![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
52 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Draw orbital notation boxes up to 6s |
|
|
|
Hund's rule |
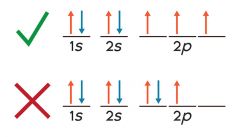
every orbital in a square is filled with one electron before any orbital is filled with two. |
|
|
Aufbau principle |
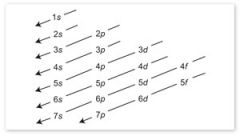
electrons fill lowest available energy levels before filling higher levels |
|
|
Pauli Exclusion Principle |
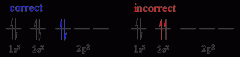
no two electrons can have the same four electronic quantum numbers. The two electrons in an orbital must have opposing spins. |
|
|
Why does fluorine have a higher ionization energy than iodine? |
Fluorine has a smaller atomic radius so the positive protons can exert a greater pull on the negative electron. |
|
|
Why do elements in the same family generally have similar properties? |
They have the same valence shell e- arrangement. |
|
|
Atomic Radius (excluding noble gasses): Increase or decrease from left to right? |
Decrease |
|
|
First ionization energy: Increase or decrease from left to right? |
Increase |
|
|
Electronegativity: Increase or decrease from left to right? |
Increase |
|
|
What trend in ionization energy occurs across a period on the periodic table? What causes this trend? |
Ionization energy increases across a period because as metals become less metallic, it requires more energy to remove a negative electron (e-). |
|
|
What trend in atomic radius down a group on the periodic table? What causes this trend? |
Atomic radius increases down a group because energy levels (shells) are added. |
|
|
Define Electronegativity |
The ability of an atom to gain an e-. Also the strength of an atom's attraction for the electron's chemical bond. |
|
|
Period table top to bottom: Principle energy level |
Increases |
|
|
Period table top to bottom: Valence electrons |
Stays the same |
|
|
Which properties are most common in nonmetals? |
High ionization energy and high electronegativity. |
|
|
On a group which area has the least attraction for electrons? |
The bottom |
|
|
On a group which area has the greatest tendency to gain electrons? |
The top |
|
|
What does the atomic number represent? |
Protons or electrons. |
|
|
What does the atomic mass represent? |
Protons plus neutrons. |
|
|
How many electrons can each level hold? 1st, 2nd, and 3rd... |
1st = 2 2nd = 8 3rd = 18 |
|
|
What term is used for the electrons in the outermost shell or energy level? |
VALENCE |
|
|
SI Units: Time: Length: Mass: Temp: |
Time: second Length: metre Mass: kilogram Temp: kelvin |
|
|
Density formula and Mass formula |
Mass/volume and density x volume. |
|
|
What are isotopes? |
Atoms of the same element that have different mass #s (Same # of protons but different # of neutrons). |
|
|
Identify the four blocks of the periodic table based on their electron configuration. |
s is groups 1 & 2, p is the groups 13 -18, D is the middle 3 - 12 f, is 2 rows on the bottom of the table . |
|
|
What part of the atom contains most of its mass? |
The nucleus. |
|
|
Define the octet rule and its exceptions. |
States that elements gain or lose electrons to attain an electron configuration of the nearest noble gas. * odd number of electrons *When an atom has less than an octet *When an atom has more than an octet |
|
|
Resonance Structure |
When there is double bonding, triple bonding, etc. so there has to be multiple lewis dot structures to represent that the multiple bonding could occur at any area. |
|
|
Summarize VSEPR bonding theory in order to predict shapes of molecules. |
*Stands for: Valence shell electron pair repulsion |
|
|
how are ions formed? |
when atoms lose or gain electrons |
|
|
how are ionic bonds formed? |
when an atom, typically a metal, loses an electron or electrons, and becomes a positive ion, or cation. |
|
|
Polyatomic ions |
(insert here...) |
|
|
Which of the following factors contributes to the lower ionization energy of the higher-atomic-number elements in a family in the periodic table? |
Greater distance from the nucleus. |
|
|
Atomic size ____ from left to right across a period. |
Increases |
|
|
Ionization energy |
The energy required to remove an an electron from a gaseous atom |
|
|
The letter "p" in the symbol 4p^3 indicates the |
Orbital shape |
|
|
If only two electrons occupy two p orbitals, what is the direction of the spins of these two electrons? |
They are both clockwise or counterclockwise. |
|
|
K degrees = |
C degrees + 273 |
|
|
F degrees = |
9/5 (C degrees) +32 |
|
|
C degrees = |
5/9 (F degrees-32) |
|
|
If the temperature of a piece of steel decreases, what happens to its density? |
The density increases. |
|
|
A liter of water is heated from 20 degrees C to 50 degrees C. What happens to its volume? |
The volume increases. |
|
|
An -ate or -ite at the end of a compound name usually indicates that the compound contains ______. |
A polyatomic ion. |
|
|
polyatomic ions are tightly wound groups of ______ |
Atoms. |
|
|
Ionic compounds are composed of _____. |
Positive and negative ions. |
|
|
Why do elements combine to fork chemical compounds? |
So their atoms can get a full shell of valence electrons and become more stable |
|
|
Compare and contrast ionic and covalent bonding |
They are both bonds that join two atoms together Covalent bonds: - pair of electrons shared between 2 atoms Ionic bonds: electrons are transferred from one atom to the other |
|
|
Shape of an s orbital? |
Spherical |
|
|
Shape of p orbital? |
dumbbell |
|
|
Convert 1 m to cm |
100 cm |
|
|
Convert 1 L to CL |
100 CL |
|
|
Convert 1 mg to g |
10^6 g |

