![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
29 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Matter |
Anything that occupies space and has mass |
|
|
Mass |
Measure of the quantity of matter that an object contains |
|
|
Classification of matter can be |
Classify according to its: Physical State Composition |
|
|
Classifying Matter |
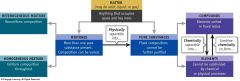
|
|
|
Pure Substances |
Elements or Compounds: Compounds can be further reduced into two or more elements |
|
|
Elements |
Consists of only one type of atom. They cannot be decomposed of further simplified by ordinary means The elements are recorded on the periodic table There are 118 recorded elements at this time |
|
|
Compound |
Combination of two or more elements in a definite, reproducible way |
|
|
Learn the names and symbols of the 1st 20 elements, alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, Ti, Fe, Cu, Ag, Au, Pb |

|
|
|
Mixtures |
A combination of two or more pure substances Homogeneous: mixture consists of two or more substances in the same phase Heterogeneous: uneven texture of the material can often be detected by the naked eye When separated, the components of both types of mixtures yields pure substances |
|
|
Mixtures may be separated by physical properties |
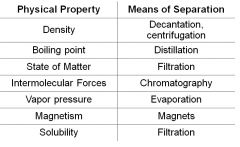
|
|
|
Heterogeneous Mixtures can be separated by ________ |
Filtration |
|
|
Homogeneous Mixtures |
Solutions: Solid/liquid Liquid/liquid Solid/Solid Solute: minor component of a solution Solvent: substance that contains solutes Compositions can vary: Amount of solute in solvent |
|
|
Chemical Compounds |

Chemical compounds are composed of two or more elements *compounds have different properties than the elements All compounds are made up of molecules or ions Ionic compounds: Molecules: Fixed Ratio Compounds represented by a chemical formula 1) Compounds have different properties than elements 2) Fixed composition ratio (definite proportion): Definite % composition by mass |
|
|
Physical Properties |
Characteristics that can be evaluated without changing the composition of the material: Color Odor Density Melting Point Thermal Conductivity Volume Hardness |
|
|
Some Physical Properties |
Color State Melting and boiling point Density (mass/unit volume) Extensive properties (mass depend upon the amount of substance) Intensive Properties (density) do not Intensive -> independent of sample size Density: ratio of mass to volume d=m/v |
|
|
Density Lab units |
Mass--> grams (g) Volume (v) Solids: cm^3 Liquids: ml Gases: L 3)Densityof acetic acid at 20 °C is1.05 g/mLWhatvolume do I need to have 275 g of acetic acid? |
|
|
Physical Change |
A change that does not entail any change in chemical composition |
|
|
Chemical Changes |
One substance or more are transformed into one or more new substances Chemical Reaction Reactants ---> Products The reactants and products are very different Involves a change in chemical composition Results in a change in composition or structure Iron reacts metal reacts with oxygen to form rust |
|
|
Physical and Chemical changes often accompanied by energy changes |
Energy ---> Capacity to do work Classified as Kinetic or Potential Kinetic energy is energy associated with motion Matter consists of atoms and molecules in motion |
|
|
Review Units of Measurements |

|
|
|
Length |
Standard=Meter (m) 1000m = 10^3m = 1 km (kilometer) 10^-2 m = 1 cm (centimeter) and 100 cm =1 m. 10^-3 m = 1 mm (millimeter) and 1000 mm =1 m. |
|
|
Sizes of molecules are in the ____ range |
Nanometer 10^-9 m = nanometer |
|
|
Selected Prefixes used in the metric system |

|
|
|
Volume |
Not a base unit --> from length Meter is length unit ---> a cubic meter is a volume unit m=length m^3= volume Common units: L mL cm^3 also as cc 1cm^3 = 1mL |
|
|
Mass |
Base Unit = Kilogram (kg) 1kg = 1000 grams Common units in chemistry are grams and milligrams (mg) n250mL of water= 250 g of water = 1 cupn250kg = 250 L --> à ~tub. |
|
|
Time |
Base Unit = second For smaller time frames Milliseconds (ms), microseconds (us) nanseconds (ns), etc. SI units prefixes |
|
|
Energy |
SI ---> joule (J) kj = kilojoule = 1000 J Non SI unit for food: calories and Calories cal Cal |
|
|
Dimensional Analysis |

|
|
|
More practice at home |
Howmany inches in ¼ mile? ¼mile= 0.250 mile 0.250mile --> inches 1mile = 5280 ft 12in= 1 ft 0.250 mile Ifthe speed of a molecule of oxygen at 25 °C is 490 m/s, and 1 mile is 1.609km, what is the speed of oxygen in mph? Speedof light --> 6.71 x 108 mph --? m/s Howmany grams in 4100 mg? |

