![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
What is an Atom? |
- simplest form of matter - single particle of matter |
|
|
What is a molecule? |
- made of 2 or more atoms |
|
|
What is a compound? |
- pure substance made of two or more elements - e.g. h2O 2 hyrdrogen and 1 oxygen |
|
|
What the structure of an atom? |
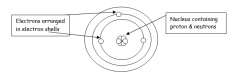
- neutrons/ protons - electrons - shells |
|
|
The electron shell numbers? |
1st: 2 elec 2nd: 8 elec 3rd: 18 elec |
|
|
How do you know the atomic number? |
Theatomic number of an atom represents itsnumber of protons. |
|
|
Are amount of protons= electrons |
yes, and has no overall charge |
|
|
The mass number = |
number of protons +number of neutronsin an atom |
|
|
What are the groups on the periodic table? |
1- alkaline metals 2- alkaline earthmetals 17- halogens 18- noble gases |
|
|
What is an ion? |
A charged atom? |
|
|
Atomic number is equal to: |
number of protons |
|
|
Vertical columns are the... |
Groups (1,2,17,18) |
|
|
Physical change is when... |
a substance changes, but no new substances are formed (e.g. freezing, melting, dissolving) |
|
|
Chemical change is when... |
a chemical reaction occurs and a new substance is formed (e.g. explosions, cooking, ripening and rotting) |
|
|
Chem reaction, what do start with? |
Reactants |
|
|
and what do you end with? |
a product |
|
|
Can you see a chemical reaction? |
Usually. Law of conservation. |
|
|
What is the law of conservation? |
matter can neither be created nor destroyed during chemical reactions |
|
|
What does the law of conservation mean in terms of the chemical reaction? |
substances pulled apart--->atoms rearrange----> form new substances |
|
|
What is an ionic compound? |
Positive ion--->attracted to negative ion---> ionic bond is formed |
|
|
What usually happens in an ionic compound? |
the positive is a metal the negative is a non-metal |
|
|
What is a cation? |
a positively charged ion, it has lost electrons |
|
|
What is an anion? |
A negatively charged ion, has more electrons than protons (gained electrons) |
|
|
What is an isotope? |
Atoms of an element with different amount of neutrons |
|
|
What does ionic bonding look like? |
The giving of an electron from one outer shell to another |
|
|
What is covalent bonding? |
When two non-metals come together, share electrons |
|
|
What does covalent bonding look like? |
when two atoms share electrons in their outer shells |
|
|
Prefix: mono |
1 |
|
|
prefix: di |
2 |
|
|
prefix: tri |
3 |
|
|
prefix: tetra |
4 |
|
|
prefix: penta |
5 |
|
|
prefix: hexa |
6 |
|
|
Monoatomic molecules |
1 atoms |
|
|
Diatomic molecules |
2 atoms |
|
|
Polyatomic molecules |
more than 2 atoms |
|
|
If magnesium looses 2 electrons to form an ion then... |
mg---> Mg + 2e- |
|
|
Metals form ions by |
losing electrons which makes it positive |
|
|
non-metals form ions by |
gaining electron which makes it negative |
|
|
Polyatomic is when |
Is when an mono ion with another ion and they have 1 overall charge |
|
|
Equation for combination reactants |
a+b----> ab 2 or more elements combine to form 1 new compound |
|
|
Equation for decomposition reactions |
ab----> a+b |
|
|
What is a combustion reaction? |
Reaction that uses oxygen and produce a flame (heat and light) |
|
|
What is a precipitate? |
a solid formed by two substances |
|
|
What happens in a precipitate reaction? |
2 solutions are mixed together and a solid forms |
|
|
What is an insoluable substance? |
substance that does not dissolve in water |
|
|
How do you identify whether a solution is a precipitate or not? |
Use the table and determine |
|
|
What does aq mean or stand for?? |
Aqueous, water, soluable |
|
|
What does s mean or stand for? |
Solid |
|
|
what is a displacement reaction? |
Where a reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal |
|
|
What things speed up a reaction? |
Temp, surface area, catalysts and amount/ concentration of reactants |

