![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
39 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Hydrocarbon:
|
compounds whose molecules contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms
|
|
|
Alkane
|

carbon carbon single bond
|
|
|
Alkenes:
|
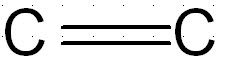
carbon carbon double bond
|
|
|
Alkynes:
|
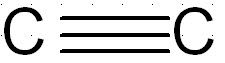
carbon carbon triple bond
|
|
|
Saturated compounds:
|
contain the max # of H's that a carbon compound can possess.
|
|
|
unsaturated:
|
posses fewer than the max # of H atoms.
|
|
|
determining the # of unsaturations:
|
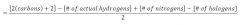
|
|
|
Benzene:
|
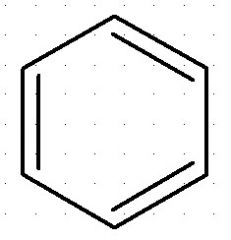
aromatic compound
|
|
|
Delocalization:
|
The moment of e-s from single to double to single...etc. "stabilizes molecules"
|
|
|
Polar Covalent Bonds:
|
- Strongly influence the physical properties & reactivity of molecules
- present in molecules that contain bonded atoms w/ different electronegativity values. --------- e-s are not shared equally. The atom with greater electronegativity draws e-s density closer to it. |
|
|
Functional Groups:
|
defined groups of atoms in a molecule that usually gives rise to the function (reactivity/ physical properties) of the molecule
|
|
|
Electronegativity:
|
the ability of an element to attract e-s that it is sharing in a covalent bond.
- the part of a molecule where most of its chemical reactions occur - effectively determines the compound's chemical properties. |
|
|
Map of Electrostatic Potential (MEP):
|
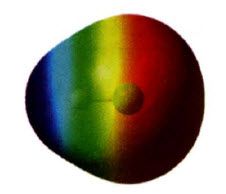
- RED: regions of an e- density surface that are more (-)
---- attract a positively charged species (or repel a negative charge) - BLUE: less (-) or positive ---- likely to attract e-s from another molecule |
|
|
Alkyl Group:
|
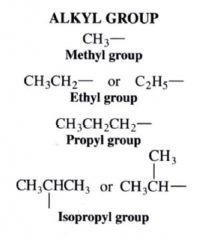
groups that we ID for naming purposes....
obtained by removing a H atom from an alkane ---- ending in -yl |
|
|
Phenyl group:
|

Benzene ring attached to some other group of atoms
|
|
|
Benzyl Group:
|
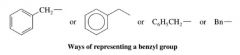
a phenyl group combined with a methylene group (-CH2-)
|
|
|
Alkyl Halids (Haloalkanes):
|
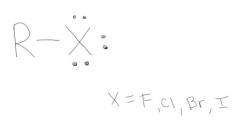
|
|
|
Alcohols:
|

are classified into 3 groups: Primary, secondary, and tertiary alcohols. This classification is based on the degree of substitution of the carbon to which the hydroxyl group is directly attached.
|
|
|
Ether:
|
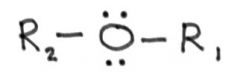
|
|
|
Amine:
|
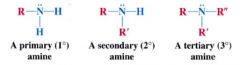
|
|
|
are amines acids or bases? strong or weak?
|
are weak bases
|
|
|
Carbonyl group:
|
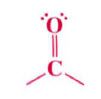
|
|
|
aldehyde:
|
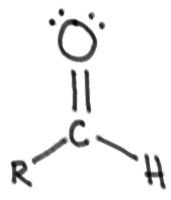
|
|
|
Ketone:
|
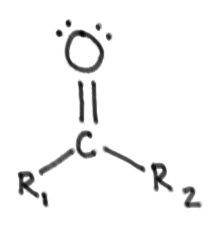
|
|
|
Carboxylic acid:
|
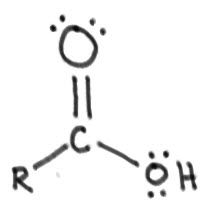
|
|
|
Ester:
|
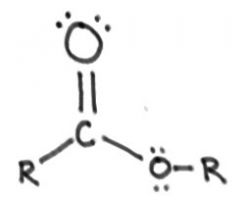
|
|
|
Amide:
|
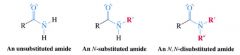
|
|
|
Nitrile:
|
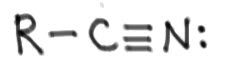
|
|
|
Melting point:
|
the temp. @ which an equilibrium exists between the well-ordered crystalline state and the more random liquid state.
|
|
|
Ion-ion forces:
|
forces that hold ions together in the crystalline state....
--- the strong electrostatic lattice forces that act between the (+) & (-) ions in the orderly crystalline structure. ---------- requires large amounts of thermo energy to break the orderly structured crystals. |
|
|
dipole-dipole forces:
|
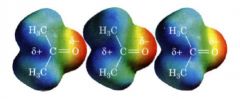
- are in most organic molecules which have a permanent dipole moment resulting from a nonuniform distribution of the bonding e-s
- cause the molecule to orient themselves so that the (+) end of one molecule is directed toward the (-) end of another. |
|
|
Hydrogen bonds:
|
- attractions between hydrogen atom bonded to small strongly electronegative atoms (O,N,F), & nonbonding e- pairs on other such electronegative atoms.
- are weaker than ordinary covalent bonds, but much stronger than dipole-dipole interactions. |
|
|
Vander Waals Forces:
|
dipole forces w/in molecules that cause attractions to other molecules of opp. force.
|
|
|
polarizability:
|
the ability of the e-s to respond to a changing electric field
- depends on how loosely/ tightly the e-s are held. |
|
|
Boiling pt. of a liquid:
|
the temp. @ which the vapor pressure of the liquid equals the pressure of the atmosphere above it
--- pressure dependent |
|
|
Solubilities:
|
The dissolution of a solid in a liquid.
the orderly crystal structure of the solid is destroyed --- results is the formation of the more disorderly arrangement of the molecules (ions) in solution. |
|
|
Hydrophobic:
|
fearing/ avoiding water
|
|
|
Hydrophilic:
|
loving/ seeking water
|
|
|
summary of Attractive Electric Forces
|
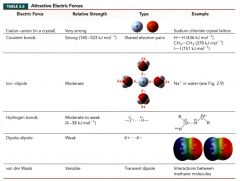
|

