![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
191 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
States of matter
|
Gas, liquid, and solid
|
|
|
|
Liquid
|
Has a distinct volume, and assumes the shape of its container
|
|
|
|
Solid
|
Has a definite shape and definite volume
|
|
|
|
Pure substance
|
Matter that has distinct properties and a composition that doesn't vary
|
Water and salt
|
|
|
Pure substance
|
Matter that has distinct properties and a composition that doesn't vary
|
Water and salt
|
|
|
Compounds
|
Two or more substances
|
|
|
|
Mixtures
|
Combinations of two or more substances and maintain its chemical identity
|
|
|
|
Mixtures
|
Combinations of two or more substances and maintain its chemical identity
|
|
|
|
Matter
|
A physical material of the universe occupies space
|
|
|
|
Mixtures
|
Combinations of two or more substances and maintain its chemical identity
|
|
|
|
Matter
|
A physical material of the universe occupies space
|
|
|
|
Property
|
Characteristics that allows us to recognize a particular type of matter and distinguish it from another
|
|
|
|
Mixtures
|
Combinations of two or more substances and maintain its chemical identity
|
|
|
|
Matter
|
A physical material of the universe occupies space
|
|
|
|
Property
|
Characteristics that allows us to recognize a particular type of matter and distinguish it from another
|
|
|
|
Atoms
|
Small building blocks of matter
|
|
|
|
Mixtures
|
Combinations of two or more substances and maintain its chemical identity
|
|
|
|
Matter
|
A physical material of the universe occupies space
|
|
|
|
Property
|
Characteristics that allows us to recognize a particular type of matter and distinguish it from another
|
|
|
|
Atoms
|
Small building blocks of matter
|
|
|
|
Molecules
|
Two or more atoms joined together in specific shapes
|
|
|
|
Law of constant composition
|
The chemical composition of a compound is always the same
|
|
|
|
Components
|
Substance making up mixtures
|
Coffee containing suger
|
|
|
Components
|
Substance making up mixtures
|
Coffee containing suger
|
|
|
Heterogeneous
|
Mixtures that don't have the same composition, properties, and appearance throughout
|
Rocks and wood
|
|
|
Components
|
Substance making up mixtures
|
Coffee containing suger
|
|
|
Heterogeneous
|
Mixtures that don't have the same composition, properties, and appearance throughout
|
Rocks and wood
|
|
|
Homogeneous
|
Mixtures that are uniform throughout
|
Also called solutions salt and water
|
|
|
Physical properties
|
Can be observed without changing the identity and composition of a substance
|
Color odor, density, melting point, boiling point, and hardness
|
|
|
Precision
|
How closely individual measurements agree with one another
|
|
|
|
Accuracy
|
How closely individual measurements agree with the correct or true value
|
|
|
|
Density
|
Amount of Mass in a unit volume of a substance
|
|
|
|
Dimensional analtsis
|
Units are multiplied together divided into each other or cancelled
|
|
|
|
Chemical properties
|
A substance that may change or react to form another substance
|
|
|
|
Intensive propertied
|
Don't depend on amount of substance and can identify substances
|
|
|
|
Extensive properties
|
Depend on amount of sample and relate to amount of substance present
|
Mass and volume
|
|
|
Physical change
|
Changes it's physical appearance but not it's composition
|
Water can be solid liquid or gas and still be just h2o
|
|
|
Chemical change or chemical reaction
|
Substance is transformed into a different chemically substance
|
|
|
|
Filtration
|
Where two can be seperated
|
|
|
|
Distillation
|
A process that depends on different abilities of a substance to form a gases
|
|
|
|
Metric system
|
Units used for scientific measurements
|
|
|
|
Mass
|
Amount if material in an object
|
|
|
|
Physical properties
|
Can be observed without changing the identity and composition of a substance
|
Color odor, density, melting point, boiling point, and hardness
|
|
|
Precision
|
How closely individual measurements agree with one another
|
|
|
|
Accuracy
|
How closely individual measurements agree with the correct or true value
|
|
|
|
Density
|
Amount of Mass in a unit volume of a substance
|
|
|
|
Dimensional analysis
|
Units are multiplied together divided into each other or cancelled
|
|
|
|
Conversion factor
|
Fraction who's denominator and numerator are the same quantity expressed in different units
|
|
|
|
Chemical properties
|
A substance that may change or react to form another substance
|
|
|
|
Intensive propertied
|
Don't depend on amount of substance and can identify substances
|
|
|
|
Extensive properties
|
Depend on amount of sample and relate to amount of substance present
|
Mass and volume
|
|
|
Physical change
|
Changes it's physical appearance but not it's composition
|
