![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
49 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
What is chemical bond? |
A force that acts between two or more atoms to hold them together as a stable molecule. |
Attractive force |
|
|
How was the term valency derived? |
The term valency was derived from the Latin word 'valentia' which means capacity. |
Valentia |
|
|
Why does chemical combination happens? |
i) Decrease in energy (becoming stable ii) to attain octet configuration |
Low energy and attaining that magic number |
|
|
What is electronic theory of valency? |
Two or more atoms in a bond try to attain a noble configuration |
|
|
|
What is formal charge? |
(No. of valence electrons in the free atom) - (no. of unshared electrons on the atom (while in the bond)) - (no. of bonds around the atom) |
Charge on a single atom in a bond |
|
|
Limitations of the octet rule |
1)the incomplete octet of the central atom 2)odd-electron molecules 3)the expanded octet 4)does not account for the shape of molecules 5)relative stability of the energy of the molecule is not explained |
Examples: BCl3, NO2, H2SO4 Many noble gases also form molecules like KrF2, XeOF2 etc |
|
|
What is an electrovalent bond? |
Just another name for ionic bond. |
|
|
|
What is a dative bond? |
A covalent bond in which both electrons of the shared pair are contributed by one of the two atoms. It is represented by A - -> B. |
|
|
|
What is electronegativity difference? |
The difference between the electronegativity of two elements in a bond |
|
|
|
How much (minimum) electronegativity is necessary for an ionic bond to occur? |
About 2 |
|
|
|
What is lattice energy ⚡? |
Energy released to form one mole of a crystal lattice of a compound is called lattice energy. |
|
|
|
What is a Crystal lattice? |
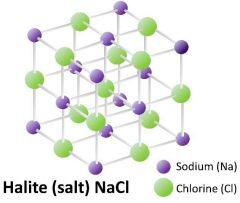
|
The symmetrical 3d arrangement of atoms inside a crystal |
|
|
General properties of ionic compounds |
-hard and possess high melting and boiling points -dissolves in polar solvents -doesn't exhibit isomerism -in aqueous solutions or in fused state, they act as conductors. |
💪 💦 |
|
|
What is a Bond length? |
The distance between the nuclei of two atoms bonded together is termed bond length or bond distance. |
|
|
|
How is a Bond length calculated? |
Spectroscopically (or) by x-ray diffraction of solids and electron diffraction of gases. |
Radius of 1st element + radius of 2nd element |
|
|
Is the bond length of C-C bond (single bond) and C=C (double bond) equal? |
No, its actually decreases as the number of bonds (single double or triple) increases.
|
|
|
|
What is a bond angle? |
Angle between two adjacent bonds of an atom in a molecule made up of three or more atoms is known as the bond angle. |
|
|
|
What is bond energy (bond enthalpy)? |
Amount of energy required to break a bond (usually one mole) in a molecule. |
|
|
|
What is H-H bond enthalpy in hydrogen molecule? |
H(g) + H(g) - > 2H(g) It's bond energy is (delta)H = 436 KJ mol^-1 |
Bond energy |
|
|
What does strength of bond depend on? |
1) bond length (shorter the length, greater is the strength) 2) bond order (single or multiple bonds) 3)no. of atoms in a molecule (monoatomic or polyatomic) Also remember that bond energy changes for an atom in different molecules or compounds.
