![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
60 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Substitution:
|

- The characteristic reactions of saturated compounds & of aromatic compounds
- one group replaces another |
|
|
Addition:
|
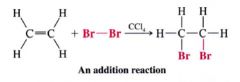
- Characteristic of compounds w/ multiple bonds
(all parts of the adding reagent appear in the product, 2 molecules become one) |
|
|
Elimination:
|
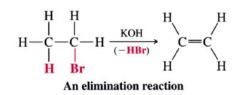
- The opposite of addition
- One molecule loses the elements of another small molecule - gives us a method for preparing compounds w/ double and triple bonds |
|
|
Rearrangement:
|
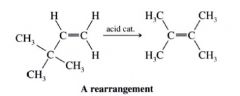
- molecules undergoes a reorganization of its constituent parts
|
|
|
Reactions of organic chemistry always involve the making and breaking of what kind of bonds?
|
covalent bonds
|
|
|
Heterolysis:
|
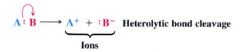
(greek: hetero means different, + lysis means lossening/cleaveage)
- the breaking of bond that leaves one fragment w/ both e-s & the other fragment with an empty orbital - produces charged fragments (ions) |
|
|
Homolytic:
|
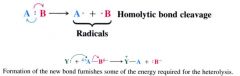
(greek: homo means same, +lysis means loosening/ cleaveage)
- the bond breaks so that each fragment takes away one of the e-s of the bond. - normally requires that the bond be polarized. |
|
|
Bronsted-Lowry acid:
|
a substance that can donate (lose) a proton
|
|
|
Bronsted-Lowry base:
|
a substance that can accept (remove) a proton.
|
|
|
Conjugate base:
|
molecule/ ion that forms when an acid loses its proton
|
|
|
Conjugate acid:
|
molecule or ion that forms when a base accepts a proton.
|
|
|
Some other strong acids that completely transfer a proton when dissolved in water:
|
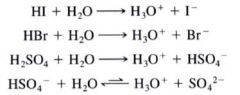
|
|
|
Lewis acid:
|
e- pair acceptor
|
|
|
Lewis base:
|
e- pair donor
|
|
|
What is one key concept that is fundamental to reactivity?
|
the attraction of oppositely charged species
|
|
|
Heterolysis of a bond to a carbon atom can lead to either which two ions?
|
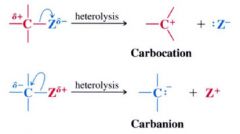
1. a carbocation
2. a carbanion |
|
|
Carbocation:
|
- positively charge on the carbon atom
- e- deficient therefore are Lewis acids - most are short-lived & highly reactive - react rapidly w/ Lewis bases molecules or ions that can donate the e- pair that they need to achieve a stable octect of e-s. |
|
|
Carbanions:
|
- negatively charged carbon atom
- are Lewis bases - seek protons or (+) centered molecules to which they can donate e-s to neutralized their (-) charge |
|
|
Electrophiles:
|
reagents which in their reactions seek the extra e-s that will give them a stable valance shell of electrons
- all Lewis acids including protons (ex: carbocation) |
|
|
Nucleophile:
|
reagents that seek a proton or some other (+) center
(ex: carboanion) |
|
|
What does a curve arrow represent in a reaction mechanism?
|
the curved arrow represents the movement of electrons
- the curved arrow begins with a covalent bond or unshared e- pair (a site of higher e- density) and points toward a site of e- deficiency |
|
|
Equilibrium constant:
|
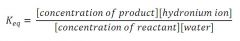
|
|
|
acidity constant:
|

when water is essentially constant ~ diluted aq. soln.
- a larger value of acidity constant means the acid is a strong acid and a small value means the acid is a weak acid. - acidity constant of ~ 10 will completely dissociate in water |
|
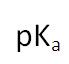
|
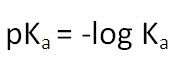
|
|
|
What does the value of pKa represent?
|
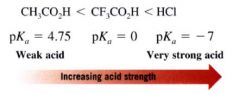
The larger the value of the pKa the weaker the acid
|
|
|
Table 3.1: Relative strength of selected acids and their conjugate bases:
|
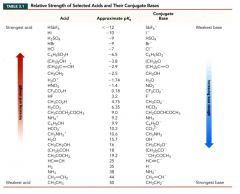
|
|
|
sp3 (single bonds) pKa?
|
~ 50+
|
|
|
sp2 (double bonds) pKa?
|
~45
|
|
|
sp (triple bonds)pKa?
|
~25
|
|
|
low pKa means?
|
stronger acid
|
|
|
the more electron dense the higher or lower the pKa?
|
lower the pKa
|
|
|
pKa for pure water?
|
15.7
|
|
|
Strength of bases:
|

