![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
27 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is aldolase?
|
-Glycolytic enzyme
-Found in muscle and other tissues -No more specific for muscle than CK |
|
|
Where is ACE found?
|
Normally found in PULMONARY endothelium
|
|
|
What does ACE do?
|
Converts angiotensin 1 to angiotensin 2.
|
|
|
When can ACE be elevated?
|
-Granumatous conditions
*Sarcoid (not specific or diagnostic, may be used to monitor activity) -Elevated in DM, AIDS, hyperthyroidism |
|
|
What are the major sources of acid phosphatase?
|
-RBC
-Prostate -Osteoclasts |
|
|
When is acid phos elevated?
|
- increased hemolysis
- when prostatic adenoCA extends beyond the capsule of the prostate -increased osteoclast activity (useful for Gaucher's disease) |
|
|
How can you separate out alk phos?
|
-Prostate: inhibited
-Osteoclasts: resistant (TRAP) |
|
|
What are the two isofroms of CK-MB and where are they located, How are they used?
|

|
|
|
In what situations can cTnT or cTnI be elevated?
|
-Renal failre/renal dialysis in the absence of AMI
-cTnT - elevated in ~15% of pts -cTnI - elevated in ~5% of pts *to diagnose AMI in patients with renal failure: LOOK FOR RISE AND FALL |
|
|
What is BNP and what does it do?
|
-Natriuetic
-Diuretic -Vasodilation |
|
|
What is CNP?
|
-Endothelial and macrophage origin
-No increase in heart failure |
|
|
What is urodilatin?
|
-Renal DCT cells
-Same gene as ANP; differential processing |
|
|
Where is CK1 (CKBB) found?
|
-Brain
-Prostate -Placenta -Fetal tissue |
|
|
Where is CKMB (CK2) found?
|
-Striated muscle
-In cardiac muscle, represents 5-20% of total CK |
|
|
What is Macro-CK2?
Why is it important? |
-It is a large mitochondiral isoenzyme present in many tissues
-Released only with very sever tissue damage and is a poor prognostic sign |
|
|
What is Macro-CK-1?
|
-In 1-2% of the population over the age of 60 and in patients with AIDS or autoimmune disease, CK isozenzymes are bound to immunoglobulin
|
|
|
Describe the structure of BNP.
What tests are available? |
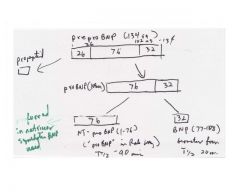
|
|
|
How is total cholesterol measured?
|

|
|
|
How do you calculate LDL?
|

|
|
|
Frederickson's classification of lipid disorders:
What are in I, IV, V? |
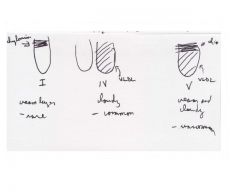
|
|
|
Frederickson lipid disorders:
What is in type IIa? |
LDL
-common |
|
|
Frederickson lipid disorders:
What is type IIB3 comprised of?` |
VLDL + LDL
-common |
|
|
Frederickson lipid disorders:
What is in type III? |
IDL
-rare |
|
|
What are the 3 types of apoE?
|
-E2: prevents receptor binding, elevated IDL (type III HLP)
-E3: normal receptor binding **E4: inhibits apoB100 binding to LDL-R (Increased risk of Alzheimer's) |
|
|
What can screw up Triglyceride measurements?
|
Ketoacidosis
|
|
|
How do you measure triglycerides?
|
-lipase: measure glycerol released
glycerol --glycerol kinase--> glycerol 3P glycerol-3-phostphate metabolized to NADH |
|
|
What lipoprotein modification increases atherogenicity and allow uptake of LDL via scavenger receptor?
|
-oxidation
-glycosylation -apo(a) addition -IDL -dense LDL |