Water can be solid liquid or gas and still be just h2o
|
|
|
Chemical change or chemical reaction
|
Substance is transformed into a different chemically substance
|
|
|
|
Filtration
|
Where two can be seperated
|
|
|
|
Distillation
|
A process that depends on different abilities of a substance to form a gases
|
|
|
|
Metric system
|
Units used for scientific measurements
|
|
|
|
Mass
|
Amount if material in an object
|
|
|
|
Physical properties
|
Can be observed without changing the identity and composition of a substance
|
Color odor, density, melting point, boiling point, and hardness
|
|
|
Precision
|
How closely individual measurements agree with one another
|
|
|
|
Accuracy
|
How closely individual measurements agree with the correct or true value
|
|
|
|
Density
|
Amount of Mass in a unit volume of a substance
|
|
|
|
Dimensional analysis
|
Units are multiplied together divided into each other or cancelled
|
|
|
|
Conversion factor
|
Fraction who's denominator and numerator are the same quantity expressed in different units
|
|
|
|
Subatomic particles
|
What atoms are composed of
|
|
|
|
Chemical properties
|
A substance that may change or react to form another substance
|
|
|
|
Intensive propertied
|
Don't depend on amount of substance and can identify substances
|
|
|
|
Extensive properties
|
Depend on amount of sample and relate to amount of substance present
|
Mass and volume
|
|
|
Physical change
|
Changes it's physical appearance but not it's composition
|
Water can be solid liquid or gas and still be just h2o
|
|
|
Chemical change or chemical reaction
|
Substance is transformed into a different chemically substance
|
|
|
|
Filtration
|
Where two can be seperated
|
|
|
|
Distillation
|
A process that depends on different abilities of a substance to form a gases
|
|
|
|
Metric system
|
Units used for scientific measurements
|
|
|
|
Mass
|
Amount if material in an object
|
|
|
|
Fact1
|
Particles with same charges repel one another and particles with unlike particles attract one another |
Opposites attract
|
|
|
Fact1
|
Particles with same charges repel one another and particles with unlike particles attract one another |
Opposites attract
|
|
|
Law of constant composition
|
In a given compound the relative #s and kinds of atoms are constant
|
|
|
|
Fact1
|
Particles with same charges repel one another and particles with unlike particles attract one another |
Opposites attract
|
|
|
Law of constant composition
|
In a given compound the relative #s and kinds of atoms are constant
|
|
|
|
Law of conservation mass
|
The total mass of materials present as a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass present before the reaction
|
|
|
|
Fact1
|
Particles with same charges repel one another and particles with unlike particles attract one another |
Opposites attract
|
|
|
Law of constant composition
|
In a given compound the relative #s and kinds of atoms are constant
|
|
|
|
Law of conservation mass
|
The total mass of materials present as a chemical reaction is the same as the total mass present before the reaction
|
|
|
|
Law of multiple proportions
|
If two elements A and B combine to form more than 1 compound the masses of B that can combine with a given mass of A are in ratio of small whole #s
|
|
|
|
Fact 2
|
All atoms of an given element are identical, but the atoms of one element are diff. From the atoms of all other elements
|
|
|
|
Cathode rays
|
Radiation produced between electrodes
|
|
|
|
Cathode rays
|
Radiation produced between electrodes
|
|
|
|
Atomic mass
|
Used to express the weight of atoms
|
|
|
|
Cathode rays
|
Radiation produced between electrodes
|
|
|
|
Atomic mass
|
Used to express the weight of atoms
|
|
|
|
Angstrom
|
Convenient non SI unit of length used for atomic dimensions
|
|
|
|
Cathode rays
|
Radiation produced between electrodes
|
|
|
|
Atomic mass
|
Used to express the weight of atoms
|
|
|
|
Angstrom
|
Convenient non SI unit of length used for atomic dimensions
|
|
|
|
Atomic number
|
The # of protons in a atom
|
|
|
|
Cathode rays
|
Radiation produced between electrodes
|
|
|
|
Atomic mass
|
Used to express the weight of atoms
|
|
|
|
Angstrom
|
Convenient non SI unit of length used for atomic dimensions
|
|
|
|
Atomic number
|
The # of protons in a atom
|
|
|
|
Mass #
|
Protons plus the neutrons
|
12 mass#
6 atomic # |
|
|
Atomic weight
|
Average atomic mass of an element
|
|
|
|
Period
|
Horizontal rows on the periodic table
|
H and He is in period 1
|
|
|
Period
|
Horizontal rows on the periodic table
|
H and He is in period 1
|
|
|
Groups
|
The vertical columns on the periodic table
|
Be, Mg. Ca, Sr.... Are in group 2
|
|
|
Period
|
Horizontal rows on the periodic table
|
H and He is in period 1
|
|
|
Groups
|
The vertical columns on the periodic table
|
Be, Mg. Ca, Sr.... Are in group 2
|
|
|
Metals
|