The stronger the acid, the weaker will be its conjugate base.
therefore, The larger the pKa of the conjugate acid, the stronger the base. |
|
|
amines are weak or strong bases or acids?
|
typically they are weak bases
|
|
|
The more stable an acids conjugate base is, the weaker or stronger the acid?
|
stronger
|
|
|
reactions favor side with higher or lower pKa?
|
lower
|
|
|
The strength of a Bronsted-Lowry acid depends on what?
|
on the extent to which a proton can be separated from it and transferred to a base.
|
|
|
Bond strength to the proton decreases as we move down the column why?
|
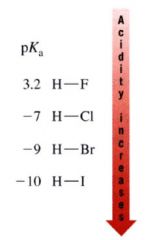
mainly due to decreasing effectiveness of orbital overlap between hydrogen 1s and the orbitals of successively larger elements in the column.
|
|
|
Looking at the rows in the periodic table how does acidity increase?
|
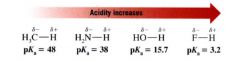
from left to right.
- bond strengths vary somewhat, but the predominate factor becomes the electronegativity of the atom bonded to the hydrogen. |
|
|
Trend in acidity within the periodic table:
|
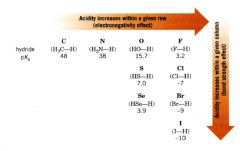
|
|
|
what are the pKa of ethyne, ethene, and ethane? Why such pKa?
|
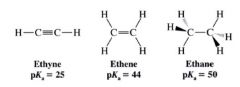
because of the hybridization state of carbon in each compound.
- having more s character means that the e-s of the anion will, on the avg. be lower in energy, and the anion will be more stable. |
|
|
Energy:
|
The capacity to do work
|
|
|
Kinetic energy:
|
- the energy an object has because of its motion
KE= (1/2)m(v^2) |
|
|
potential energy:
|
- stored energy
- exist only when an attractive/repulsive force exist between objects |
|
|
Chemical energy is a form of what kind of energy?
|
potential energy
b/c it exists because attractive and repulsive electrical forces exist between different pieces of the molecules. |
|
|
The relative stability of a system is inversely related to its relative potential energy. This means what?
|
the more potential energy an object has, the less stable it is.
|
|
|
Looking at covalent bonds the state of greatest potential energy is what state of the atom?
|
the state of free atoms.
(atoms are not bonded to each other @ all) |
|
|
Heat of reaction:
|
Measures the change in enthalpy of the atoms of the reactants as they are converted to products.
|
|
|
Are carboxylic acids weak or strong acids? range of pKa?
|
weak acids
pKa:3-5 |
|
|
pKa of alcohols?
|
pKa: 15-18
(essentially do not give up a proton unless exposed to a very strong base) |
|
|
dispersal of charge always makes a species ______?
|
more stable
|
|
|
What creates a stronger acid?
|
1. a more stable conjugate base
-------- the delocalizaiton effect by resonance. -------- an inductive electron-withdrawing effect (stabilizing charge throughout the atom) -------- the larger the molecule the lesser e- withdraw effect. |
|
|
Protic solvent:
|
one that has a H atom attached to a strongly electronegative element such as oxygen or nitrogen
ex: water |
|
|
What occurs during solvation:
|
the solvation of any species decreases the entropy of the solvent b/c the solvent molecules become much more ordered as they surround molecules of the solute.
|
|
|
If an organic compound contains an atom with an unshared e- pair, it is a potential ____?
|
base
|
|
|
What compounds act as a base when treated with solutions of strong acids such as HCl, HBr, HI, H2SO4...
|
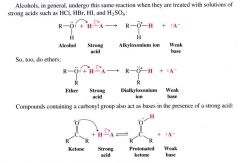
alcohols, ethers, carbonyl groups. The unshared electrons of the compounds remove the proton from the strong acid.
|
|
|
How do alkenes act like bases?
|
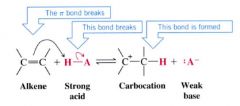
react w/ a strong acid by accepting a proton.
- e- pair of pi bond of alkene is used to form a bond between one carbon of the alkene & the proton donated by the strong acid. -- 2 bonds break: 1. pi bond of the double bond 2. bond of proton and acid -- 1 bond forms: 1. bond between carbon of the alkene & the proton. |
|
|
Leveling effect (of the solvent):
|

the solvent donates a proton to any strong base stronger than a hydroide ion (if solvent is water) therefore,
--- not possible to use a base stronger than hydroxide ion in aq. soln. |
|
|
What solvents can then be used for strong bases stronger than hydroxide ion?
|
solvents that are weaker acids than water such as hexane, diethyl ether... they will not dontate a proton.
|
|
|
Charges are more stable on some atoms than others, what are some rules to follow when looking at the negative charge on a deprotenated ion?
|
1. Negative charges are more stable on more electronegative atom. (electronegativity increases as you go up and to the right on the periodic table)
2. Negative charges are more stable on larger atoms (size of atoms increases as you go down the periodic table. negative charges perfer to rest on larger atoms b/c larger atoms allow the negative charge to delocalize over a larger space) 3. a negative charge is more stable on a larger atom than on an electronegative atom 4. negative charges prefer to rest on sp-hybridized atoms over sp2-hybridized atoms, and they prefer sp2 over sp3 atoms. |

