![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
36 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Define matter:
|
Anything that occupies space and has mass.
|
|
|
When matter changes from a solid directly into a gas:
|
Sublimation
|
|
|
When matter changes from a gas directly into a solid:
|
Deposition
|
|
|
Draw out the classifications of matter:
|
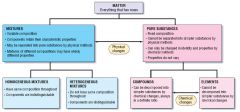
|
|
|
What are the two main classifications of matter:
|
Pure substances and Mixtures
|
|
|
Define a pure substance:
|
Substance made of only one kind of element or compound.
|
|
|
Define a mixture:
|
a substance made up of different kinds of atoms/molecules; variable composition.
|
|
|
What is the difference between heterogeneous and homogeneous mixtures?
|
homogeneous mixtures have the same composition throughout.
|
|
|
Define an Element:
|
A substance made up of only one kind of atom. Cannot be separated by chemical means.
|
|
|
Define a Compound:
|
Two or more elements always found in the same proportions; can be separated by chemical means but not physical means.
|
|
|
1 cal = __J
|
1 cal = 4.184J
|
|
|
Define a calorie:
|
The amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of 1g of H₂O by 1˚C.
|
|
|
What are the three types of energy:
|
Potential
Kinetic & chemical |
|
|
Define Heat:
|
the exchange of thermal energy.
|
|
|
Define Heat Capacity:
|
the heat required to change something by 1˚C
|
|
|
Define Specific Heat:
|
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of a substance by 1˚C
|
|
|
What is the formula for Specific Heat:
|
q=msΔT
|
|
|
Define the Law of Conservation of Mass:
|
Matter is neither created nor destroyed.
|
|
|
Define the Law of Conservation of Energy:
|
Energy is neither created or destroyed, only converted between forms.
|
|
|
Define Physical change:
|
When matter takes on a different form w/ out changing its composition.
|
|
|
Define Chemical change:
|
When matter changes and forms new substances.
|
|
|
Define a physical property:
|
Those properties that can be observed without changing the material's chemical identity.
|
|
|
Define a chemical property:
|
involves a chemical change.
|
|
|
What are some physical properties?
|
mass, volume, density, melting point, taste, odor, color, shape, etc.
|
|
|
What are some chemical properties?
|
Acidity, Alkalinity, Causticity, Corrosiveness, Inertness, Explosiveness, etc.
|
|
|
Describe the two ways solid matter arrange themselves:
|
in cyrstalline or amorphous structures
|
|
|
Describe crystalline structure:
|
atoms or molecules are arranged in geometric patterns with long-range order.
|
|
|
Describe amorphous structure:
|
atoms or molecules do not have a long-range order.
|
|
|
Define "properties" (of a substance).
|
The characteristics we use to distinguish one substance from another.
|
|
|
Define physical properties:
|
Those characteristics that a substance displays without changing its composition. ie.. the odor of gasoline.
|
|
|
Define chemical properties:
|
Those characteristics that a substance displays only through changing its composition.
|
|
|
Physical properties include:
|
odor, taste, color, appearance, melting and B.P., and density.
|
|
|
Chemical properties include:
|
flammability and other chemical activities.
|
|
|
Define energy:
|
the capacity to do work
|
|
|
Define the Law of conservation of mass and the Law of conservation of energy:
|
Law of conservation of mass:Matter can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Law of conservation of energy: Energy can neither be created nor destroyed. |
|
|
1 kilowatt-hour (kWh) =
|
3.60 X 10⁶ J
|

