter |
|
|
crystallization |
results in a solid forming out of a super saturated solution |
|
|
chromatography |
separates the components of a mixture, the mobile phase, on the basis of tendency of each to travel or be drawn across the surface of another material, stationary phase has to do with color |
|
|
periodic table |
elements arranged based on physical and chemical properties groups are vertical columns (16) |
|
|
chemical properties |
characteristics of a substance that can change into a different substance acidity, enthalpy, flammability, reactivity, electronegativity, oxidation state |
|
|
chemical changes |
change in fundamental components of the substance, a given substance changes into a different substance or substances also called chemical reactions composition always changes |
|
|
reactants |
initial substance before the reaction |
|
|
product |
the substance produced during the reaction |
|
|
indicators of a chemical reaction |
change of color bubbles/ formation of gas formation of a solid transfer of energy |
|
|
law of conservation of mass |
mass is neither created nor destroyed |
|
|
solving conservation of mass problems |
step 1: identify products and reactants step 2: write a reaction step 3: substitute given values step 4: solve for unknowns |

