![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
170 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
- 3rd side (hint)
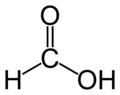
|
formic acid
|
|
|
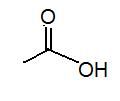
|
acetic acid
|
|
|
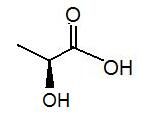
|
lactic acid
|
|
|
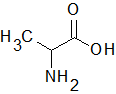
|
Alanine
|
|
|
|
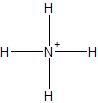
Ammonium Ion
|
|
|
|
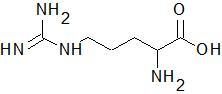
Arginine
|
|
|
|
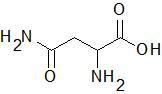
Asparagine
|
|
|
|
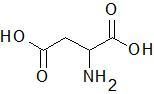
Aspartic Acid
|
|
|
|
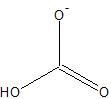
Bicarbonate Ion
|
|
|
|
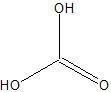
Carbonic Acid
|
|
|
|
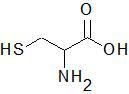
Cysteine
|
|
|
|
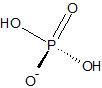
Dihydrogen Phosphate
|
|
|
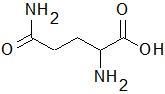
|
Glutamine
|
|
|
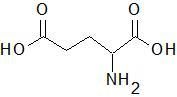
|
Glutemic Acid
|
|
|
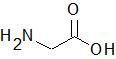
|
Glycine
|
|
|
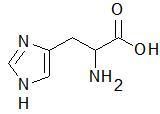
|
Histidine
|
|
|
|
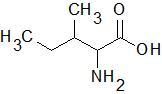
Isoleucine
|
|
|
|
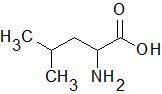
Leucine
|
|
|
|
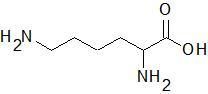
Lysine
|
|
|
|
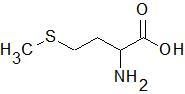
Methionine
|
|
|
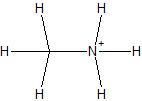
|
Methylammonium Ion
|
|
|
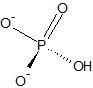
|
Monohydrogen Phosphate Ion
|
|
|
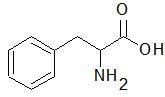
|
Phenylalanine
|
|
|
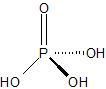
|
Phosphoric Acid
|
|
|
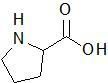
|
Proline
|
|
|
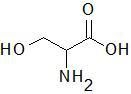
|
Serine
|
|
|
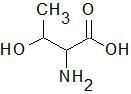
|
Threonine
|
|
|
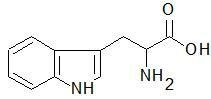
|
Tryptophan
|
|
|
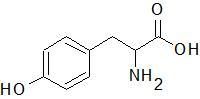
|
Tyrosine
|
|
|
|
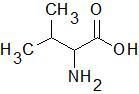
Valine
|
The 'R' group ends in a "V"
|
|
|
Average pKa of Amino Group
|
9.5 ± 0.6
|
|
|
|
Definition:
Amino Acids/Proteins |
Polymer of ɑ-amino acids linked by a peptide [amide] bond
|
|
|
|
Definition:
Carbohydrates |
Polyhydroxyl ketones or polydydroxyl aldehydes and their derivatives.
|
|
|
|
Definition:
Lipids |
Biomolecules which are insoluble or slightly soluble in water and usually extractable by organic [nonpolar] solvents.
|
|
|
|
Definition:
Nucleic Acids |
Biopolymers consisting of nitrogenous bases which are linked to ribose or deoxyribose linked by phosphodiester bonds.