Metals are brown
|
|
|
|
Period
|
Horizontal rows on the periodic table
|
H and He is in period 1
|
|
|
Groups
|
The vertical columns on the periodic table
|
Be, Mg. Ca, Sr.... Are in group 2
|
|
|
Metals
|

Metals are brown
|
Luster and high electrical and conducts heat
|
|
|
Non metals
|

Non metals are green
|
Can be solids liquids and gases
|
|
|
Metalloids
|

Purple section
|
|
|
|
Metalloids
|

Purple section
|
|
|
|
Diatomic molecule
|
A molecule that made up of two atoms
|
|
|
|
Metalloids
|

Purple section
|
|
|
|
Diatomic molecule
|
A molecule that made up of two atoms
|
|
|
|
Molecular compounds
|
Compounds composed of molecules contain more that one type of atom
|
|
|
|
Metalloids
|

Purple section
|
|
|
|
Diatomic molecule
|
A molecule that made up of two atoms
|
|
|
|
Molecular compounds
|
Compounds composed of molecules contain more that one type of atom
|
|
|
|
Molecular formulas
|
Chemical formulas that give only the relative # of atoms of each type in molecule
|
|
|
|
Metalloids
|

Purple section
|
|
|
|
Diatomic molecule
|
A molecule that made up of two atoms
|
|
|
|
Molecular compounds
|
Compounds composed of molecules contain more that one type of atom
|
|
|
|
Molecular formulas
|
Chemical formulas that give only the relative # of atoms of each type in molecule
|
|
|
|
Empirical formulas
|
Chemical formulas that give only the relative # of atoms of each type in a molecule
|
|
|
|
Metalloids
|
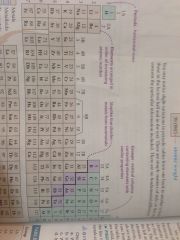
Purple section
|
|
|
|
Diatomic molecule
|
A molecule that made up of two atoms
|
|
|
|
Molecular compounds
|
Compounds composed of molecules contain more that one type of atom
|
|
|
|
Molecular formulas
|
Chemical formulas that give only the relative # of atoms of each type in molecule
|
|
|
|
Empirical formulas
|
Chemical formulas that give only the relative # of atoms of each type in a molecule
|
|
|
|
Ion
|
A charged particle that forms When electrons are removed from or added to an atom
|
|
|
|
Metalloids
|

Purple section
|
|
|
|
Diatomic molecule
|
A molecule that made up of two atoms
|
|
|
|
Molecular compounds
|
Compounds composed of molecules contain more that one type of atom
|
|
|
|
Molecular formulas
|
Chemical formulas that give only the relative # of atoms of each type in molecule
|
|
|
|
Empirical formulas
|
Chemical formulas that give only the relative # of atoms of each type in a molecule
|
|
|
|
Ion
|
A charged particle that forms When electrons are removed from or added to an atom
|
|
|
|
Cation
|
Ion with a positive charge
|
|
|
|
Metalloids
|

Purple section
|
|
|
|
Diatomic molecule
|
A molecule that made up of two atoms
|
|
|
|
Molecular compounds
|
Compounds composed of molecules contain more that one type of atom and generally composed of non metals only
|
|
|
|
Molecular formulas
|
Chemical formulas that give only the relative # of atoms of each type in molecule
|
|
|
|
Empirical formulas
|
Chemical formulas that give only the relative # of atoms of each type in a molecule
|
|
|
|
Ion
|
A charged particle that forms When electrons are removed from or added to an atom
|
|
|
|
Cation
|
Ion with a positive charge
|
|
|
|
Anion
|
Negatively charged ions
|
|
|
|
Ionic compounds
|
Made up of cations and ions and are generally metals combined with non metals
|
|
|
|
Polyatomic ions
|
Ions that consist of atoms joined as in a molecule but they have a net positive or negative charge
|
|
|
|
Oxyanions
|
Polyatomic anions containing oxygen have names ending in either -ate or- ite
|
|
|
|
Isomers
|
Compounds with the same molecular formula but diff. Arrangements of atoms.
|