|
Bond length, order and the # of atoms in a molecule |
|
|
How does the no. of bonds (single or multiple bonds) affect the strength of bond? |
Triple bond>double bond>single bond between the same atoms of diatomic molecules |
|
|
|
What does a larger bond dissociation enthalpy means? |
It means that larger the bond energy, stronger will be the bond in the molecule. |
Dissociation = (chemistry) the splitting of a molecule into smaller molecules, atoms or ions, especially by a reversible process. |
|
|
How is the bond enthalpy measured in case of polyatomic molecules like, H2O? |
H2O(g) - > H(g) + OH(g) ; Here (delta)H = 502 KJ mol^-1 & OH(g) - > H(g) + OH(g) ; Here (delta)H = 427 KJ mol^-1 Now we take the avg of the two bonds broken = (502 + 427)/2 = 464.5 KJ mol^-1 |
H2O 💦 H-O-H (it has two bonds to be broken)
|
|
|
Why is mean or average bond enthalpy used? |
It is used in the case of polyatomic molecules (like H2O). It is done as: H2O 💦 H-O-H (it has two bonds to be broken) if you break a bond you will get OH(g) and H(g). Now for the second bond you need to break the OH(g) molecule which requires less energy than H(g) and OH(g). # Now you just need to divide the total bond dissociation enthalpy by the number of bonds broken. You can also break the O atom first which would yield 2H(g) + O(g); (delta)H = 926 kj mol^-1 |
To find the bond energy required to break a single bond in a polyatomic molecule. |
|
|
What is bond order? |
No. of bonds (or) number of shared electron pairs between two atoms in a molecule |
# of bonds |
|
|
Isoelectronic molecules (or) ions and bond order? |
They have same bond order. |
|
|
|
What is the role of resonance in the changing of bond order? |
Resonance changes the bond order. Bond order = total no. of bonds between two atoms all the structures/total no. of resonating structures |
|
|
|
What is resonance? |
Whenever a single Lewis structure cannot describe a given molecule accurately (doesn't agree with the experimental results), a no. of structures can be written for a molecule (those structures are correct according to the Lewis structure rules but aren't accurate), then the actual structure is said to be a resonance hybrid or mesomeric hybrid of all these alternative structures. |
A hybrid variety (which is the really real one) of all the possible structures that can be drawn for it. |
|
|
What is a canonical form (in resonance structures)? |
The various structures of which the molecule is a resonance hybrid are known as canonical or mesomeric forms. |
Pseudo structures of the hybrid (true) molecule |
|
|
How are the canonical structures denoted? |
The are denoted by the symbol <----> between them. |
What is the symbol? |
|
|
Difference between the energy of resonance hybrid and canonical forms of a single atom? |
Energy of resonance hybrid is less than that of any single canonical structures |
|
|
|
What is polarity of covalent bond? |
In reality no bond of compound is either completely covalent or ionic in nature. |
Polar = directly opposite in character or tendency. |
|
|
What are non-polar bonds? |
When the shared electron pairs are equally attracted by the two atoms and therefore spend same amounts of time near each nucleus makes the molecule neutral or non-polar. |
Eg:H2, O2, Cl2, F2 etc (homonuclear diatomic molecules) |
|
|
What are polar (covalent) bonds? |
In case of heteronuclear atoms, the shared pairs of electrons shifts more towards the atom with more electronegativity. Due to this the molecules gets two (partial or sometimes full (in case of ions)) oppositely charged poles, and the bond is said to be a polar covalent bond. |
Eg:HF, HCl, HBr, HI, CsCl etc (heteronuclear diatomic nuclear) |
|
|
What is dipole moment? |
The polarity of a molecule is indicated in terms of dipole moment (μ). μ = electric charge × bond length (distance between the charges) μ = q × d |
μ = q × d |
|
|
How is dipole moment measured? |
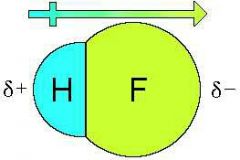
μ = q × d Dipole moment is measured in 'Debye' units (D), where 1 D = 3.33 x 10^-30 coulomb metre Further dipole moment is a vector quantity and is depicted by the symbol +---> (shown in the above picture). + sign on positive end and arrow head on negative end. |
Debye |
|
|
Calculation of dipole moment of molecules with more than two atoms. |
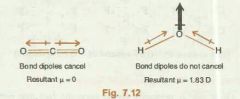
-As dipole moment is a vector quantity it's resultant will be equal to all the bond dipoles (individual dipole moments of bonds) added. -normal vector addition can be used (think or triangle law or parallelogram law of vector addition) |
