![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
13 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What occurs in chemical change? change? |
Existing bonds are broken between the original substances and new substances are formed. The existing molecules and atoms rearrange themselves in new patterns |
- |
|
|
What is needed for the breaking of bonds |
Energy |
|
|
|
What law is also appIicable to chemical change? |
Law of conservation of mass. The total mass of the particles before the reaction is equal to the total mass of the particles after the reaction. |
|
|
|
Can chemical reactions be reversed? |
Only very few. (Wood burns into ash but is not reversiblel back into longs) |
|
|
|
How is energy transferred in a chemical reaction? |
It can be absorbed or released; forming an endothermic or exothermic reaction |
|
|
|
What is a synthesis reaction? |
A chemical reaction in which an element or compound combine to ALWAYS form a compound |
|
|
|
What is a decomposition reaction? |
A reaction in which a single compound breaks into two or more element or compounds |
|
|
|
What is a single replacement reaction? |

A reaction in which an element reacts with a compound and replaces another element in that compound |
|
|
|
What is a double replacement reaction? |
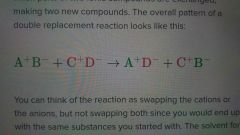
A reaction in which parts of two ionic compounds exchange; making two new compounds |
|
|
|
What is the state of the: - reactants in a single replacement reaction? - products in a single replacement reaction? |
Reactants: free metals are solids Compounds ae aqueous Products: same as reactants |
|
|
|
What is the state of the:- reactants in a double replacement reaction?- products in a double replacement reaction? |
Reactants: all are aqueous (so ions are free to replace) Products: One compound will be a precipitate (solid); another will be aqueous |
|
|
|
What occurs to the kenetic energy in a chemical reaction? |
The kenetic energy stays the same |
|
|
|
Describe potential energy of particles when in a chemical reaction |
It increases as a substance melts |
|