|
|
|
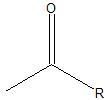
|
Acyl group
|
|
|
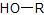
|
Alcohol
|
|
|
|
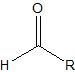
Aldehyde
|
|
|
|
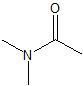
Amide linkage
|
|
|
|
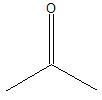
Carbonyl group
|
|
|
|
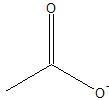
Carboxylate anion
|
|
|
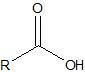
|
carboxylic acid
|
|
|
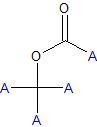
|
ester linkage
|
|
|
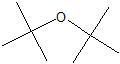
|
ether linkage
|
|
|

|
hydroxyl group
|
|
|
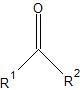
|
Ketone
|
|
|
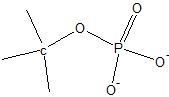
|
phosphate ester link
|
|
|
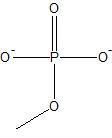
|
phosphate ion
|
|
|
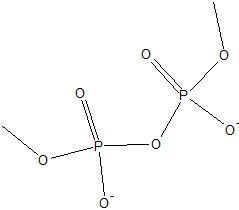
|
Phosphoanydride link
|
|
|
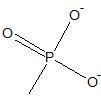
|
phosphoryl group
|
|
|
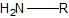
|
primary amine
|
|
|
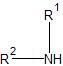
|
secondary amine
|
|
|
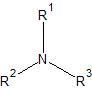
|
tertiary amine
|
|
|

|
thiol
(sulfhydryl) |
|
|
|
Definition:
Buffer |
A weak acid or base, present in acid-base pair, which resists changes in pH when another acid or base is added.
|
|
|
|
pH = [formula?]
|
pH = - log [H+]
eq. 2.9, pg 40. |
|
|
|
Definition:
Chromatography |
Separation based on the relative affinity of the solute for moving and stationary phases.
|
|
|
|
Definition:
Electrophoresis |
Separation based on the movement of charged molecules in the presence of an electric field.
|
|
|

|
Sodium Dodecyl Sulfate (SDS)
(C12H25SO4Na) |
|
|
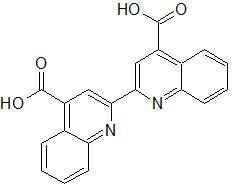
|
Bicinchoninic acid (BCA)
|
|
|
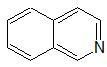
|
quinoline rings
|
|
|
|
The number of amino acids in RNase?
|
124
|
|
|
|
Describe the Anfinsen Experiment
|
(see page 109)
|
|
|
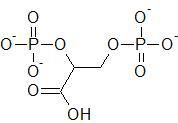
|
2,3-Bisphosphoglycerate
(notice 2 chiral carbons) |
|
|
|
Describe hemoglobin's "cooperative" trait.
|
As it picks up, and drops off, oxygen, it becomes easier for it to continue either picking up, or dropping off oxygen.
|
|
|
|
Carboxylic Acid pKa
|
~5
|
|
|
|
Amines pKa
|
~10
|
|
|
|
Alcohol pKa
|
~16
|
|
|
|
Mercaptans/thiols pKa
|
~8
|
|
|
|
Phosphate pKa
|
~2, ~7, ~12
|
|
|
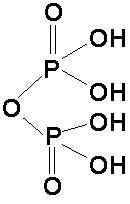
|
pyrophosphate
|
|
|
|
Pyrophosphate pKa
|
1.52, 2.36, 6.6, 9.25
|
|
|
|
What four residues are found in hemoglobin?
|
Valine, Phenylalanine, and two Histidines.
|
|
|
|
What form of iron does hemoglobin utilize in order to bind oxygen?
|
Ferrous (Fe^2+)
|
|
|
|
What is the oxidation state of iron found in hemoglobin while oxygen is being transported?
