![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
76 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Length SI unit |
m |
|
|
Mass SI unit |
Kg |
|
|
Time SI unit |
s |
|
|
Giga- |
G 10^9 billion |
|
|
Mega- |
M 10^6 million |
|
|
Kilo- |
K 10^3 thousand |
|
|
Centi- |
C 10^-2 one hundredth |
|
|
Milli- |
m 10^-3 one thousandth |
|
|
Micro |
µ 10^-6 one millionth |
|
|
Nano |
n 10^-9 one billionth |
|
|
Pico |
P 10^-12 one trillionth |
|
|
Accuracy |
How close you are to the real result |
|
|
Precision |
How close are the measurements to one another |
|
|
< 5 > 5 = 5 |
Round up Round down Round to even number |
|
|
Atomic number (Z) |
Number of protons |
|
|
Mass number (A) |
Number of protons + neutrons |
|
|
Isotope |
same element with different mass number |
|
|
Periodic table of elements labeling |
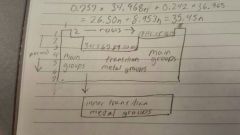
|
|
|
Metals/non metals wall |
Po Bi Sn Al |
|
|
Speed formula |
Length / time |
|
|
Volume formula |
Length^3 |
|
|
Density formula |
Mass / volume |
|
|
°F to °C |
T(°F)=(9/5)T(°C)+32 |
|
|
K to °C |
T(K)=T(°C)+273.15 |
|
|
Proton (symbol and charge) |
P+ |
|
|
Electron (symbol and charge) |
e- -1 |
|
|
Neutron (symbol and charge) |
n neutral |
|
|
atomic volume is determined by... |
electrons |
|
|
atomic mass is determined by... |
protons and neutrons |
|
|
neutrons function |
to diffuse the +1 charge of protons and allows them to exist together in the nucleus |
|
|
What is AMU/U/Da |
Atomic Mass Units |
|
|
Natural Abundance (or Percent Abundance) |
the mixture of different isotopes of the same element as found in nature (take the AVERAGE MASS of all isotopes) |
|
|
Group 1 of elements |
Alkali metals |
|
|
Group 2 of elements |
Alkali earth metals |
|
|
Group 13 of elements |
no name (boron group) |
|
|
Group 16 of elements |
Chalogens |
|
|
Group 17 of elements |
Halogens |
|
|
Group 18 of elements |
Noble gases |
|
|
Monotomic |
1 atom |
|
|
Diatomic |
2 atoms |
|
|
Triatomic |
3 atoms |
|
|
Polyatomic |
> 1 atom |
|
|
What three characteristics define a molecule |
1. specific number of atoms 2. specific types of element 3. specific arrangement of atoms |
|
|
What is a compund |
bond with two or more elements (H2O) |
|
|
Name the three types of compounds |
ionic covalent metallic |
|
|
allotrope |
different elemental forms of the same element (O2 & O3) |
|
|
ionic bond |
attaction of + and - |
|
|
Constant charge cations |
elements thatalways produce the same positive charge |
|
|
1+ cations |
All elements in group 1 Silver |
|
|
2+ cations |
All elements in group 2 Zinc |
|
|
3+ cations |
All elements in group 13 |
|
|
Variable charge cations |
Any other metals |
|
|
Constant charge anions |
groups 15, 16, and 17 |
|
|
Hydrogen charge |
can be either + or - |
|
|
Covalent bond |
a bond in which atoms share electons |
|
|
Covalent compund Ionic compound |
covalent bond only ionic or ionic + covalent |
|
|
Polyatomic ion |
atoms are in a network, which has a net charge |
|
|
Isomers |
Molecules with the same atoms but with a different shape |
|
|
Binary Diatomic |
2 different elements (CO) 2 atoms (O2) |
|
|
X1, X2, X3, X4, X5, X6, X10 |
mono, di, tri, tetra, penta, hexa, deca |
|
|
% composition |
% composition = (# atoms)(atomic mass) / total mass of formula unit |
|
|
Empirical formula |
smallest molar ratio of elements in a compound |
|
|
True formula |
multiplier X emperical formula |
|
|
Multiplier |
true formula / empirical formula |
|
|
reagent |
either a reactant or product |
|
|
reactant |
a reagent on the left side of the chemical equation |
|
|
product |
a reagent on the right side of the chemical equation |
|
|
combustion |
a reaction between O2 and any one element or compound |
|
|
If a reactant of a combustion is C or a C compound, one of the products must be... |
CO2 |
|
|
If a reactant of a combustion is H or a H compound, one of the products must be... |
H20 |
|
|
If a reactant of a combustion is metal or a metal compound, one of the products must be... |
metal oxide |
|
|
4 steps to stoichiometry |
1. balance the equation 2. convert given unit to moles 3. use stoichiometric ratio 4. convert moles to desired units |
|
|
% yield |
actual yield / theoretical yield |
|
|
concentration |
amount of solute / amount of solvent or solution |
|
|
% concentration |
mass (or volume) or solute / sum of masses or volumes of all components |
|
|
malarity (m) |
mol solute / L solvnet |

