![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
55 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What are Hydrocarbons |
A group of compounds that only contain Hydrogen and Carbon atoms chemically joined together |
|
|
|
What is Crude oil? |
A fossil fuel Complex mixture Different kinds of hydrocarbon molecules |
|
|
|
What happens during fractional distillation |
Crude oil (containing different hydrocarbon molecules) is not very useful so by using fractional distillation you break down the crude oil into more useful fractions such as gas, petrol and heating oil. Simpler mixture than crude oil |
|
|
|
What is gas used for? |
Heating and cooking in homes |
|
|
|
What is petrol used for? |
Fuel in cars |
|
|
|
What is Kerosene used for? |
Fuel for aircraft |
|
|
|
What is diesel oil used for? |
Some cars and trains |
|
|
|
What is fuel oil used for? |
Large ships and some power stations |
|
|
|
What is bitumen used for? |
Surfacing roads and roofs |
|
|
|
The properties of gasses |
*Smallest no. Of atoms in molecules *Low boiling point *Easy to set alight *Runny, Low Viscosity |
|
|
|
Properties of Bitumen |
*Lots of atoms in each molecule *High boiling point *Difficult to set alight *Thick and Sticky (High Viscosity) |
|
|
|
Combustion of Methane |
*Metane+oxygen>Carbon Dioxide+Water *CH4 (g) + 202 (g) >CO2 (g) + 2H2O (L) *Oxidised, combustion is an example of an oxidation reaction |
|
|
|
What is complete combustion? |
Where there is plenty of Oxygen available and if all the hydrocarbon is oxidised (only products are carbon dioxide and water) |
|
|
|
What is produced during incomplete combustion |
If there is not enough Oxygen the hydrogen atoms will turn into water and the carbon atoms will either turn into: Carbon dioxide, Carbon monoxide or soot (solid carbon) |
|
|
|
What uses incomplete combustion? |
Vehicle engines Faulty gas boilers |
|
|
|
How is sulfur dioxide formed? |
*Hydrocarbon fuels contain impurities *Such as Sulfur *When the hydrocarbons burn *The sulfur oxidises to for Sulfur dioxide |
|
|
|
How is acid rain caused? |
*Waste gases from power stations and vehicles contain sulfur dioxide *Sulfur dioxide dissolves in to the water vapour *rain is more acidic than normal |
|
|
|
What are the effects of acid rain? |
*Rivers, lakes and soils are more acidic - this harms living organisms *Trees are damaged *Speeds up weathering of buildings and statues |
|
|
|
How have Europe and North America reducing the problem of acid rain? |
*Removing sulfur from petrol, diesel and fuel oil *Removing acidic gasses from power station emissions |
|
|
|
What is the affect of green house gasses on the atmosphere? |
The heat and sun rays from the sun cannot get back out into space because of the carbon dioxide, methane and water vapour. Without these gases the average temp o earth would be -18°c |
|
|
|
How has the amount of CO2 and Methane change in the past? |
In the 1800s the amount of CO2 has increased due to the burning of fossil fuels, methane has also increased due to the amount of farming. |

|
|
|
2 methods of trying to see how much CO2 there is in the atmosphere / Control the amount of CO2 |
*Seeding the oceans with iron compounds. This may encourage microscopic plants to grow. The plants would normally use carbon in photosynthesis. The carbon would eventually be incorporated into shells and end up in sediments *Capturing the CO2 from power stations and converting it into hydrocarbons to be used as fuels |
|
|
|
What are biofuels and what are they used for? |
*Obtained from living organisms *Can be used as a substitute for fossil fuels *Renewable resource *More plants can be grown to replace the others |
|
|
|
How is using a biofuel carbon neutral? And definition |
*Crops absorb CO2 for photosynthesis *Crops made into biofuel. *Biofuel used by vehicles *CO2 emitted in waste gas *And so on DOES NOT INCREASE THE TOTAL AMOUNT OF CO2 IN THE ATMOSPHERE WHEN IT BURNS |
|
|
|
What do biofuel include? |
*Plants grown to be burned (Wood) *Sugar cane which can be converted into ethanol (used instead of petrol) so reduces demand for petrol. |
|
|
|
Advantages of biofuels |
*Renewable *Add less CO2 to the atmosphere than fossil fuels |
|
|
|
Disadvantages of biofuels |