|
Ferric (Fe^3+)
|
|
|
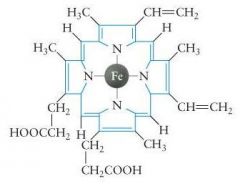
|
heme B
(most common heme) |
|
|
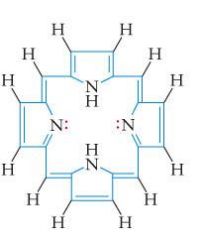
|
porphine
|
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Glycine
|
2.4
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Alanine
|
2.4
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Valine
|
2.3
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Leucine
|
2.3
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Isoleucine
|
2.3
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Methionine
|
2.1
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Proline
|
2
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Phenylalanine
|
2.2
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Tryptophan
|
2.5
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Serine
|
2.2
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Cysteine
|
1.9
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Tyrosine
|
2.2
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Asparagine
|
2.1
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Glutamine
|
2.2
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Aspartic Acid
|
2
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Glutamic Acid
|
2.1
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Lysine
|
2.2
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Arginine
|
1.8
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Carboxyl group pKa of Histidine
|
1.8
|
Carboxylic acid group pKa = ~ 2.2 +/- 0.2
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Glycine
|
9.8
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Alanine
|
9.9
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Valine
|
9.7
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Leucine
|
9.7
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Isoleucine
|
9.8
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Methionine
|
9.3
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Proline
|
10.6
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Phenylalanine
|
9.3
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Tryptophan
|
9.4
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Serine
|
9.2
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Threonine
|
9.1
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Cysteine
|
10.7
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Tyrosine
|
9.2
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Asparagine
|
8.7
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Glutamine
|
9.1
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Aspartic Acid
|
9.9
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Glutamic Acid
|
9.5
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Lysine
|
9.1
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Arginine
|
9
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
Amino pKa of Histidine
|
9.3
|
Amino group pKa = ~ 9.5 +/- 0.6
|
|
|
G
|
glycine
|
|
|
|
gly
|
glycine
|
|
|
|
A
|
alanine
|
|
|
|
ala
|
alanine
|
|
|
|
V
|
valine
|
|
|
|
val
|
valine
|
|
|
|
L
|
leucine
|
|
|
|
Leu
|
leucine
|
|
|
|
I
|
isoleucine
|
|
|
|
ile
|
isoleucine
|
|
|
|
F
|
phenylalanine
|
|
|
|
phe
|
phenylalanine
|
|
|
|
Y
|
tyrosine
|
|
|
|
tyr
|
tyrosine
|
|
|
|
W
|
tryptophan
|
W stands for Wishbone. Turkeys have wishbones, and thanksgiving makes you sleepy.
|
|
|
trp
|
tryptophan
|
|
|
|
S
|
serine
|
|
|
|
ser
|
serine
|
|
|
|
T
|
threonine
|
|
|
|
thr
|
threonine
|
|
|
|
C
|
cysteine
|
|
|
|
cys
|
cysteine
|
|
|
|
M
|
methionine
|
|
|
|
met
|
methionine
|
|
|
|
D
|
aspartate
|
|
|
|
asp
|
aspartate
|
|
|
|
E
|
glutamate
|
|
|
|
glu
|
glutamate
|
|
|
|
N
|
asparagine
|
|
|
|
asn
|
asparagine
|
|
|
|
Q
|
glutamine
|
|
|
|
gln
|
glutamine
|
|
|
|
K
|
lysine
|
|
|
|
lys
|
lysine
|
|
|
|
R
|
arginine
|
|
|
|
arg
|
arginine
|
|
|
|
H
|
histidine
|
|
|
|
his
|
histidine
|
|
|
|
P
|
proline
|
|
|
|
pro
|
proline
|
|
|
|
Essential Amino Acids (for humans)
|
Leu, Met, His, Ile, Lys, Trp, Thr, Val, Phe.
|
There are nine:
"Lou Met His Ill sister Lisa for a Trip Through the Valley of Phe." |
|
|
pKa of Formic Acid
|
3.8
|
|
|
|
pKa of Acetic Acid
|
4.8
|
|
|
|
pKa of Lactic Acid
|
3.9
|
|
|
|
pKa of Phosphoric Acid
|
2.2
|
|
|
|
pKa of Dihydrogen Posphate Ion
|
7.2
|
|
|
|
pKa of Monohydrogen Phosphate Ion
|
12.7
|
|
|
|
pKa of Carbonic Acid
|
6.4
|
|
|
|
pKa of Bicarbonate Ion
|
10.2
|
|
|
|
pKa of Ammonium ion
|
9.2
|
|
|
|
pKa of Methylammonium Ion
|
10.7
|
|
|
|
net charge when pH > pI
|
negative
|
|
|
|
net charge when pH < pI
|
positive
|
|
|
|
net charge when pH = pI
|
zero
|
|

