![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
48 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
|
Explain the difference between an element and a compound using examples. |
An element is a pure substance containing only one type atom ex: gold An compound is a pure substance made up of different types of atoms that are bonded together ex: NaCl |
|
|
|
How to find density? |
Density = mass/ volume |
|
|
|
Explain the difference between chemical and physical properties using examples. |
Physical Properties are properties of a substance that can be observed without changing the chemical composition ex. Color Chemical properties are a property of a substance that can ONLY be observed durring a chemical reaction ex. Bubbling |
|
|
|
Explain the difference between intensive and extensive using examples. |
Intensive property- a property of a substance that is NOT dependent upon sample size ex. Color Extensive property- a property of a substance that is dependent upon sample size ex. Volume |
|
|
|
Explain how to use the periodic table to determine if a substance is a metal, non metal, or metalloid. |
You can use the line that separates the metals, non metals, and metalloids, an element that is touching on 2 sides are metalloids, elements to the left of the line are metals and elements to the right of the line are non metals. |
|
|

Fill in the chart |
Hyphen notation : potassium - 42 Protons : 19 Neutrons : 23 Electrons : 19 Electron Configuration : 2, 8, 8, 1 |

|
|

Fill in the chart |
Nuclear symbol : 36 / 17 Cl Protons : 17 Neutrons : 19 Electrons : 17 Electron Configuration : 2, 8, 7 |

|
|

Fill in the chart |
Nuclear symbol : 36 / 16 Hyphen notation : sulfur - 36 Electrons : 16 Electron Configuration : 2, 6 |

|
|

Fill in the chart |
Nuclear symbol : 17 / 8 O Hyphen notation : oxygen - 17 Protons : 8 Electron configuration : 2, 6 |

|
|
|
Give 2 reasons why atoms cannot be counted. |
1) Atoms are VERY small so it is very hard to count them 2) There are a ton of atoms, so many it is impossible to count them all |
|
|
|
Explain the rules for determining the number of sig figs in a multiplication calculation. Give an example as part of the explanation. |
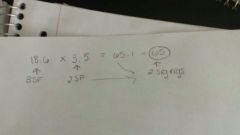
Round the answer to the same number of significant figures as the price of data with the LEAST amount of sig figs. See picture for example. |
|
|
|
When are zeros significant in a number? Use example as part of your explanation. |
♡Zeros between significant digits ex: 302 or 102,307 ♡Zeros at the end of a number after a decimal ex: 2.60 = 3 SF or 0.0020310 = 5 SF |
|
|
|
Write a procedure for determining the saturation level of a solution. Include an explanation of how to interpret the data that could be collected from the procedure. |
When a solute is added to a solvent at a specific temperature if the solute "dissappears" it is UNSATURATED. If the solute sinks to the bottom in a "clump" it is SATURATED. If the solution turns to a solid it is SUPERSATURATED. |
|
|
|
When naming acids -ic goes to what? |
-ous |
|
|
|
When are zeros NOT significant in a number? Use example as part of your explanation. |
◇At the beginning of a number ex. 0.0372 = 3 SF ◇At the end of a number before a decimal ex. 103,200 = 4 SF |
|
|
|
Stoichiometry |
The study of mass and quantity relationships in a chemical reaction |
|
|
|
Mole ratio |
A fraction created from the balancing numbers of a reaction to compare the quantities of each substance |
|
|
|
% yeild definition and equation |
A measure of the efficiency of a reaction % yeild = actual / theoretical X 100 |
|
|
|
Limiting reactant |
The chemical that runs out first causing the reaction to stop. |
|
|
|
Actual yeild |
The amount found in the lab. |
|
|
|
Theoretical yeild |
The amount found using stoichiometry (it is the limiting reactant) |
|
|
|
Why do chemists need stoichiometry? |
To calculate how much of a chemical is produced when a certain amount of another chemical is used. |
|
|
|
Why is it necessary to balance a reaction before doing stoichiometry? |
So that you know how many moles of each chemical are in the reaction so you can compare the quantities of each substance. |
|
|
|
Double displacement general form |
AX + By ➡ AY + BX |
|
|
|
Single Displacement general form |
A + Bx ➡ Ax + B |
|
|
|
Combustion general form |
A + O2 ➡ AO2 |
|
|
|
Synthesis general form |
A + B ➡ AB |
|
|
|
Decomposition general form |
AB ➡ A + B |
|
|
|
Dissociation general form |
AB (s) ➡(H2O) A (aq) + B (aq) |
|
|
|
What are spectator ions and why are they not included in net ionic equations? |
They are ions in a reaction that do not react so they are not included in net ionic equations. |
|
|
|
Titration |
The process of finding the concentration of a solution by using a second solution of unknown concentration |
|
|
|
Titrant |
The solution of KNOWN concentration |
|
|
|
Titrate |
The solution of UNKNOWN concentration |
|
|
|
pH |
Shows how acidic or basic a solution is |
|
|
|
Indicator |
Changes color to show the pH of a solution |
|
|
|
Equivalence point |
Point when a solution is stoichiometrally equal and the indicator changes color |
|
|
|
List three things you need to do as part of the process to clean a buret. |
1) make sure the valve is closed and pour 10-15 ml of the intended solution into the buret 2) swish the solution through the entire buret 3) empty through the valve in order to clean the valve. Repeat the process 3 times |
|
|
|
Write neutralization reactions for the following: Hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide |
HCl + NaOH ➡ H2O + NaCl |
|
|
|
Write neutralization reactions for the following: Carbonic acid and lithium hydroxide |
HCO3 + H2Li ➡ H2O + LiCO3 |
|
|
|
Write the procedure for doing a titration. |
1) clean each buret 2) fill each with the intended solution 3) remove any air bubbles 4) record initial volume 5) put 20 - 25 ml of acid in the beaker 6) put 3 drops of indicator in the beaker 7) while consistently swirling the acid and indicator add base until it remains pink for 30 seconds 8) record final volume 9) repeat for 3 trials |
|
|
|
Molarity definition and equation |
The number of moles of solute per liter M = moles solute / liters of solution = moles / l |
|
|
|
Solution |
Stable homogenous mixture of 2 or more substances ex. Kool-aid and water |
|
|
|
Solute |
Substance that gets dissolved ex. Hit cocoa mix |
|
|
|
Solvent |
Substance that causes the solute to dissolves ex. Water when cocoa is added |
|
|
|
1 mole = what |
1 mole = 6.02 × 10 ^23 = atomic mass of element |
|
|
|
Stoichiometry general form |

|
|
|
|
Process for writing a chemical formula |
1) determine the symbol and charge for the first word in the name using the periodic table or the charge table 2) determine the symbol and charge for the second word in the name 3) add subscripts so the positives and negatives are equal to one another (so charges cancel) 4) polyatomic ions that need a subscript should be in parenthesis |
|
|
|
Write a formula for chromium sulfide |
Cr2S3 Work: Cr+3 S-2 Cr+3 S-2 S-2 |
|

