![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
22 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Addition reactions |
Atoms added across a carbon-carbon double or triple bond (at least 1 double bond needed) Acid catalyst used sometimes Symmetrical= 1 product Asymmetrical=2 (M's rule) |
|
|
Elimination |
Atoms removed from molecule to produce double bond |
|
|
Elimination of alcohol |
alkene + h2o |
|
|
Haloalkane + base (elimination) |
Alkene + alcohol + simple ionic compound |
|
|
Elimination: H atom being removed is most likely to be removed |
From the C with the most C bonds (major product) |
|
|
Substitution reaction |
H or functional group replaced by a diff atom or func group |
|
|
Features of substitution reaction |
2 cmpnds= 2 diff cmpnds
C atoms have same # of bonds in reactant and product Catalysts are often used |
|
|
Substitution: alcohol + HX(acid w halogen) |
Haloalkane + h2o |
|
|
Haloalkane + hydroxide ion |
Subs Alcohol + halogen ion |
|
|
Aromatics + Cl or Br |
W a catalyst, = x |
|
|
Benzene + acid |
Subs H2o + aromatic derivatives |
|
|
Condensation rxtion |
2 molecules form a larger molecule and water Form amino acids and esters |
|
|
Hydrolysis |
H on one side OH on the other |
|
|
Group in aldehydes |
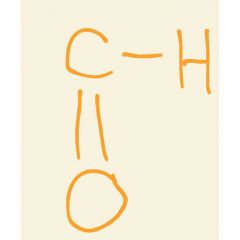
Carbonyl |
|
|
Group in alcohol |

|
|
|
Group in haloalkane |

|
|
|
Group found in carboxylic acid |
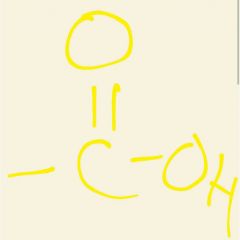
Carboxyl |
|
|
Group found in amines |

|
|
|
Group found in amides |
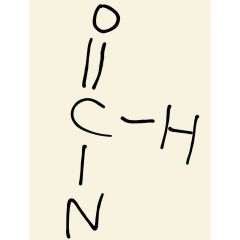
|
|
|
Group found in ketones |
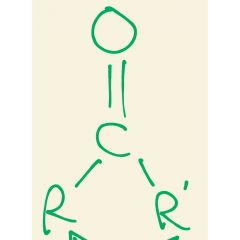
Ketone |
|
|
Group found in esters |
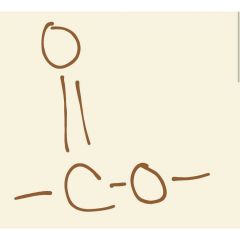
Ketone + O |
|
|
Group found in ether |

|