*Growing crops take up space which could be used to grow food. *Higher food prices and may lead to some people being short on food |
|
|
|
A good fuel should... |
B urn easily E nergy (produce alot) P roduce ash/smoke (should not) S tore and transport easily |
|
|
|
What fuels are non-renewabke and obtained from crude oil? |
Petrol, Kerosene and diesel oil |
|
|
|
What fuels are obtained from natural gas and are non-renewable? |
Methane |
|
|
|
What is hydrogen used for? |
A fuel in rockets. Burnt to release energy. Also be used in cars etc by using a fuel cell |
|
|
|
What are the variables when you are investigating fuels? |
*Time Taken to heat the water to 50°c *Amount of water *Amount of fuel before and after |
|
|
|
Advantages of petrol |
*Burns easily *No smoke or ash *releases more energy per kg when it burns than coal or wood *liquid so easy to store and transport |
|
|
|
Disadvantages of petrol |
Produces CO2 and Carbon Monoxide as well as water when burned |
|
|
|
Advantages of Hydrogen |
*Burns easily *No smoke or ash *only produces water when burned *releases nearly 3x as much energy per kg than petrol |
|
|
|
Disadvantages of Hydrogen |
*A gas so has to be stored at high pressure *Filling stations would have to be adapted for hydrogen to be used in cars |
|
|
|
What are alkanes and alkenes? |
2 groups of hydrocarbon molecules |
|
|
|
Differences between Alkanes and Alkene: |
*Alkanes are saturated, alkenes are unsaturated *Alkanes have single bonds, alkenes have double bonds |
|
|
|
What is it called when an alkane has 1, 2 & 3 Carbon atoms |
*Methane (CH4) *Ethane (C2H6) *Propane (C3H8) |
|
|
|
What is it called when an alkene had 1, 2 & 3 Carbon atoms |
*you can't have only 1 carbon atom with a double bond *Ethene (C2H4) *Propene (C3H6) |
|
|
|
What is bromide used for? |
Used to find if the liquid contains double bonds, if it becomes colourless it is mixed with unsaturated molecules |
|
|
|
What happens during cracking? |
The long molecules which aren't very useful get broken down by heating them. This then produces shorter chain alkanes which are used as fuels and a smaller alkene which are used to make polymers |
|
|
|
What does crude oil contain? |
A mixture of long and short alkane molecules, but the short ones are most useful because they are easier to burn and store. |
|
|
|
How do you crack paraffin in a laboratory ? |
*Porous pot, heated strongly *Liquid paraffin is heated and evaporates *The vapour passes over the hot porous pot and the hydrocarbon molecules break down *One of the products is ethene which collects in the tube as a gas. |
|
|
|
What apparatus do you need to crack paraffin in a laboratory? |
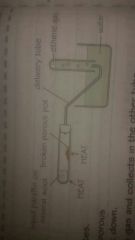
|
|
|
|
Which fractions of crude oil are most needed but there is not enough of? |
*Gases *Petrol *Diesel |
|
|
|
Which fractions of crude oil is there enough and more demand for? |
*Kerosene *Fuel oil and bitumen |
|
|
|
Lots of ethene molecules join up to form... |
One long molecule called poly(ethene). They only have single bonds between the carbon atoms |
|
|
|
What can ethane monomers do? |
Polymerise (react together) to form long chains of poly(ethene) |
|
|
|
What are the properties and uses of poly(ethene) |
*Flexible, cheap, good electrical insulator *Plastic bags, bottles and clingfilm |
|
|
|
What are the properties and uses of poly(propene)? |
*Flexible, shatterproof, high softening point *buckets and bowls |
|
|
|
What are the properties and uses of poly(chloroethene)? *PVC* |
*tough, cheap, long lasting, good electrical insulator *window frames, gutters and pipes, insulation for electrical wires |
|
|
|
What are the properties and uses of PTFE? |
*Tough, slippery, resistant to corrosion, good electrical insulator *Non-stick coating for frying pans and skis. Contains of corrosive substances, insulation for electrical wires |
|
|
|
Good types of ways to dispose of polymers |
Recycling: *Melting or breaking down polymers to make new objects Biodegradable polymers *being developed *they will rot away in landfill sites |
|
|
|
Bad types of ways to dispose of polymers |
Landfill sites: *Polymers ate not biodegradable *they last got many years *we are running out of landfill sites Burning: *polymers release toxic gases when they burn |
|