Vector addition |
|
|
What are symmetrical molecules? |
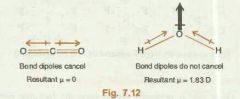
CO2, BF3, CH4, CCl4 are symmetrical and have zero resultant dipole moment. They are symmetrical because their central atom doesn't contains lone pair of electrons in addition to the bond pairs. They are non-polar even though it contains polar bonds, as the symmetrical bonds cancel each other out |
|
|
|
What are unsymmetrical polyatomic molecules? |

H2O, CH3Cl, NH3, etc are unsymmetrical non-linear polyatomic molecules. As their central atom has lone pairs in addition to bond pairs,it causes distortion in the geometry of the molecule. |
|
|
|
What are fajan's rules? |
-For a given cation, covalent character increases with increase in size of the anion -For a given anion, covalent character increases with decrease in size of the cation -Covalent character increases with increasing charge either on cation or on anion -Covalent character is high for compounds with cations with pseudo noble gas electronic configuration (18 electrons in the valence shell) compared to compounds with cations with noble gas electronic configuration (8 electrons in the valence shell) |
Just as all covalent bonds have some partial ionic character, the ionic bond also have partial covalent character. |
|
|
What is VSEPR theory? |
Valence Shell Electron-Pair Repulsion theory. It predicts the shapes of molecules |
Prediction of shapes |
|
|
What is vsepr theory based on? |
It is based on the repulsive interactions of the electron pairs (bonded or non-bonded) in the valence shell of the atoms - It suggests that these electron pairs tend to occupy such positions in space that minimize repulsion and thus maximize separation between them. |
Repulsive interactions of the electron pairs |
|
|
What is the order of repulsive interaction of electron pairs (between lone pairs and bond pairs) |
Lone pair = lp; Bond pair = bp lp - lp > lp - bp > bp - bp |
|
|
|
Why does lone pair electrons occupy more space as compared to bond pair electrons? |
While the lone pair electrons are localized on the central atom, each bond pair electrons are shared between the two atoms. This leads to the lone pairs occupying more space than bond pair electrons. |
Bond pairs are shared |
|
|
How to apply VSEPR method? |

Draw a Lewis structure of the molecule or ion. -note down the number of electron groups around the central atom (Note 📝 : a double and a triple bond each is counted as as one electron group) -identify the election group geometry and molecular geometry (from the above table) Electron group geometry is just the geometrical shape without any lone pairs i.e.,the first one of every group in the above table (they are linear, trigonal planar, tetrahedral, trigonal bipyramidal, octahedral) |
Need to memorize the molecular geometry table. |
|
|
Why was valence bond theory (or) molecular orbital theory developed? |
The Lewis or octet concept doesn't explain: -the cause of covalent bond formation -nature of the forces acting between them -why different amounts of energy is released during the formation of different molecules -shape of the molecules -why the molecules are stable even though there are less than or more than 8 electrons in the valence shell & the vsepr theory only explains the shapes of the molecules. So to explain the above limitations the valence bond theory and molecular orbital theory based on quantum mechanics have been proposed. |
As lewis, octet and vsepr theories have limitations |
|
|
What are the forces that arises when two atoms approach each other? |
°Attractive forces between 1)the nucleus of one atom and its own electron(s) 2)the nucleus of one atom and the electron(s) of other atom & °Repulsive forces between 1)electrons of both the atoms 2)nuclei of both the atoms. If the magnitude of newly formed attractive forces are more than repulsive forces, they bond. |

|
|
|
What happens to the the potential energy of two atoms approaching each other? |
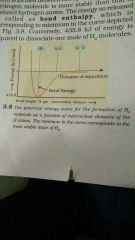
The potential energy steadily decreases as they comes closer. Ultimately a stage is reached where the net force of attraction balances the force of repulsion and system acquires minimum energy. At this stage the atoms are said to be bonded together to form a stable molecule. (Note:The graph is to be studied from left to right & the energy which is released when the bond is formed is given by the minimum in the curve) |
Decreases |
|
|
Difference between Sigma(σ) and pi bonds(π)? |

|
|

