![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
20 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Carbon-13 NMR spectroscopy:
|
gives us evidence about the connectivity and environment of carbon atoms in a molecule.
- can help us confirm the structure of a molecule for which we already have some structural information, or it can give us evidence that can help us elucidate the structure of an entirely unknown compound. |
|
|
one signal for each unique carbon:
|
each carbon atom that occupies a unique environment in a molecule produces one signal in a carbon-13 spectrum. Carbon atoms that are equivalent by molecular symmetry also produce one signal.
|
|
|
what influences the chemical shift/ signals in NMR spectra?
|
differences in electron density.
|
|
|
Chart of carbon-13 NMR chemical shifts:
|

|
|
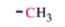
C-13 NMR shift range of
|
10-25
|
|

C-13 NMR shift range of
|
20-50
|
|
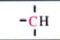
C-13 NMR shift range of
|
25-60
|
|
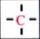
C-13 NMR shift range of
|
30-40
|
|

C-13 NMR shift range of
|
40-90
|
|
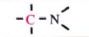
C-13 NMR shift range of
|
20-70
|
|
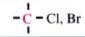
C-13 NMR shift range of
|
20-90
|
|
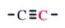
C-13 NMR shift range of
|
70-90
|
|

C-13 NMR shift range of
|
110-150
|
|

C-13 NMR shift range of
|
120-150
|
|

C-13 NMR shift range of
|
110-125
|
|
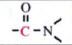
C-13 NMR shift range of
|
150-170
|
|

C-13 NMR shift range of
|
155- <180
|
|
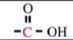
C-13 NMR shift range of
|
>160 - <190
|
|
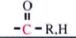
C-13 NMR shift range of
|
190-220
|
|
|
Using C-13 NMR:
|
1. count # of signals
---- indicate # of C occupying unique environments in molecule 2. compare chemical shifts w/ chart may show "type" of C. 3. considering pts. 1 & 2.... propose structure. |

