![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Atom |
The fundamental building block of all materials; it consists of a cluster of protons and neutrons surrounded by a cloud of electrons |
|
|
Atomic Model |
Scientist representation of an atom determined by experiment and indirect observation |
|
|
Atomic Number |
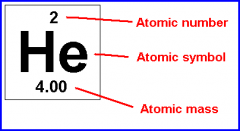
The number of protons in a nucleus |
|
|
Atomic Symbol |
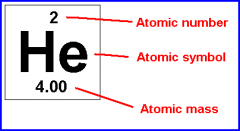
A short-hand notation describing and atom |
|
|
Compound |
A pure substance that is made up of two or more different types of atoms chemically joined |
|
|
Crystal Lattice |
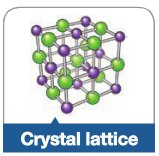
A gride-like structure of atoms or ions where each particle is bonded to all of its neighboring atoms |
|
|
Electron |
a small negatively charged particle; clouds of electrons surrounded the nucleus of an atom |
|
|
Electron Shell |
Part of the electron cloud; it is a layer that surrounds the nucleus and can only hold a certain number of electrons |
|
|
Element |
A substance made up of only one type of atom |
|
|
Isotopes |
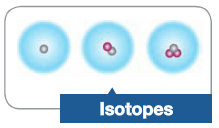
Atoms that have the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons in their nucleus |
|
|
Mass Number |
The number of protons and neutrons in an atom |
|
|
Molecule |
A cluster of atoms that makes up an element or a compound |
|
|
Neutral |
Having no overall charge |
|
|
Neutron |
A particle with no electric charge; it is found in the nucleus of an atom |
|
|
Nucleus |
A cluster of neutrons and protons at the center of an atom |
|
|
Proton |
A positivity charged particle in the nucleus |
|
|
Anion |
A negatively charged ion |
|
|
Cation |
A positively charged ion |
|
|
Ion |
an atom that has lost or gained electrons and therefore has an electric charge |
|
|
Ionic Bond |
A bond between a cation and an anion due to electrostatic attraction of their opposite charges |
|
|
Ionic Compound |
A compound made up of cations and anions |
|
|
Solubility |
How easily a substance dissolves |
|
|
Alpha Decay |
A nuclear reaction in which a nucleus ejects an alpha particle |
|
|
Alpha Particle |
A particle made up of two protons and two neutrons, making it identical to helium nucleus |
|
|
Beta Decay |
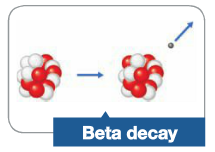
A form of nuclear reaction in which beta particle is ejected from the nucleus |
|
|
Beta Particle |
A small, negatively charged particle that can be ejected from a nucleus during a nuclear reaction; it is identical to an electron |
|
|
Beta Radiation |
Nuclear radiation that is made up of beta particles |
|
|
Carbon Dating |

A method for judging the age of fossils by analysing the amount of carbon - 14 in the fossil |
|
|
Cosmic Radiation |
Radiation that comes to Earth from distant stars |
|
|
Dose (Radiation) |
The amount of radiation absorbed over a period of time |
|
|
Electromagnetic Radiation |
Radiation that travels through a vacuum as waves rather than particles |
|
|
Fission |
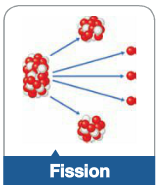
A nuclear reaction in which a very large nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei of similar mass number |