|
|
|
Reactants
|
Chemical formula to the left of the arrow representing the starting substance.
|
|
|
|
Polyatomic ions
|
Ions that consist of atoms joined as in a molecule but they have a net positive or negative charge
|
|
|
|
Oxyanions
|
Polyatomic anions containing oxygen have names ending in either -ate or- ite
|
|
|
|
Isomers
|
Compounds with the same molecular formula but diff. Arrangements of atoms.
|

|
|
|
Reactants
|
Chemical formula to the left of the arrow representing the starting substance.
|
|
|
|
Product
|
The formula to the right of the arrow represents the substance that is produce in the reaction
|
|
|
|
Coefficient
|
The number in front of the formulas
|
|
|
|
Polyatomic ions
|
Ions that consist of atoms joined as in a molecule but they have a net positive or negative charge
|
|
|
|
Oxyanions
|
Polyatomic anions containing oxygen have names ending in either -ate or- ite
|
|
|
|
Isomers
|
Compounds with the same molecular formula but diff. Arrangements of atoms.
|
|
|
|
Reactants
|
Chemical formula to the left of the arrow representing the starting substance.
|
|
|
|
Product
|
The formula to the right of the arrow represents the substance that is produce in the reaction
|
|
|
|
Coefficient
|
The number in front of the formulas
|
|
|
|
Polyatomic ions
|
Ions that consist of atoms joined as in a molecule but they have a net positive or negative charge
|
|
|
|
Oxyanions
|
Polyatomic anions containing oxygen have names ending in either -ate or- ite
|
|
|
|
Isomers
|
Compounds with the same molecular formula but diff. Arrangements of atoms.
|
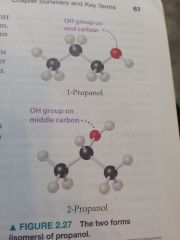
|
|
|
Reactants
|
Chemical formula to the left of the arrow representing the starting substance.
|
|
|
|
Product
|
The formula to the right of the arrow represents the substance that is produce in the reaction
|
|
|
|
Coefficient
|
The number in front of the formulas
|
|
|
|
Combination reactant
|
Two or more substances react to form one product
|
|
|
|
Decomposition reaction
|
One substance undergoes a reaction to produce two or more other substances
|
|
|
|
Combustion reaction
|
Rapid reactions that produce a flame
|
|
|
|
Polyatomic ions
|
Ions that consist of atoms joined as in a molecule but they have a net positive or negative charge
|
|
|
|
Oxyanions
|
Polyatomic anions containing oxygen have names ending in either -ate or- ite
|
|
|
|
Isomers
|
Compounds with the same molecular formula but diff. Arrangements of atoms.
|
|
|
|
Reactants
|
Chemical formula to the left of the arrow representing the starting substance.
|
|
|
|
Product
|
The formula to the right of the arrow represents the substance that is produce in the reaction
|
|
|
|
Coefficient
|
The number in front of the formulas
|
|
|
|
Combination reactant
|
Two or more substances react to form one product
|
|
|
|
Decomposition reaction
|
One substance undergoes a reaction to produce two or more other substances
|
|
|
|
Combustion reaction
|
Rapid reactions that produce a flame
|
|
|
|
Polyatomic ions
|
Ions that consist of atoms joined as in a molecule but they have a net positive or negative charge
|
|
|
|
Oxyanions
|
Polyatomic anions containing oxygen have names ending in either -ate or- ite
|
|
|
|
Isomers
|
Compounds with the same molecular formula but diff. Arrangements of atoms.
|

|
|
|
Reactants
|
Chemical formula to the left of the arrow representing the starting substance.
|
|
|
|
Product
|
The formula to the right of the arrow represents the substance that is produce in the reaction
|
|
|
|
Coefficient
|
The number in front of the formulas
|
|
|
|
Combination reactant
|
Two or more substances react to form one product
|
|
|
|
Decomposition reaction
|
One substance undergoes a reaction to produce two or more other substances
|
|
|
|
Combustion reaction
|
Rapid reactions that produce a flame
|
|
|
|
Formula weight
|
Sum of the atomic weights of the atoms in the chemical su
|
|

