![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
23 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Pale green flame |
Barium chloride dihydrate
|
|
|
Orange flame |
Sodium chloride |
|
|
Green blue flame |
Cooper chloride |
|
|
Lilac flame |
Potassium chloride |
|
|
Yellow red flame |
Calcium chloride |
|
|
Red flame |
Strontium chloride |
|
|
Red flame |
Lithium chloride |
|
|
What causes the flame colour |
Cation. Because it is what is changing if it where the anion (chloride) then the colour would stay the same |
|
|
Why is light created |
As they gain energy from the bunsen flame they move to a higher orbit then as they drop back down they release their energy as light |
|
|
Why there's Different colours |
Differences in the amount of energy between electron shells which produce different energy levels of light |
|
|
Any limitations |
Not all metal ions produce a color when heated in a flame e.g. iron and aluminum |
|
|
Not all metals produce light why |
They energy their electrons amit is above or below the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum |
|
|
Schrodinger model |
S 1 P 3 D 5 F 7 |
|
|
Alpha radiation |
Helium nuclei Not penetrating New element created |
|
|
Beta radiation |
Negative electrons They convert one neutron into a proton |
|
|
Gamma radiation |
Is emitted when alpha and beta happen Highly penetrating. Ionizing radiation can destroy dna |
|
|
Calculating percenty composition |

|
|
|
Metal properties |
Lustorus Ductile Malleable Dense High melting point High boiling point Good conductor of heat and electricity |
|
|
Non metals |
Not malleable Not ductile Dull in color, not shiny Not dense when compared to metal Lower mp and bp Poor conductors of heat and electricity |
|
|
Proton charge |
Positive |
|
|
Neutron charge |
Neutral |
|
|
Electron charge |
Negative |
|
|
How to work out relative atomic mass |
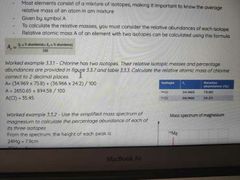
|

