![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
51 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
atmos (greek) =
|
invisible
|
|
|
Scanning tunneling microscopy (STM):
|
- discovered by Gerd Binning and Heinrich Rohrer.
- technique that can image (make a visual representation of), and even move, individual atoms and molecules. - works by moving an extremely sharp electrode (a conductor through which electricity can enter or leave) over a surface and measuring the resulting tunneling current. |
|

Tunneling Current:
|
the electrical current flows between the tip of the electrode & the surface even though the two are not in physical contact.
|
|
|
atom:
|
smallest identifiable unit of an element.
|
|
|
Law of conservation of mass:
|

by Antonine Lavoisier
"in a chemical reaction, matter is neither created nor destroyed" |
|
|
Law of Definite Proportions:
|
by Joseph Proust
"All samples of a given compound, regardless of their source or how they were prepared, have the same proportions of their constituent elements." |
|
|
Law of multiple Proportions:
|

by John Dalton
"when two elements (call them A & B) form two different compounds, the masses of element B that combines with 1 g of element A can be expressed as a ratio of small whole numbers. |
|
|
Explain the difference between the law of definite proportions and the law of multiple proportions.
|
the law of definite proportions applies to two or more samples of the same compound and states that the ratio of one element to the other in the sample will always be the same. The law of multiple proportions applies to two different compounds containing the same two elements (A and B) and states that the masses of B that combine with 1 g of A are related as a small whole number ratio
|
|
|
John Dalton's Atomic Theory:
|
1. each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms.
2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from the atoms of other elements 3. atoms combine in simple, whole-number ratios to form compounds 4. atoms of one element cannot change into atoms of another element. In a chemical reaction, atoms change the way that they are bound together with other atoms to form a new substance. |
|
|
Cathode:
|
negatively charged electorde
|
|
|
anode:
|
positively charged electrode
|
|
|
What did J.J. Thomas Discover?
|

- Found that cathode rays were actually streams of particles with the following properties:
- they traveled in straight lines - they carried a (-) electrical charge. - Discovered the electron, (-) charged, low mass particle present within all atoms. |
|
|
Electrical charge:
|

a fundamental property of some of the particles that compose atoms and results in attractive and repulsive forces (electrostatic forces) between them.
|
|
|
Millikan's Oil Drop Experiment:
|
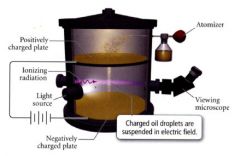
- oil was sprayed into fine droplets using an atomizer.
- droplets were allowed to fall through a small hole into the lower portion of the apparatus where they could be viewed with the help of a light source and a microscope. - during their fall, the drops acquired electrons that had been produced when the air was bombarded with a type of energy called ionizing radiation. - the negatively charged drops then interacted with the negatively charged plate at the bottom of the apparatus. - by varying the amount of charge on teh plate, the fall of the drops could be slowed, stopped, or even reversed. |
|
|
Plum-Pudding model:
|

proposed by J.J Thomas
negatively charged electrons were small particles held within a positively charged sphere. |
|
|
What did Ernest Rutherford Discover?
|

- proved the plum-pudding model wrong.
- in the experiment, he directed the positively charged alpha particles at an unltrathin sheet of gold foil. -Particles were to act as probes of the gold atoms structure. - what was suppose to happen: speeding probes should pass right though the gold foil with min. deflection since gold atoms were spread throughout the entire vol. of the atom. - results: a majority of the particles did pass directly thought the foil, but some particles were deflected and some even bounced back. - realized, the mass & (+) charges of an atom must be concentrated in a space smaller than the atom ** discovered the nucleus*** |
|
|
Nuclear Theory:
|
by Rutherford
1. most of the atom's mass and all of its (+) charge are contained in a small core called the nucleus 2. most of the volume of the atom is empty space, throughout which tiny, (-) charged electrons are dispersed. 3. there are as many negatively charged electrons outside the nucleus as there are positively charged particles (protons) within the nucleus, so the atom is electrically neutral. |
|
|
What did James Chadwick discover?
|
the unaccounted mass of an atom was due to the presence of neutrons (neutral particles within the nucleus).
|
|
|
Subatomic particles:
|

