![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
18 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
|
Two Reasons why a reaction might be zero order? |
Spectator ions may not be involved
Adding more reactant to a saturated catalyst will not cause the reaction to speed up. |
|
|
Can a 5th order reaction occur? Explain |
Yes, it takes at least four steps |
|
|
Why do reactions tend to speed up when you heat them? |
They are hitting each other more often so molecules have energy to exceed EA |
|
|
What term must be added to a reaction to account for a catalyst? |
[Kcat (Cat) +1] |
|
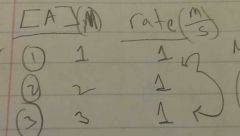
Rate law & is this a 0th, 1st, or 2nd order? |
0th order : no change in rate when [A] changes Rate= K [A]^0 |
|
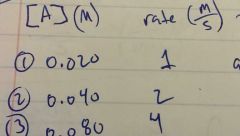
0th, 1st, or 2nd order? Rate law? |
As [A] doubles, the rate doubles. 1st order
Rate = K [A]^1 |
|
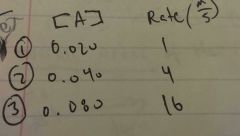
Rate law and is this a 0th, 1st, or 2nd order? |
Rate= k[A]^2 2nd order. As the [A] doubles, the rate quadruples |
|
|
Notes on units: Rate: molarity/seconds (M/s) Reactants: molarity (M) Rate constant 'k' varies on rxn 1st order: rate = k[A]^1 what is k?
|

|
|
|
If Rate: molarity/seconds (M/s)Reactants: molarity (M)Rate constant 'k' varies on rxn What is 'k' for a 2nd order rate = k[A]^2 |
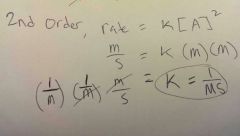
|
|
|
Rate: molarity/seconds (M/s)Reactants: molarity (M)Rate constant 'k' varies on rxn What's 'k' for 0th order? Rate = k [A]^0 |
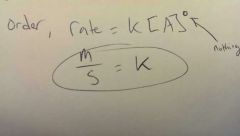
|
|

Determine the rate laws for [No] & [F2] |

|
|
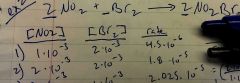
Rate laws for [No2] & [Br2]? Overall order reaction? |

& overall reaction is 3rd Rate=k [No2]^2 [Be2]^1 2+1=3 |
|
|
What is one (or all) facts about 0th order? |
1) concentration of that reactant has no affect on RXN2) Spectator ions 3) units for k: Rate (M/s) = k (M/s) |
|
|
What is one (or all) facts about 1st order? |
1) as [concentration] doubles then expect the rate to double 2) radio active decay 3) only one molecule involved in slowest (rate limiting) step 4) Rate (M/s) = k (M) thus, k = 1/s |
|
|
What is one (or all) facts about 2nd order? |
1) as [concentration] doubles then expect the rate to quadruple 2) two molecules involved (P.S important for problem solving) |
|
|
Is a 5th order possible? |
Yes, but more than one step is needed |
|

|

Rate law : Rate = k [No]^2 [H2]^1 Overall order: 2+1 is (3) Rate constant units = 1/M^2s Rate constant: 250 1/M^2s = k for trial #1 |
|
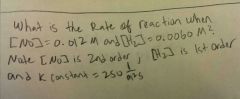
|

First find units = M/s (correct rate units are constants) Rate= 2.16*10^-4 M/s |

