![]()
![]()
![]()
Use LEFT and RIGHT arrow keys to navigate between flashcards;
Use UP and DOWN arrow keys to flip the card;
H to show hint;
A reads text to speech;
32 Cards in this Set
- Front
- Back
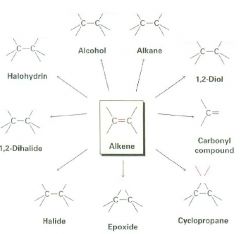
Fill in what's missing.
|
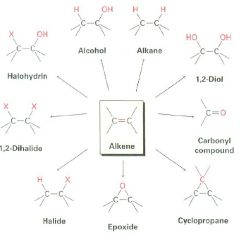
|
|
|
alkenes are usually made from what precursors?
|
alcohols in biological system or alcohols or alkyls halides in the laboratory
|
|
|
Many addition reactions involve the addition of _____ or ________ to an alkene to form an alkyl halide or alcohol
|
HBr or H2O
|
|
|
Many elimination reactions involve the loss of _____ or ________ to an alkene to form an alkyl halide or alcohol
|
HBr or H2O
|
|
|
What are the most common elimination reactions?
|
dehydrohalogenation and dehydration
|
|
|
dehydration
|
the loss of water from an alcohol
|
|
|
dehydrohalogenation
|
the loss of HX from an alkyl halide
|
|
|
dehydrogalogenation usually occurs by reaction of an alkyl halide with a _______ such as __________
|
strong base such as potassium hydroxide (KOH)
|
|
|
dehydration is often carried out by treatment of an alcohol with a _____________ such as _________
|
strong acid such as aqeuous sulfuric acid
|
|
|
What is the formula for sulfuric acid?
|
H2SO4
|
|
|
What does THF stand for?
|
tetrahydrofuran (a common solvent)
|
|
|
Draw THF
|

|
|
|
What does ACP stand for?
|
acyl carrier protein
|
|
|
Why isn't fluorine generally used in the laboratory? Iodine?
|
Fluorine is too reactive. Iodine does not react with most alkenes.
|
|
|
Haloperoxidase
|
peroxidases that are able to mediate the oxidation of halides by hydrogen peroxide.
|
|
|
What's the formula for hydrogen peroxide?
|
H2O2
|
|
|
halohydrin
|
a haloalcohol
|
|
|
What does NBS stand for?
|
N-bromosuccinimide
|
|
|
Water adds to alkenes to yield ____, a process called _________
|
alcohols; hydration
|
|
|
What does THF stand for?
|
tetrahydrofuran
|
|
|
What is NaBH4 called?
|
Sodium borohydride
|
|
|
carbene
|
R2C
a neutral molecule containing a divalent carbon with only six electrons in its valence shell |
|
|
What is the formula for choloroform?
|
CHCl3
|
|
|
stereospecific
|
only a single stereoisomer is formed as product
|
|
|
reduction
|
gain of electron density by crabon
caused either by bond formation between carbon and a less electronegative atom or by bond-breaking between carbon and a more electronegative atom |
|
|
Adam's catalyst
|
PtO2
Where Pt is platinum |
|
|
oxidation
|
a reaction that results in a loss of electron density by carbon
caused either by bond formation between carbon and a more electronegative atom--sually oxygen, nitrogen, or a halogen---or by bond breaking between carbon and a less electronegative atom--usually hydrogen |
|
|
hydroxylation
|
the addition of an --OH group to each of the two double-bond carbons
|
|
|
OsO4 is called
|
Osmium teroxide
|
|
|
What is the formula for ozone?
|
O3
|
|
|
What is the formula for potassium permanganate?
|
KMnO4
|
|
|
What's the formula for periodic acid?
|
HIO4
|