|
|
|
If all atoms are composed of the same subatomic particles, then what makes the atoms of one element different from those of another?
|
- the # of these particles
- the # that is most important for the identity of an atom is the # of protons in its nucleus - # of protons defines the element |
|
|
Atomic # (Z):
|
# of protons in an atom's nucleus.
|
|
|
periodic table:
|
|
|
|
Isotopes:
|
atoms with the same # of protons but different # of neutrons.
|
|
|
Mass # (A):
|
the sum of the # of neutrons & protons in an atom.
|
|
|
How are isotopes often symbolized:
|

|
|
|
Ion:
|
charged atom
|
|
|
anion:
|
(-) charged ion
|
|
|
cation:
|
(+) charged ion.
|
|
|
In light of the nuclear model for the atom, which of the following statements is most likely to be true?
(a) the isotope of an atom with a greater number of neutrons is larger than one with a smaller number of neutrons (b) the size of an anion is greater than the size of the corresponding neutral atom (c) the size of a cation is greater than the size of the corresponding neutral atom |
(b) the number of neutrons in the nucleus of an atom does not affect the atom's size because the nucleus is miniscule compared to the atom itself. The number of electrons however, does affect the size of the atom because most of the vol. of the atom is occupied by electrons, and electrons repel one another. Therefore, an anion, with a greater number of electrons, is larger than the corresponding neutral atom.
|
|
|
Dmitri Mendeleev discovered:
|
the periodic table.
|
|
|
Periodic law:
|
by Mendeleev
"when the elements are arranged in order of increasing mass, certain sets of properties recur periodically." |
|
|
Modern periodic table:
|

|
|
|
Metals:
|
- found on the lower left side and middle of the periodic table.
Properties: - good conductors of heat & electricity - can be pounded into flat sheets (malleability) - can be drawn into wires (ductility) - often shiny - tend to lose electrons when they undergo chemical changes |
|
|
Nonmetals:
|
- found on the upper right side of the periodic table.
properties: - some are solids @ room temp. others are liquids or gases. - poor conductors of heat & electricity - tend to gain electrons when they undergo chemical changes. |
|
|
Metalloids:
|
- show mixed properties
- some are semiconductors because of their intermediate (& highly temp. dependent) electrical conductivity. |
|
|
Main-group elements:
|
properties tend to be largely predictable based on their position in the periodic table.
|
|
|
transition elements (transition metals):
|
properties tend to be less predictable based simply on their position in the periodic table.
|
|
|
the periodic table: main-group and transition elements:
|

|
|
|
Family (group):
|
columns within the main-group regions of periodic table
|
|
|
noble gases:
|
- group 8A elements
- mostly unreactive |
|
|
Alkali metals:
|
- group 1A elements
- all reactive metals |
|
|
Alkaline earth metals:
|
- group 2A elements
- fairly reactive |
|
|
Halogens:
|
- group 7A elements
- very reactive nonmetals |
|
|
A main-group metal tends to what?
|
lose electrons, forming a cation with the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas
|
|
|
A main-group nonmetal tends to what?
|
gain electrons, forming an anion with the same number of electrons as the nearest noble gas.
|
|
|
Elements that form ions with predictable charges:
|

|
|
|
Atomic Mass:
|
- is listed directly beneath the element's symbol in the periodic table
- represents the avg. mass of the isotopes that compose that element. |
|
|
How to calculate the atomic mass of an atom:
|

|
|
|
Avogadro's # =
|

"one mole of anything is 6.022 x 10^23 units of that thing"
|
|
|
Converting between # of moles and # of atoms
|

|
|
|
molar mass:
|
- the mass of 1 mol of atoms of an element.
- an element's molar mass in grams per mole is numerically equal to the element's atomic mass in atomic mass units. |

